
Acacia hopperiana is a small tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.

Acacia intorta is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to arid parts of central Western Australia.

Acacia jibberdingensis, also known as Jibberding wattle or willow-leafed wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to Western Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia pellita is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to parts of tropical northern Australia.

Acacia richardsii is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.
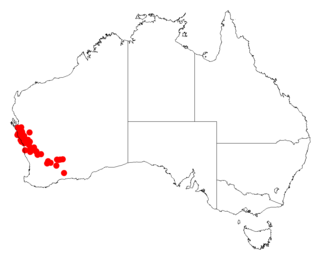
Acacia signata is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to western Australia.
Acacia stanleyi, commonly known as Stanley's rock wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia juncifolia, commonly known as rush-leaf wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to north eastern Australia.
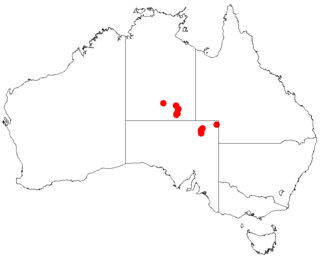
Acacia pickardii, commonly known as Pickard's wattle or birds nest wattle, is a tree or shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia. It is listed as a vulnerable species according to Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.

Acacia lacertensis is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to tropical parts of northern central Australia.

Acacia gracilifolia, commonly known as graceful wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves native to a small area of central southern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.
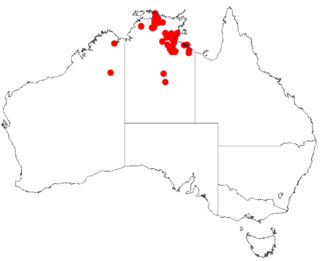
Acacia conspersa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia curranii, also known as curly-bark wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is listed as vulnerable under the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
Acacia minniritchi is a shrub of the genus Acacia that is native to the Kimberley region of Western Australia.

Acacia meiosperma is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia striatifolia is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia pycnostachya, also known as Bolivia wattle, is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to eastern Australia.


















