
The coconut tree is a member of the palm tree family (Arecaceae) and the only living species of the genus Cocos. The term "coconut" can refer to the whole coconut palm, the seed, or the fruit, which botanically is a drupe, not a nut. They are ubiquitous in coastal tropical regions and are a cultural icon of the tropics.

A pest is any organism harmful to humans or human concerns. The term is particularly used for creatures that damage crops, livestock, and forestry or cause a nuisance to people, especially in their homes. Humans have modified the environment for their own purposes and are intolerant of other creatures occupying the same space when their activities impact adversely on human objectives. Thus, an elephant is unobjectionable in its natural habitat but a pest when it tramples crops.

Spider mites are members of the Tetranychidae family, which includes about 1,200 species. They are part of the subclass Acari (mites). Spider mites generally live on the undersides of leaves of plants, where they may spin protective silk webs, and can cause damage by puncturing the plant cells to feed. Spider mites are known to feed on several hundred species of plants.

Varroa destructor, the Varroa mite, is an external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on honey bees and is one of the most damaging honey bee pests in the world. A significant mite infestation leads to the death of a honey bee colony, usually in the late autumn through early spring. Without management for Varroa mite, honey bee colonies typically collapse within 2 to 3 years in temperate climates. These mites can infest Apis mellifera, the western honey bee, and Apis cerana, the Asian honey bee. Due to very similar physical characteristics, this species was thought to be the closely related Varroa jacobsoni prior to 2000, but they were found to be two separate species after DNA analysis.

Osmia cornifrons, also known as the horned-face bee, is a species of solitary bee indigenous to Northern Asia. Physically, this species of bee is recognized for its horn-like extensions originating from its lower face. Populations of O. cornifrons have been recorded in multiple locations, including Japan, Korea, China, and Russia. O. cornifrons are more docile as compared to other species of bees and are less prone to sting when aggravated.

In the flowering plants, an ovary is a part of the female reproductive organ of the flower or gynoecium. Specifically, it is the part of the pistil which holds the ovule(s) and is located above or below or at the point of connection with the base of the petals and sepals. The pistil may be made up of one carpel or of several fused carpels, and therefore the ovary can contain part of one carpel or parts of several fused carpels. Above the ovary is the style and the stigma, which is where the pollen lands and germinates to grow down through the style to the ovary, and, for each individual pollen grain, to fertilize one individual ovule. Some wind pollinated flowers have much reduced and modified ovaries.

Abacarus hystrix, the cereal rust mite or grain rust mite, belongs to the family Eriophyidae. They are extremely small with adults measuring up to 1 millimetre in length and only have four legs at the front of the body. Viewing by the human eye requires a 10 – 20X lens. The adult mites are usually yellow but also have been seen to be white or orange. The cereal rust mite was first found on Elymus repens, a very common perennial grass species. It has now been found on more than 60 grass species including oats, barley, wheat and ryegrass, found in Europe, North America, South Africa and Australia. Mites migrate primarily through wind movement and are usually found on the highest basal sections of the top two leaf blades. Abacarus hystrix produces up to twenty overlapping generations per year in South Australian perennial pastures, indicating that the species breeds quite rapidly. It has been noted that the cereal rust mite can cause losses in yield of up to 30-70%.

Aceria chondrillae is a gall-forming deuterogynous eriophyid mite. It is often used as a biological control of the noxious weed Chondrilla juncea, a highly competitive herbaceous perennial composite found in Europe, Asia, Australia and North America.

Eriophyoidea are a superfamily of herbivorous mites. All post-embryonic instars lack the third and fourth pairs of legs, and the respiratory system is also absent.

Trombiculidae, commonly referred to in North America as chiggers and in Britain as harvest mites, but also known as berry bugs, bush-mites, red bugs or scrub-itch mites, are a family of mites. Chiggers are often confused with jiggers – a type of flea. Several species of Trombiculidae in their larva stage bite their animal host and by embedding their mouthparts into the skin cause "intense irritation", or "a wheal, usually with severe itching and dermatitis". Humans are possible hosts.

Aceria sheldoni, commonly called the citrus bud mite, is a species of mite belonging to the family Eriophyidae. It feeds in leaf- and flower-buds of Citrus spp., causing deformation to leaves, flowers and fruit, and is a worldwide pest of citrus fruit production.
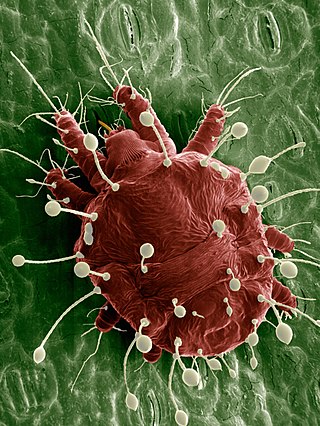
Raoiella indica, commonly known as the red palm mite, is a species of mite belonging to the family Tenuipalpidae. A pest of several species of palm in the Middle East and South East Asia, it is now becoming established throughout the Caribbean. The invasion of this species is the biggest mite explosion ever observed in the Americas.

Brevipalpus phoenicis, also known as the false spider mite, red and black flat mite, and in Australia as the passionvine mite, is a species of mite in the family Tenuipalpidae. This species occurs globally, and is a serious pest to such crops as citrus, tea, papaya, guava and coffee, and can heavily damage numerous other crops. They are unique in having haploid females, a condition caused by a bacterium that change haploid males into females.

Bryobia is a genus of mites in the spider mite family, Tetranychidae. The taxonomy of the genus is difficult. The genus has been revised several times. It is difficult to distinguish these tiny species from each other on the basis of morphological characters, and there is little agreement on which characteristics are of importance. Also, species can be variable in morphology. Over 130 species have been described, but many of the names are likely synonyms.

Mites are small crawling animals related to ticks and spiders. Most mites are free-living and harmless. Other mites are parasitic, and those that infest livestock animals cause many diseases that are widespread, reduce production and profit for farmers, and are expensive to control.

Aculops fuchsiae, commonly known as fuchsia gall mite, is a species of mite in the family Eriophyidae. It feeds on Fuchsia plants, causing distortion of growing shoots and flowers. It is regarded as a horticultural pest.
Eriophyes tulipae, commonly known as the dry bulb mite, is a species of mite in the genus Eriophyes. This mite feeds on members of the lily family, and has damaged garlic crops. At one time, it was also thought to feed on wheat and other grasses, but the wheat curl mite is now regarded as a different species, Aceria tosichella.
Magdalena Kathrina Petronella Smith Meyer was a South African acarologist who was regarded as a world authority on plant-feeding mites of agricultural importance and was known as the "mother of red-spider mites of the world". She described more than 700 new species and 25 new genera, mostly of mites of agricultural importance. Meyer was involved in the promotion of biological control of mites using predatory mites, spiders and insects.

Nalepella, the rust mites, is a genus of very small Trombidiform mites in the family Phytoptidae. They are commonly found on a variety of conifers, including hemlock, spruce, balsam fir, and pine. They sometimes infest Christmas trees in nurseries. Nalepella mites are vagrants, meaning they circulate around the tree; females overwinter in bark cracks. Infested spruce emit a characteristic odour.
Aceria cynodoniensis, the bermudagrass mite, is widely distributed, but only infests bermudagrass and its hybrids. It lives and develops under the leaf sheaths of its host plant. Infestations of the mite can cause destructive damage to bermudagrass turf and it is often regarded as a harmful pest.


















