This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |
| Millennium |
|---|
| 1st millennium BC |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
This article concerns the period 449 BC – 440 BC.
This article needs additional citations for verification .(January 2021) |
| Millennium |
|---|
| 1st millennium BC |
| Centuries |
| Decades |
| Years |
| Categories |
This article concerns the period 449 BC – 440 BC.
The Histories by Herodotus was written that contain the knowledge of the Greco Persian wars. [7]
448 BC
446 BC
445 BC
440 BC
449 BC
444 BC
443 BC
442 BC
441 BC
440 BC
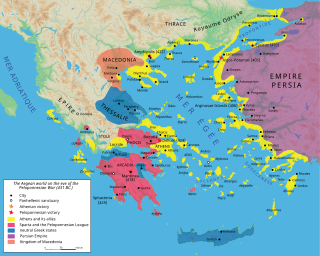
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece.

The Peloponnesian War was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided for a long time, until the decisive intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet, built with Persian subsidies, finally defeated Athens and started a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.

Pericles was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed by Thucydides, a contemporary historian, as "the first citizen of Athens". Pericles turned the Delian League into an Athenian empire and led his countrymen during the first two years of the Peloponnesian War. The period during which he led Athens, roughly from 461 to 429 BC, is sometimes known as the "Age of Pericles", but the period thus denoted can include times as early as the Persian Wars or as late as the following century.
This article concerns the period 479 BC – 470 BC.
This article concerns the period 469 BC – 460 BC.
This article concerns the period 459 BC – 450 BC.
This article concerns the period 439 BC – 430 BC.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.

This is a timeline of ancient Greece from its emergence around 800 BC to its subjection to the Roman Empire in 146 BC.
Year 440 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Macerinus and Lanatus. The denomination 440 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 445 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Augurinus and Philo. The denomination 445 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 449 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Third year of the decemviri and the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Barbatus. The denomination 449 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 457 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pulvillus and Augurinus or Cincinnatus and Vibulanus. The denomination 457 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Year 460 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Poplicola and Sabinus. The denomination 460 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

The decemviri or decemvirs refer to official 10-man commissions established by the Roman Republic.
The Megarian Decree was a set of economic sanctions levied upon Megara c. 432 BC by the Athenian Empire shortly before the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War. This move is considered one of the first uses of economics as a foreign policy tool. The decree addressed the Megarians' supposed trespass on land sacred to Demeter known as the Hiera Orgas, the killing of the Athenian herald who was sent to their city to reproach them, and giving shelter to slaves who had fled from Athens. The Megarian decree effectively blocked Megara from trading in any port within the Delian League, isolating the city and greatly damaging its economy. The exact influence the Megarian Decree had on the beginning of the Peloponnesian War is a matter that is highly debated to this day.

Cimon or Kimon was an Athenian strategos and politician.

Pentecontaetia is the term used to refer to the period in Ancient Greek history between the defeat of the second Persian invasion of Greece at Plataea in 479 BC and the beginning of the Peloponnesian War in 431 BC. The term originated with a scholiast commenting on Thucydides, who used it in their description of the period. The Pentecontaetia was marked by the rise of Athens as the dominant state in the Greek world and by the rise of Athenian democracy, a period also known as Golden Age of Athens. Since Thucydides focused his account on these developments, the term is generally used when discussing developments in and involving Athens.
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.