
South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands (SGSSI) is a British Overseas Territory in the southern Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote and inhospitable collection of islands, consisting of South Georgia and a chain of smaller islands known as the South Sandwich Islands. South Georgia is 165 kilometres (103 mi) long and 35 kilometres (22 mi) wide and is by far the largest island in the territory. The South Sandwich Islands lie about 700 kilometres (430 mi) southeast of South Georgia. The territory's total land area is 3,903 km2 (1,507 sq mi). The Falkland Islands are about 1,300 kilometres (810 mi) west from its nearest point.

Acaena is a genus of about 60 species of mainly evergreen, creeping herbaceous perennial plants and subshrubs in the family Rosaceae, native mainly to the Southern Hemisphere, notably New Zealand, Australia and South America, but with a few species extending into the Northern Hemisphere, north to Hawaii and California.

Sanguisorba minor, the salad burnet, garden burnet, small burnet, burnet, pimpernelle, Toper's plant, and burnet-bloodwort, is an edible perennial herbaceous plant in the family Rosaceae. It has ferny, toothed-leaf foliage; the unusual crimson, spherical flower clusters rise well above the leaves on thin stems. It generally grows to 25–55 cm tall. The large, long, taproots store water, making it drought-tolerant.

Embothrium is a genus of two to eight species in the plant family Proteaceae, native to southern South America, in Chile and adjacent western Argentina; the genus occurs as far south as Tierra del Fuego. Common names include Chilean firebush in English, notro in Argentina, ciruelillo, fosforito or notro chileno in Chilean Spanish.

Acaena novae-zelandiae, commonly known as red bidibid, bidgee widgee, buzzy and piri-piri bur, is a small herbaceous, prostrate perennial, native to New Zealand, Australia and New Guinea, of the family Rosaceae.

Thatcher Peninsula is a mountainous peninsula in north-central South Georgia. Its total area is approximately 5,640 hectares, with roughly 1,620 ha covered in vegetation. It terminates to the north in Mai Point, rising between Cumberland West Bay to the west, and Cumberland East Bay and Moraine Fjord to the east. It is bounded to the southwest and south by Lyell Glacier and Hamberg Glacier. King Edward Cove on the east side of the peninsula is the site of the British Antarctic Survey (BAS) Grytviken station and the disused whaling station of the same name.

Acaena dumicola is a species of perennial plant found only in scrubby and rocky habitats at altitudes of between 300 and 1200 m in the South Island of New Zealand.

Acaena juvenca is a species of perennial plant found in scrubland and forest margins up to an altitude of 1200 m on the eastern side of both North and South Islands, New Zealand.
Acaena tesca is a species of low growing perennial plant restricted to the upper slopes of the mountains of central Otago and northern Southland in the South Island of New Zealand.

Acaena magellanica, commonly called buzzy burr or greater burnet, is a species of flowering plant whose range includes the southern tip of South America and many subantarctic islands.

Acaena sericea is a species of low growing perennial plant native to southern Chile and Patagonia.
Festuca contracta, commonly known as tufted fescue or land tussac, is a species of true grass (Poaceae). It is native to many subantarctic islands in, and the coasts bordering, the Southern Ocean. The specific epithet comes from the Latin contractus, with reference to the inflorescence.

Peperomia tetraphylla, known as the acorn peperomia or four-leaved peperomia, is a small plant in the Peperomia genus and the Piperaceae family that grows natively in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. Additionally in can found on Easter Island as an introduced species.

Acaena echinata, commonly known as sheep's burr, is a species of perennial herb, in the Rosaceae family, native to Australia.

Acaena microphylla, the bidibid or piripiri, and outside New Zealand, New Zealand-bur, is a small herbaceous, prostrate perennial flowering plant in the rose family Rosaceae, native to both the North and South Islands of New Zealand. There are two varieties:
Acaena antarctica is a small herbaceous plant in the Rosaceae family native to Argentina, Chile and the Falkland Islands.
Hymenophyllum falklandicum, the Falklands filmy fern, is a plant in the fern family Hymenophyllaceae. It is native to southern South America and some subantarctic islands.
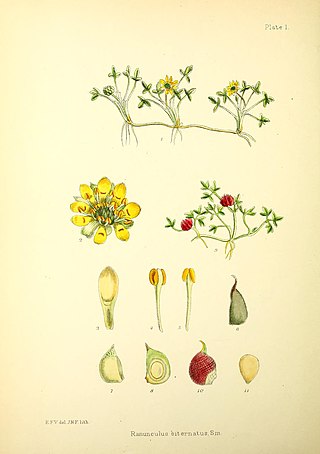
Ranunculus biternatus, the Antarctic buttercup, is a plant in the buttercup family Ranunculaceae. It is native to southern South America and some subantarctic islands.

Acaena ovalifolia is a species of flowering plant belonging to the family Rosaceae.














