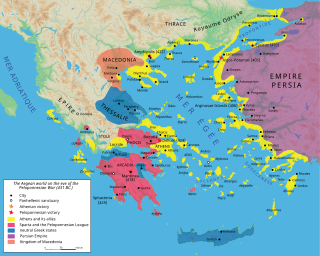
The Delian League, founded in 478 BC, was an association of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, under the leadership of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece.

The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens, Greece, and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. The word Acropolis is from the Greek words ἄκρον and πόλις. The term acropolis is generic and there are many other acropoleis in Greece. During ancient times the Acropolis of Athens was also more properly known as Cecropia, after the legendary serpent-man Cecrops, the supposed first Athenian king.

The Parthenon is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are considered some of the high points of classical Greek art, an enduring symbol of Ancient Greece, democracy and Western civilization.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.

Pericles was a Greek politician and general during the Golden Age of Athens. He was prominent and influential in Ancient Athenian politics, particularly between the Greco-Persian Wars and the Peloponnesian War, and was acclaimed by Thucydides, a contemporary historian, as "the first citizen of Athens". Pericles turned the Delian League into an Athenian empire and led his countrymen during the first two years of the Peloponnesian War. The period during which he led Athens, roughly from 461 to 429 BC, is sometimes known as the "Age of Pericles", but the period thus denoted can include times as early as the Persian Wars or as late as the following century.
This article concerns the period 459 BC – 450 BC.
This article concerns the period 449 BC – 440 BC.
This article concerns the period 439 BC – 430 BC.
This article concerns the period 429 BC – 420 BC.

Phidias or Pheidias was an Ancient Greek sculptor, painter, and architect, active in the 5th century BC. His Statue of Zeus at Olympia was one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. Phidias also designed the statues of the goddess Athena on the Athenian Acropolis, namely the Athena Parthenos inside the Parthenon, and the Athena Promachos, a colossal bronze which stood between it and the Propylaea, a monumental gateway that served as the entrance to the Acropolis in Athens. Phidias was the son of Charmides of Athens. The ancients believed that his masters were Hegias and Ageladas.
Year 449 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Third year of the decemviri and the Year of the Consulship of Potitus and Barbatus. The denomination 449 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Fifth-century Athens is the Greek city-state of Athens in the time from 480 to 404 BC. Formerly known as the Golden Age of Athens, the latter part being the Age of Pericles, it was buoyed by political hegemony, economic growth and cultural flourishing. The period began in 478 BC, after the defeat of the Persian invasion, when an Athenian-led coalition of city-states, known as the Delian League, confronted the Persians to keep the liberated Asian Greek cities free.

The Erechtheion or Temple of Athena Polias is an ancient Greek Ionic temple on the north side of the Acropolis, Athens, which was primarily dedicated to the goddess Athena.

The Pnyx is a hill or hillside in central Athens, the capital of Greece. Beginning as early as 507 BC, the Athenians gathered on the Pnyx to host their popular assemblies, thus making the hill one of the earliest and most important sites in the creation of democracy.

Athens is one of the oldest named cities in the world, having been continuously inhabited for perhaps 5,000 years. Situated in southern Europe, Athens became the leading city of Ancient Greece in the first millennium BC, and its cultural achievements during the 5th century BC laid the foundations of Western civilization.
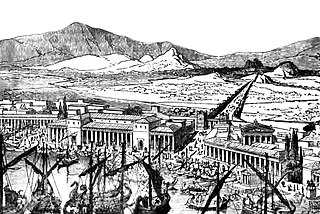
Although long walls were built at several locations in ancient Greece, notably Corinth and Megara, the term Long Walls generally refers to the walls that connected Athens' main city to its ports at Piraeus and Phaleron. Built in several phases, they provided a secure connection to the sea even during times of siege. The walls were about 6 km (3.7 mi) long. Construction began in the mid-5th century BC, and the walls were destroyed by the Spartans in 403 BC after Athens' defeat in the Peloponnesian War. They were rebuilt with Persian support during the Corinthian War in 395–391 BC. The Long Walls were a key element of Athenian military strategy, since they provided the city with a constant link to the sea and thwarted sieges conducted by land alone.
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.

The city of Athens during the classical period of ancient Greece was the major urban centre of the notable polis (city-state) of the same name, located in Attica, Greece, leading the Delian League in the Peloponnesian War against Sparta and the Peloponnesian League. Athenian democracy was established in 508 BC under Cleisthenes following the tyranny of Isagoras. This system remained remarkably stable, and with a few brief interruptions remained in place for 180 years, until 322 BC. The peak of Athenian hegemony was achieved in the 440s to 430s BC, known as the Age of Pericles.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to ancient Greece:

The Achaemenid destruction of Athens was carried out by the Achaemenid Army of Xerxes I during the Second Persian invasion of Greece, and occurred in two phases over a period of two years, in 480–479 BCE.











