Acacia incongesta, also known as Peak Charles wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia

Acacia laccata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia oncinocarpa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to northern Australia.

Acacia oncinophylla, commonly known as hook-leaved acacia, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae.

Acacia richardsii is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is endemic to north western Australia.

Acacia dentifera, commonly known as tooth-bearing acacia, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to south western Australia.

Acacia leptospermoides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae and is endemic to a large area of south western Australia.

Acacia densiflora is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.

Acacia phlebocarpa, also known as tabletop wattle, is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves and is native to northern Australia.
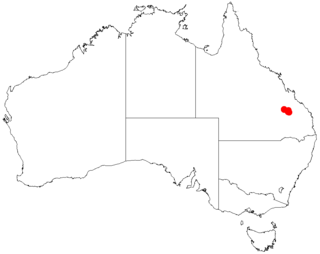
Acacia hockingsii, also known as Hocking's wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of north eastern Australia.

Acacia polifolia is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is native to parts of eastern Australia.
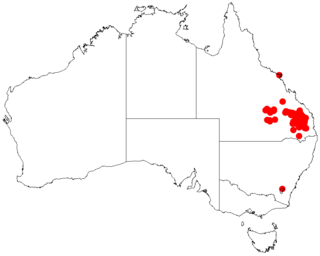
Acacia pustula is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to north eastern Australia.
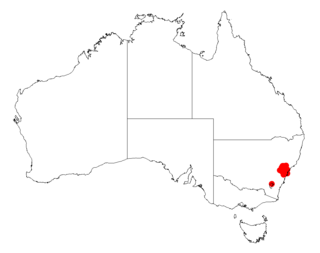
Acacia saliciformis is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae native to eastern Australia.

Acacia linearifolia, commonly known as stringybark wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Phyllodineae that is endemic to eastern Australia.
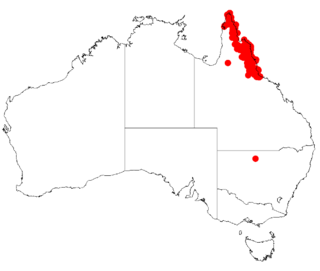
Acacia calyculata is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia cataractae is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to northern Australia.

Acacia cretata is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia linarioides is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north Australia.

Acacia torulosa is a shrub or tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia kalgoorliensis is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an area of south western Australia.



















