
Chlorine is a chemical element; it has symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine.
Acetic acid bacteria (AAB) are a group of Gram-negative bacteria which oxidize sugars or ethanol and produce acetic acid during fermentation. The acetic acid bacteria consist of 10 genera in the family Acetobacteraceae. Several species of acetic acid bacteria are used in industry for production of certain foods and chemicals.

Aqua regia is a mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid, optimally in a molar ratio of 1:3. Aqua regia is a fuming liquid. Freshly prepared aqua regia is colorless, but it turns yellow, orange or red within seconds from the formation of nitrosyl chloride and nitrogen dioxide. It was so named by alchemists because it can dissolve noble metals like gold and platinum, though not all metals.

An oxidizing agent is a substance in a redox chemical reaction that gains or "accepts"/"receives" an electron from a reducing agent. In other words, an oxidizer is any substance that oxidizes another substance. The oxidation state, which describes the degree of loss of electrons, of the oxidizer decreases while that of the reductant increases; this is expressed by saying that oxidizers "undergo reduction" and "are reduced" while reducers "undergo oxidation" and "are oxidized". Common oxidizing agents are oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and the halogens.

Chlorine dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula ClO2 that exists as yellowish-green gas above 11 °C, a reddish-brown liquid between 11 °C and −59 °C, and as bright orange crystals below −59 °C. It is usually handled as an aqueous solution. It is commonly used as a bleach. More recent developments have extended its applications in food processing and as a disinfectant.

In chemistry, hypochlorite, or chloroxide is an anion with the chemical formula ClO−. It combines with a number of cations to form hypochlorite salts. Common examples include sodium hypochlorite and calcium hypochlorite. The Cl-O distance in ClO− is 1.69 Å.
In chemistry, disproportionation, sometimes called dismutation, is a redox reaction in which one compound of intermediate oxidation state converts to two compounds, one of higher and one of lower oxidation state. The reverse of disproportionation, such as when a compound in an intermediate oxidation state is formed from precursors of lower and higher oxidation states, is called comproportionation, also known as symproportionation.

Sodium chlorite (NaClO2) is a chemical compound used in the manufacturing of paper and as a disinfectant.

Lead(IV) oxide, commonly known as lead dioxide, is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula PbO2. It is an oxide where lead is in an oxidation state of +4. It is a dark-brown solid which is insoluble in water. It exists in two crystalline forms. It has several important applications in electrochemistry, in particular as the positive plate of lead acid batteries.
Calcium hypochlorite is an inorganic compound with chemical formula Ca(ClO)2, also written as Ca(OCl)2. It is a white solid, although commercial samples appear yellow. It strongly smells of chlorine, owing to its slow decomposition in moist air. This compound is relatively stable as a solid and solution and has greater available chlorine than sodium hypochlorite. "Pure" samples have 99.2% active chlorine. Given common industrial purity, an active chlorine content of 65-70% is typical. It is the main active ingredient of commercial products called bleaching powder, used for water treatment and as a bleaching agent.

The lingual artery arises from the external carotid artery between the superior thyroid artery and facial artery. It can be located easily in the tongue.
Monochloramine, often called chloramine, is the chemical compound with the formula NH2Cl. Together with dichloramine (NHCl2) and nitrogen trichloride (NCl3), it is one of the three chloramines of ammonia. It is a colorless liquid at its melting point of −66 °C (−87 °F), but it is usually handled as a dilute aqueous solution, in which form it is sometimes used as a disinfectant. Chloramine is too unstable to have its boiling point measured.

Bleach is the generic name for any chemical product that is used industrially or domestically to remove colour from fabric or fiber or to disinfect after cleaning. It often refers specifically to a dilute solution of sodium hypochlorite, also called "liquid bleach".
Bleaching of wood pulp is the chemical processing of wood pulp to lighten its color and whiten the pulp. The primary product of wood pulp is paper, for which whiteness is an important characteristic. These processes and chemistry are also applicable to the bleaching of non-wood pulps, such as those made from bamboo or kenaf.

Sodium bismuthate is an inorganic compound, and a strong oxidiser with chemical formula NaBiO3. It is somewhat hygroscopic, but not soluble in cold water, which can be convenient since the reagent can be easily removed after the reaction. It is one of the few water insoluble sodium salts. Commercial samples may be a mixture of bismuth(V) oxide, sodium carbonate and sodium peroxide.
The Pinnick oxidation is an organic reaction by which aldehydes can be oxidized into their corresponding carboxylic acids using sodium chlorite (NaClO2) under mild acidic conditions. It was originally developed by Lindgren and Nilsson. The typical reaction conditions used today were developed by G. A. Kraus. H.W. Pinnick later demonstrated that these conditions could be applied to oxidize α,β-unsaturated aldehydes. There exist many different reactions to oxidize aldehydes, but only a few are amenable to a broad range of functional groups. The Pinnick oxidation has proven to be both tolerant of sensitive functionalities and capable of reacting with sterically hindered groups. This reaction is especially useful for oxidizing α,β-unsaturated aldehydes, and another one of its advantages is its relatively low cost.

Paper chemicals designate a group of chemicals that are used for paper manufacturing, or modify the properties of paper. These chemicals can be used to alter the paper in many ways, including changing its color and brightness, or by increasing its strength and resistance to water. The chemicals can be defined on basis of their usage in the process.

Thiourea dioxide or thiox is an organosulfur compound that is used in the textile industry. It functions as a reducing agent. It is a white solid, and exhibits tautomerism.
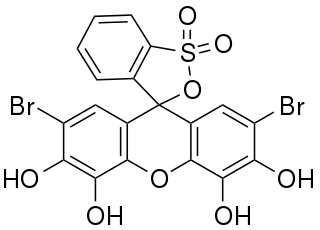
Bromopyrogallol red is frequently used in analytical chemistry as a reagent for spectrophometric analysis and as an complexometric indicator.

Chlorine-releasing compounds, also known as chlorine base compounds, is jargon to describe certain chlorine-containing substances that are used as disinfectants and bleaches. They include the following chemicals: sodium hypochlorite, chloramine, halazone, and sodium dichloroisocyanurate. They are widely used to disinfect water and medical equipment, and surface areas as well as bleaching materials such as cloth. The presence of organic matter can make them less effective as disinfectants. They come as a liquid solution, or as a powder that is mixed with water before use.












