Related Research Articles

Chi Serpentis is a solitary star in the Serpens Caput section of the equatorial constellation Serpens. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 14.84 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 222 light years from the Sun. The star is bright enough to be faintly visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of +5.30.
Epsilon Sextantis, Latinized from ε Sextantis, is a solitary, yellow-white hued star in the equatorial constellation of Sextans. With an apparent visual magnitude of 5.24, it is faintly visible to the naked eye on a dark night. The distance to this star, based upon an annual parallax shift of 16.86 mas, is about 193 light years. It is drifting further away from the Sun with a radial velocity of +15 km/s.
4 Arietis is a single star in the northern constellation of Aries, the ram. 4 Arietis is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a dim, blue-white hued star with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.86. The star has an annual parallax shift of 11.46±0.15 mas, which is equivalent to a distance of 285 light-years from the Sun. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +6 km/s.
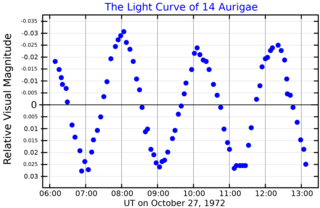
14 Aurigae is a quadruple star system located 269 light years away from the Sun in the zodiac constellation of Auriga. It has the variable star designation KW Aurigae, whereas 14 Aurigae is the Flamsteed designation. It is visible to the naked eye as a faint, white-hued star with a combined apparent visual magnitude of 5.01. The system is moving closer to the Sun with a heliocentric radial velocity of −9 km/s.

Alpha Chamaeleontis, Latinized from α Chamaeleontis, is a solitary star in the southern circumpolar constellation of Chamaeleon. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 4.06 and thus is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. With an annual parallax shift of 51.12 mas, it is located 63.8 light years from the Sun. The star is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −13 km/s, and is predicted to come to within 47 light-years in 666,000 years.

Tau Centauri, Latinized from τ Centauri, is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Centaurus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of +3.86. The distance to this star, based upon an annual parallax shift of 24.85 mas, is 131 light years. There is a 98% chance that it is a co-moving companion of Gamma Centauri; the two stars have an estimated separation of 1.7 ly (0.53 pc).
HD 118889 is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Boötes. It is faintly visible to the naked eye as a point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.57. The system is located at a distance of approximately 196 light years from the Sun based on stellar parallax, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −26 km/s.

Pi Herculis is a third-magnitude star in the constellation Hercules. As one of the four stars in the Keystone asterism, it is one of the constellation's more easily recognized. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.2, which is visible to the naked eye and makes it one of its brighter members. The Gaia spacecraft mission estimated its distance at roughly 112 parsecs from Earth, or about 367 light years away. The overall reduction in the star's visual magnitude due to extinction from the intervening cosmic dust is 0.11.
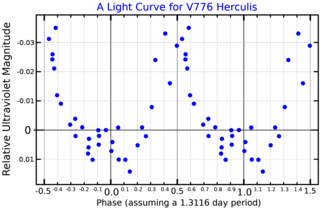
45 Herculis is a solitary variable star in the northern constellation Hercules. It has the Bayer designation l Herculis and the variable star designation V776 Herculis. The Flamsteed designation for this star comes from the publication Historia Coelestis Britannica by John Flamsteed. It is the 45th star in Flamsteed list of stars in the constellation Hercules, and is visible to the naked eye with a baseline apparent visual magnitude of 5.22. Parallax measurements show this star to be about 400 light-years away from the Solar System. It is moving closer to the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of −16 km/s.

Gamma Crateris is a binary star system, divisible with a small amateur telescope, and located at the center of the southern constellation of Crater. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.06. With an annual parallax shift of 39.62 mas as seen from Earth, this star is located 82.3 light years from the Sun. Based upon the motion of this system through space, it is a potential member of the Castor Moving Group.
Tau3 Eridani, Latinized from τ3 Eridani, is a star in the constellation Eridanus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.10. Using the parallax method, the distance to this star can be estimated as 88.6 light years. In 2001 it was reported as a candidate Vega-like star, meaning it appears to radiate an infrared excess from an orbiting circumstellar disk. However, this has not been confirmed.

Sigma Herculis, Latinized from σ Her, is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.18, making it bright enough to be visible to the naked eye. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.36 mas as seen from Earth, Sigma Herculis is located about 310 light years away from the Sun.

Phi Herculis is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 15.99 mas as seen from Earth, it is located around 204 light years from the Sun. With a combined apparent visual magnitude of 4.24, it is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye.
Chi Herculis, Latinized from χ Herculis, is a Sun-like star in the northern constellation of Hercules. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 63.16 mas as seen from Earth, it is located 51.6 light years from the Sun. The star is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.59. It has a relatively high proper motion, showing a transverse movement of 0.769 arc seconds per year and is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −56 km/s.
29 Herculis is a single star located around 351 light years away from the Sun in the northern constellation of Hercules, a few degrees away from Omega Herculis. It has the Bayer designation h Herculis, while 29 Herculis is the Flamsteed designation. This star is visible to the naked eye as a faint, orange-hued point of light with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.84. It is moving further from the Earth with a heliocentric radial velocity of +3 km/s. The star has a relatively high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 0.195 arc seconds per annum.
Upsilon2 Hydrae, Latinised from υ2 Hydrae, is a solitary star in the equatorial constellation of Hydra. Visible to the naked eye, it is photometrically stable with an apparent visual magnitude of 4.59. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 10.40 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 314 light-years from the Sun.
Kappa1 Lupi is a solitary star in the southern constellation of Lupus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.86, and forms a double star with Kappa2 Lupi. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 18.12 mas as seen from Earth, it is located about 180 light years from the Sun. Both Kappa1 Lupi and its neighbor Kappa2 Lupi are members of the Hyades Stream, which is a moving group that is coincident with the proper motions of the Hyades cluster.

