| CEERS-93316 | |
|---|---|
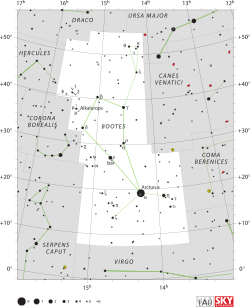
Location of the CEERS-93316 galaxy is in the upper just right-of-center area of the Boötes constellation. | |
| Observation data (J2000 epoch) | |
| Constellation | Boötes [1] [2] |
| Right ascension | 14h 19m 39.48s [1] |
| Declination | 52° 56′ 34.92″ [1] |
| Redshift | 4.912±0.001 [3] |
| Distance |
|
| Other designations | |
| CR2-z16-1 [5] | |
CEERS-93316 is a high-redshift galaxy with a spectroscopic redshift z=4.9. [3] Significantly, the redshift that was initially reported was photometric (z = 16.4) and would have made CEERS-93316 the earliest and most distant known galaxy observed. [1] [6] [7] [8]
Contents
CEERS-93316 has a light-travel distance (lookback time) of 12.6 billion years, and, due to the expansion of the universe, a present proper distance of 25.7 billion light-years. [4]