
Chemotherapy is the type of cancer treatment that uses one or more anti-cancer drugs in a standard regimen. Chemotherapy may be given with a curative intent, or it may aim only to prolong life or to reduce symptoms. Chemotherapy is one of the major categories of the medical discipline specifically devoted to pharmacotherapy for cancer, which is called medical oncology.

Angiography or arteriography is a medical imaging technique used to visualize the inside, or lumen, of blood vessels and organs of the body, with particular interest in the arteries, veins, and the heart chambers. Modern angiography is performed by injecting a radio-opaque contrast agent into the blood vessel and imaging using X-ray based techniques such as fluoroscopy.
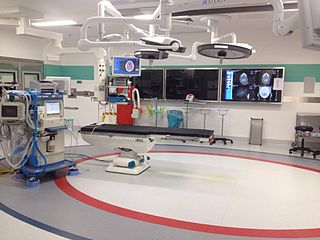
Interventional radiology (IR) is a medical specialty that performs various minimally-invasive procedures using medical imaging guidance, such as x-ray fluoroscopy, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, or ultrasound. IR performs both diagnostic and therapeutic procedures through very small incisions or body orifices. Diagnostic IR procedures are those intended to help make a diagnosis or guide further medical treatment, and include image-guided biopsy of a tumor or injection of an imaging contrast agent into a hollow structure, such as a blood vessel or a duct. By contrast, therapeutic IR procedures provide direct treatment—they include catheter-based medicine delivery, medical device placement, and angioplasty of narrowed structures.
In biology, hemostasis or haemostasis is a process to prevent and stop bleeding, meaning to keep blood within a damaged blood vessel. It is the first stage of wound healing. Hemostasis involves three major steps:

Polyvinyl alcohol (PVOH, PVA, or PVAl) is a water-soluble synthetic polymer. It has the idealized formula [CH2CH(OH)]n. It is used in papermaking, textile warp sizing, as a thickener and emulsion stabilizer in polyvinyl acetate (PVAc) adhesive formulations, in a variety of coatings, and 3D printing. It is colourless (white) and odorless. It is commonly supplied as beads or as solutions in water. Without an externally added crosslinking agent, PVA solution can be gelled through repeated freezing-thawing, yielding highly strong, ultrapure, biocompatible hydrogels which have been used for a variety of applications such as vascular stents, cartilages, contact lenses, etc.
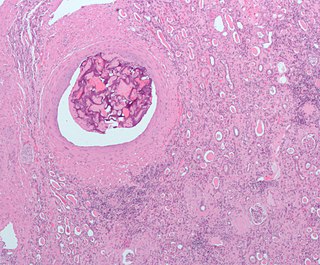
Embolization refers to the passage and lodging of an embolus within the bloodstream. It may be of natural origin (pathological), in which sense it is also called embolism, for example a pulmonary embolism; or it may be artificially induced (therapeutic), as a hemostatic treatment for bleeding or as a treatment for some types of cancer by deliberately blocking blood vessels to starve the tumor cells.
Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a minimally invasive procedure performed in interventional radiology to restrict a tumor's blood supply. Small embolic particles coated with chemotherapeutic drugs are injected selectively through a catheter into an artery directly supplying the tumor. These particles both block the blood supply and induce cytotoxicity, attacking the tumor in several ways.

Mitomycin C is a mitomycin that is used as a chemotherapeutic agent by virtue of its antitumour activity.

Uterine artery embolization is a procedure in which an interventional radiologist uses a catheter to deliver small particles that block the blood supply to the uterine body. The procedure is primarily done for the treatment of uterine fibroids and adenomyosis. Since uterine fibroids are the most common indication, it is also often referred to as uterine fibroid embolization. Compared to surgical treatment for fibroids such as a hysterectomy, in which a woman's uterus is removed, uterine artery embolization may be beneficial in women who wish to retain their uterus. Other reasons for uterine artery embolization are postpartum hemorrhage and uterine arteriovenous malformations.

Tirapazamine is an experimental anticancer drug that is activated to a toxic radical only at very low levels of oxygen (hypoxia). Such levels are common in human solid tumors, a phenomenon known as tumor hypoxia. Thus, tirapazamine is activated to its toxic form preferentially in the hypoxic areas of solid tumors. Cells in these regions are resistant to killing by radiotherapy and most anticancer drugs. Thus the combination of tirapazamine with conventional anticancer treatments is particularly effective. As of 2006, tirapazamine is undergoing phase III testing in patients with head and neck cancer and gynecological cancer, and similar trials are being undertaken for other solid tumor types.

The enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect is a controversial concept by which molecules of certain sizes tend to accumulate in tumor tissue much more than they do in normal tissues. The general explanation that is given for this phenomenon is that, in order for tumor cells to grow quickly, they must stimulate the production of blood vessels. VEGF and other growth factors are involved in cancer angiogenesis. Tumor cell aggregates as small as 150–200 μm, start to become dependent on blood supply carried out by neovasculature for their nutritional and oxygen supply. These newly formed tumor vessels are usually abnormal in form and architecture. They are poorly aligned defective endothelial cells with wide fenestrations, lacking a smooth muscle layer, or innervation with a wider lumen, and impaired functional receptors for angiotensin II. Furthermore, tumor tissues usually lack effective lymphatic drainage. All of these factors lead to abnormal molecular and fluid transport dynamics, especially for macromolecular drugs. This phenomenon is referred to as the "enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect" of macromolecules and lipids in solid tumors. The EPR effect is further enhanced by many pathophysiological factors involved in enhancement of the extravasation of macromolecules in solid tumor tissues. For instance, bradykinin, nitric oxide / peroxynitrite, prostaglandins, vascular permeability factor, tumor necrosis factor and others. One factor that leads to the increased retention is the lack of lymphatics around the tumor region which would filter out such particles under normal conditions.

