Acacia cultriformis, known as the knife-leaf wattle, dogtooth wattle, half-moon wattle or golden-glow wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub of the genus Acacia native to Australia. It is widely cultivated, and has been found to have naturalised in Asia, Africa, North America, New Zealand and South America. A. cultriformis grows to a height of about 4 m (13 ft) and has triangle-shaped phyllodes. The yellow flowers appear from August to November in its natural range. Its attractive foliage and bright flowers make it a popular garden plant.

Acacia melanoxylon, commonly known as the Australian blackwood, is an Acacia species native to south-eastern Australia. The species is also known as blackwood, hickory, mudgerabah, Tasmanian blackwood, or blackwood acacia. The tree belongs to the Plurinerves section of Acacia and is one of the most wide-ranging tree species in eastern Australia and is quite variable mostly in the size and shape of the phyllodes.

Acacia harpophylla, commonly known as brigalow, brigalow spearwood or orkor, is an endemic tree of Australia. The Aboriginal Australian group the Gamilaraay peoples know the tree as Barranbaa or Burrii. It is found in central and coastal Queensland to northern New South Wales. It can reach up to 25 m (82 ft) tall and forms extensive open-forest communities on clay soils.

Acacia denticulosa, commonly known as sandpaper wattle, is a species of Acacia native to the south-west of Western Australia. A spindly shrub 1–4 m high, it flowers from September to October, producing dense, curved, yellow flower spikes.

Acacia meiantha is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to a small area in eastern Australia. It was listed as Endangered in 2018 according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
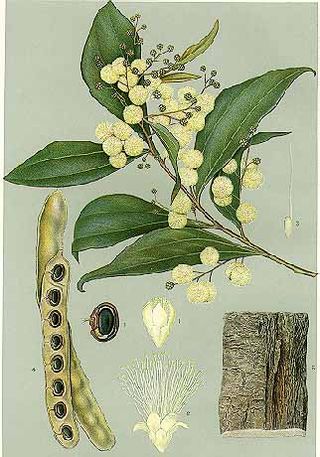
Acacia binervata, commonly known as two-veined hickory, is a shrub or tree that is endemic to eastern Australia.

Acacia decora is a plant native to eastern Australia. Common names include the western silver wattle and the showy wattle. The species name refers to the plant's decorative qualities.

Acacia stipuligera is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae. It is native to arid and tropical parts of northern Australia.

Acacia pharangites, commonly known as Wongan gully wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to the Wongan Hills of south western Australia and is listed as endangered according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia acrionastes is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to eastern Australia. It is a spindly, glabrous shrub or tree with linear phyllodes, flowers arranged in a racemes with 10 to 15 spherical heads of flowers, each with 12 to 16 creamy yellow flowers, and leathery pods up to 10 mm (0.39 in) long.
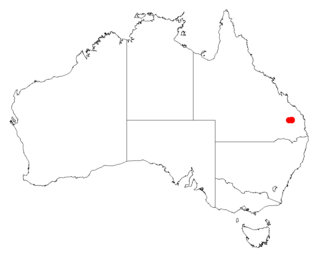
Acacia eremophiloides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to Queensland.

Acacia holotricha is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of north eastern Australia.

Acacia saxicola, commonly known as Mount Maroon wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia caroleae, also known as Carole's wattle or narrow leaf currawong, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia grandifolia is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is list as vulnerable according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia mimula is a tree in the genus Acacia. It is native to the Northern Territory, and found in open forest, from the Darwin region to western Arnhem Land.

Acacia tingoorensis, also known as Tingoora wattle, is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.

Acacia leptoloba, also known as Irvinebank wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of north eastern Australia.

Acacia melvillei, commonly known as yarran, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to south eastern Australia.

Acacia tephrina, commonly known as boree, is a tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of north eastern Australia. It is rated as being of least concern according to Nature Conservation Act 1992.