
The Maotianshan Shales are a series of Early Cambrian deposits in the Chiungchussu Formation, famous for their Konservat Lagerstätten, deposits known for the exceptional preservation of fossilized organisms or traces. The Maotianshan Shales form one of some forty Cambrian fossil locations worldwide exhibiting exquisite preservation of rarely preserved, non-mineralized soft tissue, comparable to the fossils of the Burgess Shale. They take their name from Maotianshan Hill in Chengjiang County, Yunnan Province, China.

Nectocaris pteryx is a species of possible cephalopod known from the "early Cambrian" Emu Bay Shale and Chengjiang biota, the "middle Cambrian" Burgess Shale.
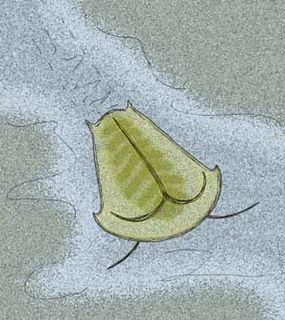
Skania is a Middle Cambrian fossil arthropod that is closely related to the Early Cambrian Primicaris larvaformis from the Chengjiang Biota, China. It bears a superficial resemblance to the Ediacaran organism Parvancorina. A single specimens of Skania are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise < 0.01% of the community. While previously enigmatic, it is now thought to be a marrellomorph.

Sidneyia is an extinct arthropod known from fossils found from the Early Cambrian-age Maotianshan Shales to the Mid Cambrian Burgess Shale formation of British Columbia. 144 specimens of Sidneyia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.27% of the community.

The halkieriids are a group of fossil organisms from the Lower to Middle Cambrian. Their eponymous genus is Halkieria, which has been found on almost every continent in Lower to Mid Cambrian deposits, forming a large component of the small shelly fossil assemblages. The best known species is Halkieria evangelista, from the North Greenland Sirius Passet Lagerstätte, in which complete specimens were collected on an expedition in 1989. The fossils were described by Simon Conway Morris and John Peel in a short paper in 1990 in the journal Nature. Later a more thorough description was undertaken in 1995 in the journal Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London and wider evolutionary implications were posed.

Anomalocarididae is an extinct family of Cambrian radiodonts, a group of stem-group arthropods.

Dinomischusis a rare fossil animal from the Cambrian period. It reached 20 mm in height, was attached to the sea floor by a stalk, and looked loosely like a flower. The cup-shaped body at the top of the stalk probably fed by filtering the surrounding seawater, and may have created a current to facilitate this. Its mouth and anus sat next to one another.
A number of assemblages bear fossil assemblages similar in character to that of the Burgess Shale. While many are also preserved in a similar fashion to the Burgess Shale, the term "Burgess Shale-type fauna" covers assemblages based on taxonomic criteria only.

Panlongia was a small-sized marine arthropod, with an oval-shaped non-calcified exoskeleton. Both the head shield and the tail shield are semi-circular. In between the cephalon and pygidium are four thoracic body segments (somites). The cephalon occupies approximately ⅓ of the body length, the thorax ¼ and pygidium about 45%. Panlongia lived during the late Lower Cambrian (Botomian) in what is today South China. In Panlongia spinosa the edge of the exoskeleton carries several small sawtooth-like spines, that are absent in P. tetranodusa.
Tommotiids are Cambrian (Terreneuvian) shelly fossils thought to belong to the Brachiopod + Phoronid lineage (Brachiozoa).

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.
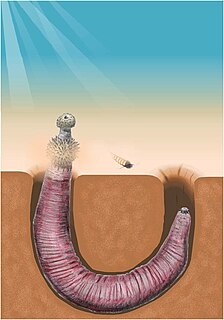
Archaeopriapulida is a group of priapulid-like worms known from Cambrian lagerstätte. The group is closely related to, and very similar to, the modern Priapulids. It is unclear whether it is mono- or polyphyletic. Despite a remarkable morphological similarity to their modern cousins, they fall outside of the priapulid crown group, which is not unambiguously represented in the fossil record until the Carboniferous. They are probably closely related or paraphyletic to the palaeoscolecids; the relationship between these basal worms is somewhat unresolved.

The palaeoscolecids are a group of extinct ecdysozoan worms resembling armoured priapulids. They are known from the Lower Cambrian to the late Silurian; they are mainly found as disarticulated sclerites, but are also preserved in many of the Cambrian lagerstätten. They take their name from the typifying genus Palaeoscolex.
Eiffelia is an extinct genus of sponges known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale as well as several Early Cambrian small shelly fossil deposits. It is named after Eiffel Peak, which was itself named after the Eiffel Tower. It was first described in 1920 by Charles Doolittle Walcott. It belongs in the Hexactinellid stem group. 60 specimens of Eiffelia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.11% of the community.
Hamptonia is an extinct genus of sea sponge known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale and the Lower Ordovician Fezouata formation. It was first described in 1920 by Charles Doolittle Walcott. 48 specimens of Hamptonia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise < 0.1% of the community.

Lingulella is a genus of phosphatic-shelled brachiopod. It is known from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale (Canada) to the Upper Ordovician Bromide Formation in North America. 346 specimens of Lingulella are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 0.66% of the community.

Allonnia is a genus of coeloscleritophoran known as complete scleritomes from the Middle Cambrian Burgess Shale. It is also a constituent of the small shelly fauna.
Mickwitziids are a Cambrian group of shelly fossils with originally phosphatic valves, belonging to the Brachiopod stem group, and exemplified by the genus Mickwitzia – the other genera are Heliomedusa and Setatella. The family Mickwitziidae is conceivably paraphyletic with respect to certain crown-group brachiopods.
Micrina is an extinct genus of tommotiids with affinities to brachiopods.

Kutorginates are early rhynchonelliform brachiopods.













