2063 Bacchus, provisional designation 1977 HB, is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 1 kilometer in diameter. The contact binary was discovered on 24 April 1977, by American astronomer Charles Kowal at the Palomar Observatory in California, United States. It was named after Bacchus from Roman mythology.
4197 Morpheus, provisional designation 1982 TA, is a highly eccentric asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 October 1982, by American astronomers Eleanor Helin and Eugene Shoemaker at Palomar Observatory in California, United States. The asteroid was later named for Morpheus from Greek mythology.

1500 Jyväskylä, provisional designation 1938 UH, is a stony Florian asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 16 October 1938, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at the Turku Observatory in Southwest Finland. It was named for the Finnish town Jyväskylä.

2062 Aten, provisional designation 1976 AA, is a stony sub-kilometer asteroid and namesake of the Aten asteroids, a subgroup of near-Earth objects. The asteroid was named after Aten from Egyptian mythology.
1049 Gotho, provisional designation 1925 RB, is a carbonaceous asteroid from the outer region of the asteroid belt, approximately 53 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 14 September 1925, by German astronomer Karl Reinmuth at Heidelberg Observatory in southwest Germany. Although the name of the asteroid is a masculine German name, it is not known to refer to a particular individual.
1462 Zamenhof, provisional designation 1938 CA, is a carbonaceous Themistian asteroid from the outer regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 27 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 6 February 1938, by Finnish astronomer Yrjö Väisälä at the Iso-Heikkilä Observatory in Finland. The asteroid was named after L. L. Zamenhof, the creator of Esperanto. It is a recognized Zamenhof-Esperanto object.
6433 Enya, provisional designation 1978 WC, is a stony background asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 18 November 1978, by Czech astronomer Antonín Mrkos at the Kleť Observatory in the Czech Republic. It was named for Irish musician Enya.
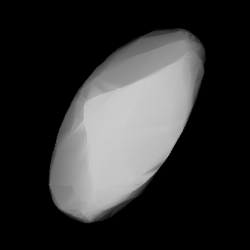
2839 Annette is a bright Flora asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 5 October 1929, by American astronomer Clyde Tombaugh at Lowell Observatory during his search for Pluto. The presumed S-type asteroid has a rotation period of 10.5 hours and measures approximately 5 kilometers in diameter. It was named after the discoverer's daughter.
1707 Chantal, provisional designation 1932 RL, is a stony background asteroid from the Florian region in the inner asteroid belt, approximately 7.5 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 8 September 1932, by astronomer Eugène Delporte at the Royal Observatory of Belgium in Uccle. The S-type asteroid has a rotation period of at least 10 hours. It was named for Chantal, the niece of Belgian astronomer Georges Roland.
1864 Daedalus, provisional designation 1971 FA, is a stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Apollo group, approximately 3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 24 March 1971, by Dutch–American astronomer Tom Gehrels at Palomar Observatory, California, and named after Daedalus from Greek mythology.
2012 Guo Shou-Jing, provisional designation 1964 TE2, is a carbonaceous asteroid and Florian interloper from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 13 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 9 October 1964, by astronomers at the Purple Mountain Observatory in Nanking, China. The asteroid was named after Chinese astronomer Guo Shoujing.
1303 Luthera, provisional designation 1928 FP, is a dark asteroid and the parent body of the Luthera family, located in the outermost regions of the asteroid belt. It measures approximately 90 kilometers in diameter. The asteroid was discovered on 16 March 1928, by astronomer Friedrich Schwassmann at the Bergedorf Observatory in Hamburg, Germany, and later named after German astronomer Robert Luther.
2696 Magion, provisional designation 1980 HB, is a dark background asteroid and a slow rotator from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 21 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 16 April 1980, by Slovak astronomer Ladislav Brožek at the Kleť Observatory in former Czechoslovakia. The X-type asteroid has an ambiguous rotation period of 480 hours and is possibly a tumbler. It was named for the first Czechoslovak satellite, Magion 1, launched in 1978.
1455 Mitchella, provisional designation 1937 LF, is a Florian asteroid, slow rotator and suspected tumbler from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 7 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 June 1937, by astronomer Alfred Bohrmann at the Heidelberg-Königstuhl State Observatory in southwest Germany. The asteroid was named after American astronomer Maria Mitchell.
1907 Rudneva, provisional designation 1972 RC2, is a stony background asteroid from the central regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 11 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 September 1972, by astronomer Nikolai Chernykh at the Crimean Astrophysical Observatory, Nauchnyj, on the Crimean peninsula. The asteroid was named after Soviet geodesist and war hero Yevgeniya Rudneva.
2608 Seneca, provisional designation 1978 DA, is a stony asteroid and sub-kilometer near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 0.9 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 17 February 1978, by German astronomer Hans-Emil Schuster at ESO's La Silla Observatory in northern Chile, and named after Roman philosopher Seneca.

1648 Shajna, provisional designation 1935 RF, is a stony asteroid from the inner regions of the asteroid belt, approximately 9 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 5 September 1935, by Russian astronomer Pelageya Shajn at Simeiz Observatory on the Crimean peninsula. Two weeks later, it was independently discovered by Cyril Jackson at Johannesburg Observatory, South Africa. It was later named after the discoverer and her husband, Russian astronomers Grigory Shajn.

1980 Tezcatlipoca, provisional designation 1950 LA, is an eccentric, stony asteroid and near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 6 kilometers (4 mi) in diameter.
(5646) 1990 TR is a probable rare-type binary asteroid classified as near-Earth object of the Amor group, approximately 2.3 kilometers in diameter. It was discovered on 11 October 1990, by Japanese astronomers Seiji Ueda and Hiroshi Kaneda at Kushiro Observatory near Kushiro, in eastern Hokkaido, Japan.
(163243) 2002 FB3, provisional designation 2002 FB3, is a stony asteroid on an eccentric orbit, classified as near-Earth object and potentially hazardous asteroid of the Athen group, approximately 1.6 kilometers (1 mile) in diameter. It was discovered on 18 March 2002, by astronomers with the Lincoln Near-Earth Asteroid Research at the Lincoln Laboratory's Experimental Test Site near Socorro, New Mexico, in the United States. The Q-type asteroid has a rotation period of 6.2 hours.







