
Gliese 570 is a quaternary star system approximately 19 light-years away. The primary star is an orange dwarf star. The other secondary stars are themselves a binary system, two red dwarfs that orbit the primary star. A brown dwarf has been confirmed to be orbiting in the system. In 1998, an extrasolar planet was thought to orbit the primary star, but it was discounted in 2000.
Struve 2398 is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Draco. Struve 2398 is star number 2398 in the Struve Double Star Catalog of Baltic-German astronomer Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve. The astronomer's surname, and hence the star identifier, is sometimes indicated by a Greek sigma, Σ. Although the components are too faint to be viewed with the naked eye, this star system is among the closest to the Sun. Parallax measurements by the Hipparcos spacecraft give them an estimated distance of about 11.6 light years away.
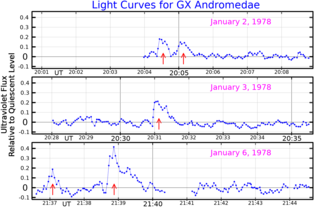
Groombridge 34 is a binary star system in the northern constellation of Andromeda. It was listed as entry number 34 in A Catalogue of Circumpolar Stars, published posthumously in 1838 by British astronomer Stephen Groombridge. Based upon parallax measurements taken by the Gaia spacecraft, the system is located about 11.6 light-years from the Sun. This positions the pair among the nearest stars to the Solar System.
Gliese 674(GJ 674) is a small red dwarf star with an exoplanetary companion in the southern constellation of Ara. It is too faint to be visible to the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 9.38 and an absolute magnitude of 11.09. The system is located at a distance of 14.8 light-years from the Sun based on parallax measurements, but is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −2.9 km/s. It is a candidate member of the 200 million year old Castor stream of co-moving stars.

Gliese 105 is a triple star system in the constellation of Cetus. It is located relatively near the Sun at a distance of 23.6 light-years. Despite this, even the brightest component is barely visible with the unaided eye (see Bortle scale). No planets have yet been detected around any of the stars in this system.
Gliese 849, or GJ 849, is a small, solitary star in the equatorial constellation of Aquarius. It has a reddish hue and is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 10.41. The distance to this star is 28.7 light years based on parallax, but it is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −15.3 km/s. It has a pair of confirmed gas giant companions.
Gliese 832 is a red dwarf of spectral type M2V in the southern constellation Grus. The apparent visual magnitude of 8.66 means that it is too faint to be seen with the naked eye. It is located relatively close to the Sun, at a distance of 16.2 light years and has a high proper motion of 818.93 milliarcseconds per year. Gliese 832 has just under half the mass and radius of the Sun. Its estimated rotation period is a relatively leisurely 46 days. The star is roughly 9.5 billion years old.
Gliese 412 is a pair of stars that share a common proper motion through space and are thought to form a binary star system. The pair have an angular separation of 31.4″ at a position angle of 126.1°. They are located 15.8 light-years distant from the Sun in the constellation Ursa Major. Both components are relatively dim red dwarf stars.
Gliese 176 is a red dwarf in the constellation of Taurus. Based upon parallax measurements from the Hipparcos mission, it is located approximately 30 light-years away. The star is orbited by a Super-Earth.
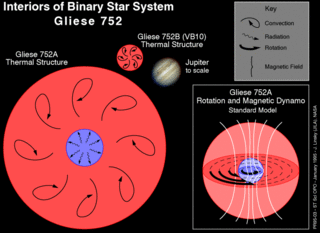
Gliese 752 is a binary star system in the Aquila constellation. This system is relatively nearby, at a distance of about 19 light years.
L 97-12 is a nearby degenerate star, located in the constellation Volans, the single known component of the system.

G 9-38, also known as EI Cancri and GJ 1116, is a binary star system consisting of two M-type stars. At 16.7 light-years from the Sun, the system is relatively nearby. The system has a very high stellar flare activity, with average five flares per hour.
Gliese 754 is a dim star in the southern constellation of Telescopium. It has an apparent visual magnitude of 12.25, which requires a telescope to view. The star is located at a distance of 19.3 light-years from the Sun based on parallax, and it is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +7 km/s. It is one of the hundred closest stars to the Solar System. Calculations of its orbit around the Milky Way showed that it is eccentric, and indicate that it might be a thick disk object.
Gliese 3323 is a nearby single star located in the equatorial constellation Eridanus, about 0.4° to the northwest of the naked eye star Psi Eridani. It is invisible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude 12.20. Parallax measurements give a distance estimate of 17.5 light years from the Sun. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +42.3 km/s. Roughly 104,000 years ago, the star is believed to have come to within 7.34 ± 0.16 light-years of the Solar System.
ADS 7251 is a binary star system 6.33 parsecs from the Sun. The components are near-identical red dwarfs separated by 17″ in 2019.
Gliese 784 is a single red dwarf star located in the southern constellation of Telescopium that may host an exoplanetary companion. The star was catalogued in 1900, when it was included in the Cordoba Durchmusterung (CD) by John M. Thome with the designation CD -45 13677. It is too faint to be viewed with the naked eye, having an apparent visual magnitude of 7.96. Gliese 784 is located at a distance of 20.1 light-years from the Sun as determined from parallax measurements, and is drifting closer with a radial velocity of −33.5 km/s. The system is predicted to come as close as 11.4 light-years in ~121,700 years time.
Gliese 3512 is a nearby star in the northern circumpolar constellation of Ursa Major. It is invisible to the naked eye but can be observed using a telescope, having an apparent visual magnitude of +15.05. The star is located at a distance of 31 light-years from the Sun based on parallax. It has a high proper motion, traversing the celestial sphere at the rate of 1.311″ yr−1. The measurement of the star's radial velocity is poorly constrained, but it appears to be drifting further away at a rate of ~8 km/s.
Gliese 49 is a star in the northern constellation of Cassiopeia. Visually, it is located 106 arc minutes north of the bright star γ Cassiopeiae. With an apparent visual magnitude of 9.56, it is not observable with the naked eye. It is located, based on the reduction of parallax data of Gaia, 32.1 light-years away from the Solar System. The star is drifting closer to the Sun with a radial velocity of −6 km/s.

Gliese 569 is a ternary star system composed of a main-sequence star orbited by a pair of brown dwarfs in the constellation of Boötes about 32 light years away.
Gliese 514, also known as BD+11 2576 or HIP 65859, is a M-type main-sequence star, in the constellation Virgo 24.85 light-years away from the Sun. The proximity of Gliese 514 to the Sun was known exactly since 1988.





