
Conium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Apiaceae. As of December 2020, Plants of the World Online accepts six species.

Strychnos nux-vomica, the strychnine tree, also known as nux vomica, poison fruit, semen strychnos, and quaker buttons, is a deciduous tree native to India and to southeast Asia. It is a medium-sized tree in the family Loganiaceae that grows in open habitats. Its leaves are ovate and 5–9 centimetres (2–3.5 in) in size. It is known for being the natural source of the extremely poisonous compound strychnine.

Passiflora foetida is a species of passion flower that is native to the southwestern United States, Mexico, the Caribbean, Central America, and much of South America. It has been introduced to tropical regions around the world, such as Southeast Asia, South Asia, Hawaii, Africa, and The Maldives. It is a creeping vine like other members of the genus, and yields an edible fruit. The specific epithet, foetida, means "stinking" in Latin and refers to the strong aroma emitted by damaged foliage.

Cucumis metuliferus, commonly called the African horned cucumber, horned melon, spiked melon, jelly melon, or kiwano, is an annual vine in the cucumber and melon family Cucurbitaceae. Its fruit has horn-like spines, hence the name "horned melon". The ripe fruit has orange skin and lime-green, jelly-like flesh. C. metuliferus is native to Southern Africa, in South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, and Angola.
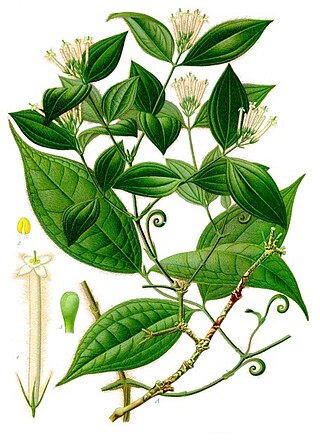
Strychnos is a genus of flowering plants, belonging to the family Loganiaceae. The genus includes about 100 accepted species of trees and lianas, and more than 200 that are as yet unresolved. The genus is widely distributed around the world's tropics and is noted for the presence of poisonous indole alkaloids in the roots, stems and leaves of various species. Among these alkaloids are the well-known and virulent poisons strychnine and curare.

Momordica balsamina is a tendril-bearing annual vine native to the tropical regions of Africa, introduced and invasive in Asia, Australia, Central America, and North America, where they have been found in some parts of Florida. In 1810, Thomas Jefferson planted this vine in his flower borders at Monticello along with larkspur, poppies, and nutmeg.
Abelmoschus caillei, the West African okra, is a plant species in the family Malvaceae. It occurs in humid areas of West and Central Africa, where it is used as a vegetable. It originated as an allopolyploid hybrid of Abelmoschus esculentus and A. manihot, and is often mistaken for either of those two plants. It was officially described elevated to the status of a species in 1988. The same hybrid was produced experimentally in Japan where it is known as Abelmoschus glutino-textile.
Acalypha bipartita is a species in the botanical family Euphorbiaceae. It occurs widely in Africa where it is eaten as a vegetable, or fed to animals. The leaves are considered nutritious, as they contain a high concentration of calcium. It is often found as undergrowth in the forest, on the edges of the forest, and in wooded grasslands, particularly in Sudan, Uganda, Kenya, eastern Zaire, Burundi, Rwanda, and Tanzania. The stems are often used in making baskets.

Acanthosicyos is a genus of thorny shrubs of the botanical family Cucurbitaceae, subfamily Cucurbitoideae. The genus name derives from the Greek words "akantha" for thorn and "sykios" for cucumber or gourd.

Adansonia grandidieri is the biggest and most famous of Madagascar's six species of baobabs. It is sometimes known as Grandidier's baobab or the giant baobab. In French it is called Baobab malgache. The local name is renala or reniala. This tree is endemic to the island of Madagascar, where it is an endangered species threatened by the encroachment of agricultural land. This is the tree found at the Avenue of the Baobabs.

Acanthosicyos horridus is an unusual melon that is endemic to the Namib desert. In English it is known as Nara, butter-nuts, or butterpips; in one of the Khoisan languages it is locally called ǃnaras or ǃnara.

Acokanthera schimperi, arrow poison tree, belonging to the family Apocynaceae, is a small tree native to eastern and central Africa as well as to Yemen.

Adansonia za is a species of baobab in the genus Adansonia of the family Malvaceae. It was originally named in French as anadzahé. Common names in Malagasy include bojy, boringy, bozy, bozybe, ringy, and za, the last of which gives the plant its specific epithet. Eight Adansonia species are recognized, with six endemic to Madagascar. Adansonia za is the most widespread of the Madagascar endemics.

Euphorbia ingens is a species of flowering plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. It is native to dry areas of southern Africa. It is popularly known as the candelabra tree or naboom. Its milky latex can be extremely poisonous and is a dangerous irritant.

Balanites aegyptiaca is a species of tree, classified as a member of either the Zygophyllaceae or the Balanitaceae. This tree is native to much of Africa and parts of the Middle East.

Momordica foetida is a perennial climbing vine native of tropical Africa, closely related to the bitter melon and balsam apple. Its species name ("bad-smelling") refers to its unpleasant smell. It was previously named M. morkorra and M. cordata (Cogn.)

Combretum erythrophyllum, commonly known as the river bushwillow, is a medium to large-sized, spreading tree found in bush along river banks in southern Africa. It is planted as a shade and ornamental tree in South Africa and the United States, and is propagated by seed.

Diospyros dichrophylla (Gand.) De Winter is a Southern African tree belonging to the ebony family of Ebenaceae and closely related to the Persimmon.

Strychnos madagascariensis, the black monkey orange, is an African tropical and sub-tropical tree belonging to the Loganiaceae family. It is a tree with characteristically large fruit but can confused with some other species of the genus.

Ximenia caffra, the sourplum, is a small tree or small shrub that is thinly branched. It is part of the Olacaceae family which is native throughout tropical regions. In particular, the sourplum is native to regions in South East Africa, mainly Botswana, Kenya, Malawi, Mozambique, South Africa, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia, and Zimbabwe. The sourplum tree produces several fruits on an annual basis. These are generally sour with a dry aftertaste, and they contain significant amounts of potassium. The tree itself is fairly hardy, with frost resistance and drought tolerance. The tree, fruit, seed, leaves, and roots are all used for human consumption, medicinally, or for fuel. The trees themselves can also be used as natural land division barriers.




















