 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Foipan |
| Other names | FOY-305 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
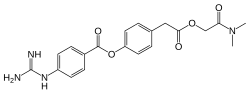
| Formula | C20H22N4O5 |
| Molar mass | 398.419 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Camostat is a serine protease inhibitor. Serine protease enzymes have a variety of functions in the body, and so camostat has a diverse range of uses. Camostat is approved in Japan for the treatment of chronic pancreatitis and postoperative reflux esophagitis. [1] [2] The oral proteolytic enzyme inhibitor has been on the market since 1985 under the trade name Foipan Tablets. The manufacturer is Ono Pharmaceutical. The drug is used in the treatment of some forms of cancer and is also effective against some viral infections, as well as inhibiting fibrosis in liver or kidney disease or pancreatitis. [3] [4] [5] [6] [7]