Iota Delphini is a star in the constellation Delphinus. It has an apparent magnitude of about 5.4, meaning that it is just barely visible to the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements made by the Gaia spacecraft, this star is located at a distance of 196 light years.
HR 6594 is the Bright Star Catalogue designation for a binary star system in the northern constellation of Hercules. It is faintly visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 5.54; according to the Bortle scale, it is sufficiently bright to be visible from dark suburban skies. The distance to this system, as determined using parallax measurements, is about 114 light years. It is drifting closer with a heliocentric radial velocity of −43.7 km/s, and is predicted to come as near as 47 light-years in 686,000 years. On the celestial sphere it is located near the star Alpha Ophiuchi; their projected separation is just 3 light years, although their actual separation is much greater.
15 Delphini is a star in the equatorial constellation Delphinus. It has an apparent magnitude of 5.99, allowing it to be faintly seen with the naked eye. The star is relatively close at a distance of 99 light years but is receding with a heliocentric radial velocity of 4.1 km/s.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Brown, A. G. A.; et al. (Gaia collaboration) (August 2018). "Gaia Data Release 2: Summary of the contents and survey properties". Astronomy & Astrophysics . 616. A1. arXiv: 1804.09365 . Bibcode: 2018A&A...616A...1G . doi: 10.1051/0004-6361/201833051 . Gaia DR2 record for this source at VizieR.
- 1 2 Høg, E.; et al. (2000). "The Tycho-2 catalogue of the 2.5 million brightest stars". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 355: L27–L30. Bibcode:2000A&A...355L..27H.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Zorec, J.; Royer, F. (2012). "Rotational velocities of A-type stars". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 537: A120. arXiv: 1201.2052 . Bibcode:2012A&A...537A.120Z. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201117691. S2CID 55586789.
- 1 2 Abt, Helmut A.; Morrell, Nidia I. (1995). "The Relation between Rotational Velocities and Spectral Peculiarities among A-Type Stars". The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series. 99: 135. Bibcode:1995ApJS...99..135A. doi: 10.1086/192182 .
- 1 2 Cowley, A.; et al. (April 1969). "A study of the bright A stars. I. A catalogue of spectral classifications". Astronomical Journal. 74: 375–406. Bibcode:1969AJ.....74..375C. doi:10.1086/110819.
- ↑ Mermilliod, J.-C. (1986). "Compilation of Eggen's UBV data, transformed to UBV (unpublished)". Catalogue of Eggen's UBV Data. Bibcode:1986EgUBV........0M.
- 1 2 Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv: 1108.4971 . Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. S2CID 119257644.
- 1 2 Wilson, Ralph Elmer (1953). "General catalogue of stellar radial velocities". Washington. Bibcode:1953GCRV..C......0W.
- ↑ Pasinetti Fracassini, L. E.; et al. (2001). "Catalogue of Apparent Diameters and Absolute Radii of Stars (CADARS) - Third edition - Comments and statistics". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 367 (2): 521–24. arXiv: astro-ph/0012289 . Bibcode:2001A&A...367..521P. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20000451. S2CID 425754.
- ↑ Allende Prieto, C.; Lambert, D. L. (1999). "Fundamental parameters of nearby stars from the comparison with evolutionary calculations: masses, radii and effective temperatures". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 352: 555–562. arXiv: astro-ph/9911002 . Bibcode:1999A&A...352..555A.
- 1 2 David, Trevor J.; Hillenbrand, Lynne A. (2015). "The Ages of Early-Type Stars: Strömgren Photometric Methods Calibrated, Validated, Tested, and Applied to Hosts and Prospective Hosts of Directly Imaged Exoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal. 804 (2): 146. arXiv: 1501.03154 . Bibcode:2015ApJ...804..146D. doi:10.1088/0004-637X/804/2/146. S2CID 33401607.
- 1 2 "60 Her". SIMBAD . Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg . Retrieved 2019-06-14.
- ↑ Eggleton, P. P.; Tokovinin, A. A. (September 2008). "A catalogue of multiplicity among bright stellar systems". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 389 (2): 869–879. arXiv: 0806.2878 . Bibcode:2008MNRAS.389..869E. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2966.2008.13596.x . S2CID 14878976.
- ↑ Redfield, Seth; et al. (June 2007). "Spitzer Limits on Dust Emission and Optical Gas Absorption Variability around Nearby Stars with Edge-on Circumstellar Disk Signatures". The Astrophysical Journal. 661 (2): 944–971. arXiv: astro-ph/0703089 . Bibcode:2007ApJ...661..944R. doi:10.1086/517516. S2CID 42241365.
- ↑ van Belle, Gerard T. (March 2012), "Interferometric observations of rapidly rotating stars", The Astronomy and Astrophysics Review, 20 (1): 51, arXiv: 1204.2572 , Bibcode:2012A&ARv..20...51V, doi:10.1007/s00159-012-0051-2, S2CID 119273474.