
Tathra is a seaside town on the Sapphire Coast found on the South Coast, New South Wales, Australia. As at the 2016 census, Tathra had a population of 1,675.

Bundanoon is a town in the Southern Highlands of New South Wales, Australia, in Wingecarribee Shire, on Gandangarra and Dharawal Country. It is an Aboriginal name meaning "place of deep gullies" and was formerly known as Jordan's Crossing. Bundanoon is colloquially known as Bundy/Bundi.

Kinglake is a town in Victoria, Australia, 56 km (35 mi) north-east of Melbourne's Central Business District, located within the Shires of Murrindindi and Nillumbik local government areas. Kinglake recorded a population of 1,662 at the 2021 census.
Fire-stick farming, also known as cultural burning and cool burning, is the practice of Aboriginal Australians regularly using fire to burn vegetation, which has been practised for thousands of years. There are a number of purposes for doing this special type of controlled burning, including to facilitate hunting, to change the composition of plant and animal species in an area, weed control, hazard reduction, and increase of biodiversity.

Yarloop is a town in the South West of Western Australia along the South Western Highway, between Waroona and Harvey. At the 2016 census, Yarloop had a population of 395. On 7 January 2016 a bushfire destroyed most of the town.

Lennox Head is a seaside village in the Northern Rivers region of New South Wales, Australia, situated on the stretch of coast between Byron Bay and Ballina in Ballina Shire local government area. It had a population of 7,741 in the 2016 Australian census.

Bawley Point is a small coastal hamlet in New South Wales, Australia, in the Shoalhaven with a population of 698 people at the 2016 census. It is located 30 minutes south of Ulladulla, New South Wales, and 30 minutes north of Batemans Bay on the South Coast of NSW. The town's name is believed to be derived from an Aboriginal word meaning "Brown snake".

Wingello is a village in the Southern Highlands of New South Wales, Australia. It has a station on NSW TrainLink's Southern Highlands Line. The surrounding area is part of the lands administrative unit of the Wingello Parish, a subdivision of Wingecarribee Shire.

One of the most extensive bushfire seasons in Australia's history. Victoria experienced the longest continuously burning bushfire complex in Australia's history, with fires in the Victorian Alps and Gippsland burning over 1 million hectares of land over the course of 69 days. See Bushfires in Australia for an explanation of regional seasons.

The Australian bushfire season ran from late December 2008 to April/May 2009. Above average rainfalls in December, particularly in Victoria, delayed the start of the season, but by January 2009, conditions throughout South eastern Australia worsened with the onset of one of the region's worst heat waves. On 7 February, extreme bushfire conditions precipitated major bushfires throughout Victoria, involving several large fire complexes, which continued to burn across the state for around one month. 173 people lost their lives in these fires and 414 were injured. 3,500+ buildings were destroyed, including 2,029 houses, and 7,562 people displaced.

A bushfire season occurred predominantly from June 2009 to May 2010. Increased attention has been given to this season as authorities and government attempt to preempt any future loss of life after the Black Saturday bushfires during the previous season, 2008–09. Long range weather observations predict very hot, dry and windy weather conditions during the summer months, leading to a high risk of bushfire occurrence.
Stanwell Tops is an exurban locality between the cities of Sydney and Wollongong on the New South Wales, Australia coastline. It lies northwest of Stanwell Park and southwest of Otford.

The summer of 2012–13, had above average fire potential for most of the southern half of the continent from the east coast to the west. This is despite having extensive fire in parts of the country over the last 12 months. The reason for this prediction is the abundant grass growth spurred by two La Niña events over the last two years.
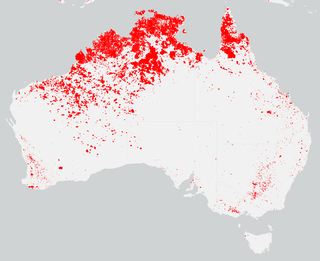
The bushfire season in the summer of 2014–15, was expected to have the potential for many fires in eastern Australia after lower than expected rainfall was received in many areas. Authorities released warnings in the early spring that the season could be particularly bad.