Trabeculectomy is a surgical procedure used in the treatment of glaucoma to relieve intraocular pressure by removing part of the eye's trabecular meshwork and adjacent structures. It is the most common glaucoma surgery performed and allows drainage of aqueous humor from within the eye to underneath the conjunctiva where it is absorbed. This outpatient procedure was most commonly performed under monitored anesthesia care using a retrobulbar block or peribulbar block or a combination of topical and subtenon anesthesia. Due to the higher risks associated with bulbar blocks, topical analgesia with mild sedation is becoming more common. Rarely general anesthesia will be used, in patients with an inability to cooperate during surgery.

Primary tumors of the heart are extremely rare tumors that arise from the normal tissues that make up the heart. The incidence of primary cardiac tumors has been found to be approximately 0.02%. This is in contrast to secondary tumors of the heart, which are typically either metastatic from another part of the body, or infiltrate the heart via direct extension from the surrounding tissues. Metastatic tumors to the heart are about 20 times more common than primary cardiac tumors.
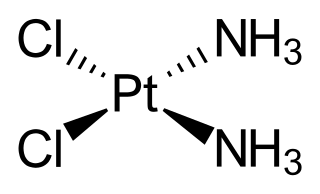
A radiosensitizer is an agent that makes tumor cells more sensitive to radiation therapy. It is sometimes also known as a radiation sensitizer or radio-enhancer.
Hepatic artery embolization, also known as trans-arterial embolization (TAE), is one of the several therapeutic methods to treat primary liver tumors or metastases to the liver. The embolization therapy can reduce the size of the tumor, and decrease the tumor's impact such its hormone production, effectively decreasing symptoms. The treatment was initially developed in the early 1970s. The several types of hepatic artery treatments are based on the observation that tumor cells get nearly all their nutrients from the hepatic artery, while the normal cells of the liver get about 70-80 percent of their nutrients and 50% their oxygen supply from the portal vein, and thus can survive with the hepatic artery effectively blocked. In practice, hepatic artery embolization occludes the blood flow to the tumors, achieving significant tumor shrinkage in over 80% of people. Shrinkage rates vary.
Interventional oncology is a subspecialty field of interventional radiology that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of cancer and cancer-related problems using targeted minimally invasive procedures performed under image guidance. Interventional oncology has developed to a separate pillar of modern oncology and it employs X-ray, ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to help guide miniaturized instruments to allow targeted and precise treatment of solid tumours located in various organs of the human body, including but not limited to the liver, kidneys, lungs, and bones. Interventional oncology treatments are routinely carried out by interventional radiologists in appropriate settings and facilities.
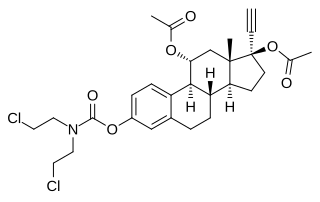
Cytestrol acetate is a steroidal antiestrogen and a cytostatic antineoplastic agent which was developed for the treatment of breast cancer but was never marketed.
Portal vein embolization (PVE) is a preoperative procedure performed in interventional radiology to initiate hypertrophy of the anticipated future liver remnant a couple weeks prior to a major liver resection procedure. The procedure involves injecting the right or left portal vein with embolic material to occlude portal blood flow. By occluding the blood flow to areas of the liver that will be resected away, the blood is diverted to healthy parts of the liver and induces hyperplasia. This may allow for a more extensive resection or stage bilateral resections that would otherwise be contraindicated resulting in better oncological treatment outcomes.
Transarterial bland embolization is a catheter-based tumor treatment of the liver. In this procedure, embolizing agents can be delivered through the tumor's feeding artery in order to completely occlude the tumor's blood supply. The anti-tumor effects are solely based on tumor ischemia and infarction of tumor tissue, as no chemotherapeutic agents are administered. The rationale for the use of bland embolization for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and/or other hyper-vascular tumors is based on the fact that a normal liver receives a dual blood supply from the hepatic artery (25%) and the portal vein (75%). As the tumor grows, it becomes increasingly dependent on the hepatic artery for blood supply. Once a tumor nodule reaches a diameter of 2 cm or more, most of the blood supply is derived from the hepatic artery. Therefore, bland embolization and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) consist of the selective angiographic occlusion of the tumor arterial blood supply with a variety of embolizing agents, with or without the precedence of local chemotherapy infusion. The occlusion by embolic particles results in tumor hypoxia and necrosis, without affecting the normal hepatic parenchyma.
Bronchial artery embolization is a treatment for hemoptysis, abbreviated as BAE. It is a kind of catheter intervention to control hemoptysis by embolizing the bronchial artery, which is a bleeding source. Embolic agents are particulate embolic material such as gelatin sponge or polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), and liquid embolic material such as NBCA, or metallic coils.













