
Zygomycota, or zygote fungi, is a former division or phylum of the kingdom Fungi. The members are now part of two phyla the Mucoromycota and Zoopagomycota. Approximately 1060 species are known. They are mostly terrestrial in habitat, living in soil or on decaying plant or animal material. Some are parasites of plants, insects, and small animals, while others form symbiotic relationships with plants. Zygomycete hyphae may be coenocytic, forming septa only where gametes are formed or to wall off dead hyphae. Zygomycota is no longer recognised as it was not believed to be truly monophyletic.
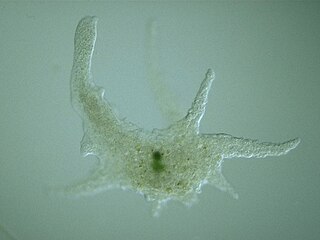
Chaos is a genus of single-celled amoeboid organisms in the family Amoebidae. The largest and best-known species, the so-called "giant amoeba" Chaos carolinense, can reach lengths of 5 mm, although most specimens fall between 1 and 3 mm.

An entomopathogenic fungus is a fungus that can act as a parasite of insects and kills or seriously disables them.

Arcellinid testate amoebae or Arcellinida, Arcellacean or lobose testate amoebae are single-celled protists partially enclosed in a simple test (shell).
Clonostachys rosea f. rosea, also known as Gliocladium roseum, is a species of fungus in the family Bionectriaceae. It colonizes living plants as an endophyte, digests material in soil as a saprophyte and is also known as a parasite of other fungi and of nematodes. It produces a wide range of volatile organic compounds which are toxic to organisms including other fungi, bacteria, and insects, and is of interest as a biological pest control agent.
The Mycotyphaceae are a family of fungi in the order Mucorales. Members of this family, rarely reported, are thought to be more common in warmer climates.

The Zoopagomycotina are a subdivision of the fungal division Zygomycota sensu lato. It contains 5 families and 20 genera. Relationships among and within subphyla of Zygomycota are poorly understood, and their monophyly remains in question, so they are sometimes referred to by the informal name zygomycetes.

Testate amoebae are a polyphyletic group of unicellular amoeboid protists, which differ from naked amoebae in the presence of a test that partially encloses the cell, with an aperture from which the pseudopodia emerge, that provides the amoeba with shelter from predators and environmental conditions.

Sarcoscypha occidentalis, commonly known as the stalked scarlet cup or the western scarlet cup, is a species of fungus in the family Sarcoscyphaceae of the Pezizales order. Fruit bodies have small, bright red cups up to 2 cm (0.8 in) wide atop a slender whitish stem that is between 1 to 3 cm long. A saprobic species, it is found growing on hardwood twigs, particularly those that are partially buried in moist and shaded humus-rich soil. The fungus is distributed in the continental United States east of the Rocky Mountains, Central America, the Caribbean, and Asia. It is distinguished from the related species S. coccinea and S. austriaca by differences in geographical distribution, fruiting season, and fruit body structure. Phylogenetic analysis has shown that it is most closely related to other Sarcoscypha species that contain large oil droplets in their spores. The species Molliardiomyces occidentalis is an imperfect form of the fungus that lacks a sexually reproductive stage in its life cycle.

Zoophagus is a genus of zygomycete fungi that preys on rotifers and nematodes. It was established in 1911 by Sommerstorff, who originally considered it to be an oomycete. It is common in a variety of freshwater habitats, such as ponds and sewage treatment plants.
Charles Drechsler was an American mycologist with 45 years of research with the United States Department of Agriculture. He spent considerable time working with cereal fungal diseases, and the genus Drechslera was named after him. Drechsler also worked extensively on oomycete fungi and their interactions with vegetable plants. Drechsler was recognized as a leading authority on helminthosporia, oomycetes, and other parasitic fungi.

Arthrobotrys oligospora was discovered in Europe in 1850 by Georg Fresenius. 'A. oligospora' is the model organism for interactions between fungi and nematodes. It is the most common nematode capturing fungus, and most widespread nematode trapping fungus in nature. It was the first species of fungi documented to actively capture nematodes.

Epichloë typhina is a haploid sexual species in the fungal genus Epichloë. It was originally described as a Sphaeria species. Today, however, it is classified in Epichloë.
Elizabeth Eaton Morse was an American mycologist. Born in Framingham, Massachusetts, she graduated from Ashland, Massachusetts, High School in 1882. For seven years she taught in elementary school before entering Wellesley College, from which she graduated with a diploma from the School of Art in 1891. After twenty years of teaching in the New York City schools Morris High School and Roosevelt High School, she returned to Wellesley College in 1924 and earned a degree in Botany in 1926. Shortly after, she registered as a part-time graduate student in the Department of Botany at the University of California, and was given storage and work space to pursue her interests in cryptogamic botany.

Amoebophilus is a genus of zygomycete fungi that parasitizes amoeba.
Capronia mansonii is a mesophilic black yeast that is a part of the Herpotrichiellaceae. The species is uncommon in nature but is saprotrophic in nature and been discovered on decaying plant matter, particularly wood. This fungus is naturally found in the Netherlands and has successfully been cultured in lab. It is a teleomorph of the ascomycota division and possesses brown spores.
Mycotypha microspora, also known as Microtypha microspora, is a filamentous fungus in the division Zygomycota. It was discovered in a Citrus aurantium peel in 1932 by E. Aline Fenner, who proposed a new genus Mycotypha to accommodate it. Mycotypha africana, which is another species in the genus Mycotypha, is closely related to M. microspora. The fungus has subsequently been isolated from both outdoor and indoor settings around the world, and is typically found in soil and dung. The species rarely causes infections in humans, but has recently been involved in the clinical manifestation of the life-threatening disease mucormycosis.
Auxarthron californiense is a fungus within the family Onygenaceae family and one of the type species of the genus Auxarthron. A. californiense is generally distributed around the world and it is frequently found on dung and in soil near the entrances of animal burrows.
Stylopage is a polytypic genus of predacious fungus in the order Zoopagales, within the subphylum Zoopagomycotina. All known species of Stylopage subsist on various species of amoebae or nematodes by trapping their prey, typically using an adhesive substance that coats their vegetative hyphae, and absorbing nutrients through the projection of a haustorium. 17 extant Stylopage species have been described thus far.










