
Benin, officially the Republic of Benin, is a country in West Africa. It was formerly known as Dahomey. It is bordered by Togo to the west, Nigeria to the east, Burkina Faso to the north-west, and Niger to the north-east. The majority of its population lives on the southern coastline of the Bight of Benin, part of the Gulf of Guinea in the northernmost tropical portion of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Porto-Novo, and the seat of government is in Cotonou, the most populous city and economic capital. Benin covers an area of 112,622 km2 (43,484 sq mi), and its population in 2021 was estimated to be approximately 13 million. It is a tropical country with an economy heavily dependent on agriculture and is an exporter of palm oil and cotton.

Benin City serves as the capital and largest metropolitan centre of Edo State, situated in southern Nigeria. Notably, it ranks as the fourth-most populous city in Nigeria, according to the 2006 national census, preceded only by Lagos, Kano, and Ibadan.

Edo, officially known as Edo State, is a state in the South-South geopolitical zone of the federal republic of Nigeria. As of 2024, the state was ranked as the 22nd most populous state (5,250,000) in Nigeria. The estimated state population is around 4,777,000 in 2022. Edo State is the 22nd largest state by landmass in Nigeria. The state's capital and largest city, Benin City, is the fourth largest city in Nigeria, and the centre of the country's rubber industry. Created in 1991 from the former Bendel State, it is also known as the heart beat of the nation. Edo State borders Kogi State to the north for 133 km and across the Niger River for 81 km to the northeast, Anambra State to the east for about four km across the Niger River, Delta State to the southeast and south for 350 km, and Ondo State to the west.

Esan people, or Esans, are an Edoid-speaking ethnic group who share a common culture and the Esan language. The Esan are traditionally known to be agriculturalists, trado-medical practitioners, mercenary warriors and hunters. They cultivate palm trees, Irvingia gabonensis (erhonhiele), Cherry (Otien), bell pepper (akoh) coconut, betel nut, kola nut, black pear, avocado pear, yams, cocoyam, cassava, maize, rice, beans, groundnut, bananas, oranges, plantains, sugar cane, tomato, potato, okra, pineapple, paw paw, and various vegetables.

Sungbo's Eredo is a system of defensive walls and ditches that is located to the southwest of the Yoruba town of Ijebu Ode in Ogun State, southwest Nigeria. It was built in 800–1000 AD in honour of the Ijebu noblewoman Oloye Bilikisu Sungbo. The location is on Nigeria's tentative list of potential UNESCO World Heritage Sites.
Igueben is a local government area of Edo State, Nigeria. Its headquarters are located in the town of Igueben, which has an area of 380 km2 (150 sq mi) and a population of 69,639 according to the 2006 census. The postal code is 310.
Ikpoba Okha is a Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Its headquarters is in the town of Idogbo, along Benin/Abraka Road. The LGA is made up of several towns and villages such as Evbuomodu, Uwusan, Obazagbon, Agedo, Evbumufi, Etiosa, Obadoloviyeyi, Obenevbugo, Obe, Oghoghobi, Okha, Obanyantor, Ekae, Utezi, Uhie, Ogheghe, Obagie Obaretin and so on. The estimated population of Ikpoba Okha is about 301,447 inhabitants, with the majority of the area's dwellers being members of the Benin/Edo ethnic division.
Orhionmwon is a Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Its headquarter is in the town of Abudu. It has an area of 2,382 km2 and a population of 206,717 at the 2006 census. The postal code of the area is 301.
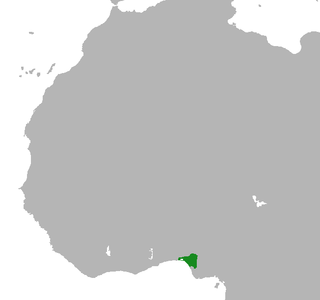
The Kingdom of Benin, also known as Great Benin or Benin Kingdom is a kingdom within what is now considered southern Nigeria. It has no historical relation to the modern republic of Benin, which was known as Dahomey from the 17th century until 1975. The Kingdom of Benin's capital was Edo, now known as Benin City in Edo State, Nigeria. The Benin Kingdom was one of the oldest and most developed states in the coastal hinterland of West Africa. It grew out of the previous Edo Kingdom of Igodomigodo around the 11th century AD; it was annexed by the British Empire in 1897.

The Benin ivory mask is a miniature sculptural portrait in ivory of Idia, the first Iyoba of the 16th century Benin Empire, taking the form of a traditional African mask. The masks were looted by the British from the palace of the Oba of Benin in the Benin Expedition of 1897.
Unuamen also spelt Unuame is an ancient village community by Ovia river in Ovia North-East Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. Unuame is about 15 kilometres (9 mi) from Benin City and 20 kilometres (12 mi) from Benin Airport. Unuame is one of the ancestral homes of Oba Esigie's maternal grandfather and home town to some group of Binis. The people of Unuame have remained loyal to the monarch since the establishment of the ancient Kingdom of Benin. Being a part of the Kingdom of Benin, Unuame is at the heart of the tropical rainforest in the southern part of Nigeria, way to the west of the delta of the Niger River and inland from the coast.
Agbede is a Muslim town in the Northern part of Edo State. It has been in existence since the 13th century. It is the door way into the North of the State.
Ugboha is a town in Esan South Local Government of Edo State Nigeria. Ugboha lies on the geographical coordinate of latitude 6°45′N6°28′E.
EbhoIkhimi popularly called Ewohimi is an Ancient Kingdom in Esan South East Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria. EbhoIkhimi lies on the geographical coordinate of latitude 6°28′N6°19′E. EbhoIkhimi consists of several towns.
Odionwere is a traditional leadership position among the Edo people of Edo State, Nigeria to refer to the oldest or most respected person in a community or family. The term Odionwere can be roughly translated as "village chief" or "elder" in the Edo language. The role of an Odionwere is significant in maintaining the cultural and social fabric of Edo communities.
Afuze is a town located in the Owan East Local Government Area of Edo State, Nigeria and serves as the administrative headquarters of the Owan East Local Government Area.
The Ovia River or Osse River is a perennial watercourse in Southwestern Nigeria, flowing through the states of; Kogi, Ondo and Edo, before emptying into the Gulf of Guinea. Its watecourse spans approximately 120 kilometers through diverse terrain.
The Oba Market is an open-air market situated at Ring Road in the center of Benin City, Edo State, Nigeria. Its roots date back to the 15th century, making it one of the most historically significant markets in the region.

Edo literature includes both written and oral works in the Edo language by the Edo people of Nigeria. It has its origins in precolonial times and has evolved over time. The literature is a reflection of Edo culture and it includes various periods, genres, and authors. It is rooted in traditional expressions such as brass-casting, wood carving, and pictorial writing. The written form became more prominent during the colonial era with the adoption of the Roman script. Folk songs are a part of Edo literature and are a part of Edo cultural heritage. These songs serve as repositories of historical narratives, moral teachings, and cultural expressions.
Ovia is a deity in the traditional religious beliefs of Nigeria, particularly among the Edo people of Benin City. This deity is associated with concepts of peace and providence. Ovia's historical origins can be traced back to the ancient Kingdom of Benin, known for its cultural traditions and governance structure. Emerging during a period of relative stability, Ovia was regarded as a symbol of peace and prosperity within the kingdom. Oral traditions and cultural practices have preserved the significance of Ovia across generations. Ovia was believed to bestow blessings that contributed to the well-being of the kingdom, fostering an environment of harmony and abundance. The deity was invoked during ceremonies, including royal coronations and harvest festivals.