The bushfire season of the summer of 2017–18, was expected to have above normal bushfire risks with an elevated fire risk for the most of eastern and south Australian coastal areas. Australia had experienced its warmest winter on record and the ninth driest winter on record leaving dry fuel loads across much of southern Australia. Expected warmer weather over the summer period would also increase the risk. Bushfires were also expected to occur earlier, before the end of winter, as a result of the warm and dry winter. Both Queensland and north-eastern New South Wales experienced the wettest October since 1975 leading to a downgrade in bushfire risk.
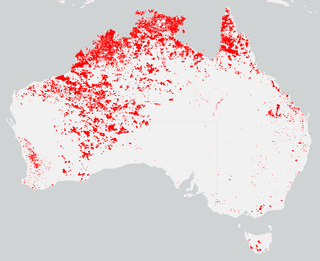
The bushfires were predicted to be "fairly bleak" in parts of Australia, particularly in the east, by the Bushfire and Natural Hazards Cooperative Research Centre (CRC) chief executive, Richard Thornton, in September 2018. Large bushfires had already burned through southern New South Wales during winter. The outlook for spring was of a higher likelihood of fires with a twice the normal chance of an El Nino for summer. Many parts of eastern Australia including Queensland, New South Wales and Gippsland, in Victoria, were already in drought. Above normal fire was also predicted for large parts of Southern Australia and Eastern Australia by the Bushfire and Natural Hazards CRC. The forecast noted that Queensland had recorded the ninth driest and fourth hottest period on record from April to November. New South Wales recorded the fourth hottest period and eighth driest on record, while Victoria experiences the 13th driest and seventh hottest period on record. Authorities in New South Wales brought forward the start of the bushfire season for much of the state from October 2018 to the beginning of August 2018.

The 2019–20 Australian bushfire season or Black Summer was a period of bushfires in many parts of Australia, which, due to its unusual intensity, size, duration, and uncontrollable dimension, is considered a megafire. The Australian National University reported that the area burned in 2019–2020 was "well below average" due to low fuel levels and fire activity in unpopulated parts of Northern Australia, but that "Despite low fire activity overall, vast forest fires occurred in southeast Australia from southeast Queensland to Kangaroo Island."
Following the devastating 2019–20 bushfires in Australia, authorities were urged to prepare early for the 2020–21 Australian bushfire season. The bushfire outlook for July to September 2020 was predicting a normal fire potential in Queensland with a good grass growth in many areas giving an increased risk of grass fires, an above normal season in the Kimberley region of Western Australia as a result of good rains from tropical cyclones, a normal but earlier season in the Northern Territory, an above normal season on the south coast of New South Wales and normal seasons elsewhere.

Conjola Park is a beach resort in the City of Shoalhaven, New South Wales, Australia. It lies on the south shore of a lagoon called Conjola Lake, just to the east of the Princes Highway on Lake Conjola Entrance Road, which connects to the resort of Lake Conjola. It lies about 15 km north of Ulladulla and 215 km south of Sydney. At the 2016 census, it had a population of 340.

Yatte Yattah is a historically significant suburb on the South Coast of New South Wales. It is located on the Princes Highway about 4km north of Milton and 2km south of Conjola Lake. At the 2021 Census, the population was 189. Settled in 1827, Yatte Yattah was a pioneer town in the decades preceding the establishment of nearby Milton and Ulladulla. Selected at the time for its highly fertile soils and lucrative red cedar, the first settlers in Yatte Yattah used convicts to procure timber, build roads and dig extensive drains along Narrawallee Creek. In 1827 a local aboriginal man helped Thomas Kendall cut a track from his land grant in Yatte Yattah to a natural bay in the south. Kendall turned the bay into a boat harbour so he could ship cedar and produce from Yatte Yattah to Sydney and Illawarra. Eventually this makeshift port would become known as Ulladulla Harbour. During this boom period Yatte Yattah had a functioning school, church and post office. Today, Yatte Yattah is characterised by picturesque farming estates and private rural retreats. There are views of Pigeon House Mountain and the Budawang Ranges. There are many surfing beaches near Yatte Yattah and with incereasing popularity the highway is known to become congested during peak holiday season.



















