Related Research Articles

In computing and electronic systems, binary-coded decimal (BCD) is a class of binary encodings of decimal numbers where each digit is represented by a fixed number of bits, usually four or eight. Sometimes, special bit patterns are used for a sign or other indications.

In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be represented as a base-ten floating-point number:

A decimal separator is a symbol used to separate the integer part from the fractional part of a number written in decimal form. Different countries officially designate different symbols for use as the separator. The choice of symbol also affects the choice of symbol for the thousands separator used in digit grouping.
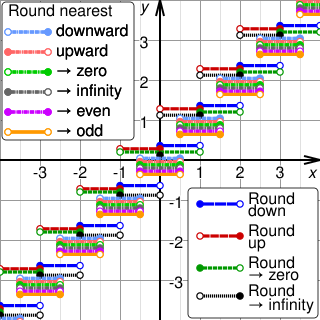
Rounding means replacing a number with an approximate value that has a shorter, simpler, or more explicit representation. For example, replacing $23.4476 with $23.45, the fraction 312/937 with 1/3, or the expression √2 with 1.414.
Significant figures of a number in positional notation are digits in the number that are reliable and necessary to indicate the quantity of something.

Positional notation usually denotes the extension to any base of the Hindu–Arabic numeral system. More generally, a positional system is a numeral system in which the contribution of a digit to the value of a number is the value of the digit multiplied by a factor determined by the position of the digit. In early numeral systems, such as Roman numerals, a digit has only one value: I means one, X means ten and C a hundred. In modern positional systems, such as the decimal system, the position of the digit means that its value must be multiplied by some value: in 555, the three identical symbols represent five hundreds, five tens, and five units, respectively, due to their different positions in the digit string.
In computing, fixed-point is a method of representing fractional (non-integer) numbers by storing a fixed number of digits of their fractional part. Dollar amounts, for example, are often stored with exactly two fractional digits, representing the cents. More generally, the term may refer to representing fractional values as integer multiples of some fixed small unit, e.g. a fractional amount of hours as an integer multiple of ten-minute intervals. Fixed-point number representation is often contrasted to the more complicated and computationally demanding floating-point representation.
Latin honors are a system of Latin phrases used in some colleges and universities to indicate the level of distinction with which an academic degree has been earned. The system is primarily used in the United States. It is also used in some Southeastern Asian countries with European colonial history, such as Indonesia and the Philippines, although sometimes translations of these phrases are used instead of the Latin originals. The honors distinction should not be confused with the honors degrees offered in some countries, or with honorary degrees.
This is an article on the grading that is used in Finland. Several systems are in use in different educational institutions in Finland.
Germany uses a 5- or 6-point grading scale (GPA) to evaluate academic performance for the youngest to the oldest students. Grades vary from 1 to 5. In the final classes of German Gymnasium schools that prepare for university studies, a point system is used with 15 points being the best grade and 0 points the worst. The percentage causing the grade can vary from teacher to teacher.
There are two grading systems used in Italy:
Academic grading in Mexico employs a decimal system, from 0 to 10, to measure the students' scores. The grades are:
This article is about the current type of grading used in the Netherlands, which has remained unchanged for several decades.
Singapore's grading system in schools is differentiated by the existence of many types of institutions with different education foci and systems. The grading systems that are used at Primary, Secondary, and Junior College levels are the most fundamental to the local education system.
Decimal floating-point (DFP) arithmetic refers to both a representation and operations on decimal floating-point numbers. Working directly with decimal (base-10) fractions can avoid the rounding errors that otherwise typically occur when converting between decimal fractions and binary (base-2) fractions.
There are four grading systems in Greece – four different GPA – one for higher education, one for secondary education, and two for primary education.
Serbia inherited the academic grading system of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The grading process uses an absolute achievement scale to determine the grade of a student.
Slovenia inherited the academic grading system of the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. A five-point grading scale is used in primary and secondary schools:
In Switzerland, the 6-point grading scale is usually applied, where 1 represents the lowest possible grade, and 6 represents the highest possible grade..
This is a list of grading systems used by countries of the world, primarily within the fields of secondary education and university education, organized by continent with links to specifics in numerous entries.