
Acacia s.l., known commonly as mimosa, acacia, thorntree or wattle, is a polyphyletic genus of shrubs and trees belonging to the subfamily Mimosoideae of the family Fabaceae. It was described by the Swedish botanist Carl Linnaeus in 1773 based on the African species Acacia nilotica. Many non-Australian species tend to be thorny, whereas the majority of Australian acacias are not. All species are pod-bearing, with sap and leaves often bearing large amounts of tannins and condensed tannins that historically found use as pharmaceuticals and preservatives.

Acacia pycnantha, most commonly known as the golden wattle, is a tree of the family Fabaceae native to southeastern Australia. It grows to a height of 8 m (26 ft) and has phyllodes instead of true leaves. Sickle-shaped, these are between 9 and 15 cm long, and 1–3.5 cm wide. The profuse fragrant, golden flowers appear in late winter and spring, followed by long seed pods. Plants are cross-pollinated by several species of honeyeater and thornbill, which visit nectaries on the phyllodes and brush against flowers, transferring pollen between them. An understorey plant in eucalyptus forest, it is found from southern New South Wales and the Australian Capital Territory, through Victoria and into southeastern South Australia.

Acacia cyclops, commonly known as coastal wattle, cyclops wattle, one-eyed wattle, red-eyed wattle, redwreath acacia, western coastal wattle, rooikrans, rooikans acacia, is a coastal shrub or small tree in the family Fabaceae. Native to Australia, it is distributed along the west coast of Western Australia as far north as Jurien Bay, and along the south coast into South Australia. The Noongar peoples of Western Australia know the plant as wilyawa or woolya wah.

Acacia, commonly known as the wattles or acacias, is a large genus of shrubs and trees in the subfamily Mimosoideae of the pea family Fabaceae. Initially, it comprised a group of plant species native to Africa and Australasia, but it has now been limited to contain only the Australasian species. The genus name is New Latin, borrowed from the Greek ἀκακία (akakia), a term used by Dioscorides for a preparation extracted from the leaves and fruit pods of Vachellia nilotica, the original type of the genus. In his Pinax (1623), Gaspard Bauhin mentioned the Greek ἀκακία from Dioscorides as the origin of the Latin name.

Acacia mearnsii, commonly known as black wattle, late black wattle or green wattle, is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae and is endemic to south-eastern Australia. It is usually an erect tree with smooth bark, bipinnate leaves and spherical heads of pale yellow or cream-coloured flowers followed by black to reddish brown pods. In some other parts of the world, it is regarded as an invasive species.

Acacia parramattensis, commonly known as Parramatta wattle, is a tree of the family Fabaceae native to the Blue Mountains and surrounding regions of New South Wales. It is a tall shrub or tree to about 15 m (50 ft) in height with finely divided bipinnate leaves and yellow flowers that appear over summer. It generally grows in woodland or dry sclerophyll forest on alluvial or shale-based soils, generally with some clay content.

Acacia decurrens, commonly known as black wattle or early green wattle, is a perennial tree or shrub native to eastern New South Wales, including Sydney, the Greater Blue Mountains Area, the Hunter Region, and south west to the Australian Capital Territory. It grows to a height of 2–15 m (7–50 ft) and it flowers from July to September.

Acacia longifolia is a species of Acacia native to southeastern Australia, from the extreme southeast of Queensland, eastern New South Wales, eastern and southern Victoria, and southeastern South Australia. Common names for it include long-leaved wattle, acacia trinervis, aroma doble, golden wattle, coast wattle, sallow wattle and Sydney golden wattle. It is not listed as being a threatened species, and is considered invasive in Portugal and South Africa. In the southern region of Western Australia, it has become naturalised and has been classed as a weed by out-competing indigenous species. It is a tree that grows very quickly reaching 7–10 m in five to six years.

Acacia vestita, with common names weeping boree, weeping acacia, and hairy wattle, is a shrub and small tree native to New South Wales, Australia.

Acacia deanei is a tree native to Australia, which is useful for controlling soil erosion. There are two subspecies: Acacia deanei subsp. deanei and Acacia deanei subsp. paucijuga.

Acacia verniciflua, commonly known as varnish wattle, is a shrub or small tree species that is endemic to Australia. It has an erect or spreading habit, growing to between 1 and 6 metres high, The phyllodes are often sticky and lustrous and vary in length, width and shape. The globular pale-yellow flowerheads appear in the leaf axils from July to November, followed by seedpods that are up to 10 cm long and unconstricted. These contain shiny black seeds. It is often found growing alongside Eucalyptus obliqua where it can dominate the understory.

Acacia euthycarpa is a shrub or small tree species that is endemic to southern Australia. It shares its common names of wallowa or reed-leaf wattle with a similar species Acacia calamifolia. It usually grows as a shrub to between 2 and 4 metres high, but certain forms may be small trees up to 10 metres high. The linear phyllodes are up to 10 cm long, dull green or grey green and have sharply pointed hooked tips. The globular golden flowerheads appear in 2-4 headed racemes between August and October, followed by curved seedpods that are up to 15 cm long.

Acacia blayana, commonly known as Blay's wattle or Brogo wattle, is a tree of the genus Acacia that is native to south eastern Australia.

Acacia filicifolia, commonly known as fern-leaved wattle, is a plant in the legume family, Fabaceae and is native to eastern Australia. It is a shrub or tree with compound leaves resembling fern fronds, and spherical heads of yellow or bright yellow flowers from autumn to late spring. It is a common and widespread species, especially on the coast and tablelands of New South Wales.

Acacia mucronata, the variable sallow wattle or narrow-leaved wattle, is a shrub or small tree to 5 m high. It is native to southeast Australia, mainly the states of Tasmania and Victoria. It often grows as an understorey tree or shrub in eucalypt forest or as a dominant in scrubland. In drier regions of its distribution, like in northeast Tasmania, it often grows along creeks and sheltered coastlines.

Acacia longissima, known colloquially as long-leaf wattle or narrow-leaf wattle, is a species of Acacia native to eastern Australia.
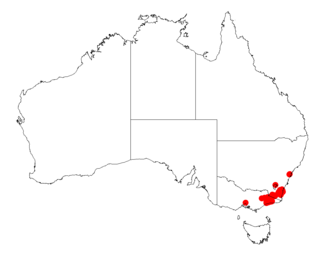
Acacia silvestris, commonly known the Bodalla silver wattle, is a tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Botrycephalae. It is native to an area in south eastern New South Wales and coastal Victoria.

Acacia barakulensis, commonly known as waajie wattle, is a shrub belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia.

Acacia grandifolia is a tree belonging to the genus Acacia and the subgenus Juliflorae that is native to north eastern Australia. It is list as vulnerable according to the Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999.
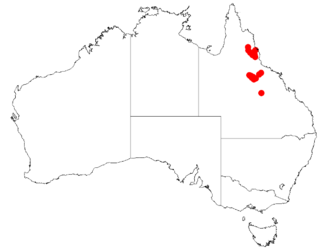
Acacia burrana is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to north eastern Australia





















