Aquaculture, also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants. Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water, and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Aquaculture is also a practice used for restoring and rehabilitating marine and freshwater ecosystems. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, is aquaculture in seawater habitats and lagoons, as opposed to freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food.

Dendrobranchiata is a suborder of decapods, commonly known as prawns. There are 540 extant species in seven families, and a fossil record extending back to the Devonian. They differ from related animals, such as Caridea and Stenopodidea, by the branching form of the gills and by the fact that they do not brood their eggs, but release them directly into the water. They may reach a length of over 330 millimetres (13 in) and a mass of 450 grams (1.0 lb), and are widely fished and farmed for human consumption.

Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place. Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies and the oceans. About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations.

The fishing industry includes any industry or activity that takes, cultures, processes, preserves, stores, transports, markets or sells fish or fish products. It is defined by the Food and Agriculture Organization as including recreational, subsistence and commercial fishing, as well as the related harvesting, processing, and marketing sectors. The commercial activity is aimed at the delivery of fish and other seafood products for human consumption or as input factors in other industrial processes. The livelihood of over 500 million people in developing countries depends directly or indirectly on fisheries and aquaculture.

Whiteleg shrimp, also known as Pacific white shrimp or King prawn, is a species of prawn of the eastern Pacific Ocean commonly caught or farmed for food.

The shrimp fishery is a major global industry, with more than 3.4 million tons caught per year, chiefly in Asia. Rates of bycatch are unusually high for shrimp fishing, with the capture of sea turtles being especially contentious.

Penaeus monodon, commonly known as the giant tiger prawn, Asian tiger shrimp, black tiger shrimp, and other names, is a marine crustacean that is widely reared for food.

The largehead hairtail or beltfish is a member of the cutlassfish family, Trichiuridae. This common to abundant species is found in tropical and temperate oceans throughout the world. The taxonomy is not fully resolved, and the Atlantic, East Pacific and Northwest Pacific populations are also known as Atlantic cutlassfish, Pacific cutlassfish and Japanese cutlassfish, respectively. This predatory, elongated fish supports major fisheries.

Acetes is a genus of small shrimp that resemble krill, which is native to the western and central Indo-Pacific, the Atlantic coast of the Americas, Pacific coast of South America and inland waters of South America. Although most are from marine or estuarine habitats, the South American A. paraguayensis is a fresh water species. Several of its species are important for the production of shrimp paste in Southeast Asia, including A. japonicus, which is the world's most heavily fished species of wild shrimp or prawn in terms of total tonnage and represent the majority of non-human animals killed for food in terms of number of individuals.

Fishing in India is a major sector within the economy of India contributing 1.07% of its total GDP. The fishing sector in India supports the livelihood of over 28 million people in the country, especially within the marginalized and vulnerable communities. India is the third largest fish producing country in the world accounting for 7.96% of the global production and second largest producer of fish through aquaculture, after China. The total fish production during the FY 2020-21 is estimated at 14.73 million metric tonnes. According to the National Fisheries Development Board the Fisheries Industry generates an export earnings of Rs 334.41 billion. Centrally sponsored schemes will increase exports by Rs 1 lakh crore in FY25. 65,000 fishermen have been trained under these schemes from 2017 to 2020. Freshwater fishing consists of 55% of total fish production.

As with other countries, the 200 nautical miles (370 km) exclusive economic zone (EEZ) off the coast of the United States gives its fishing industry special fishing rights. It covers 11.4 million square kilometres, which is the second largest zone in the world, exceeding the land area of the United States.

China, with one-fifth of the world's population, accounts for two-thirds of the world's reported aquaculture production.
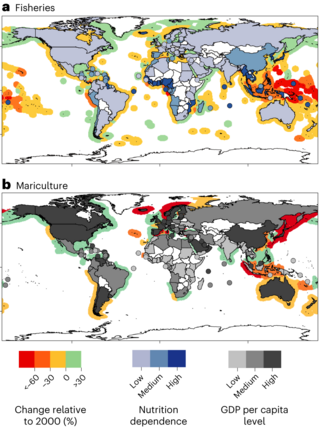
Fisheries are affected by climate change in many ways: marine aquatic ecosystems are being affected by rising ocean temperatures, ocean acidification and ocean deoxygenation, while freshwater ecosystems are being impacted by changes in water temperature, water flow, and fish habitat loss. These effects vary in the context of each fishery. Climate change is modifying fish distributions and the productivity of marine and freshwater species. Climate change is expected to lead to significant changes in the availability and trade of fish products. The geopolitical and economic consequences will be significant, especially for the countries most dependent on the sector. The biggest decreases in maximum catch potential can be expected in the tropics, mostly in the South Pacific regions.

Atlantic chub mackerel, also known as Tinker mackerel, is a pelagic schooling species of mackerel found in the Atlantic Ocean, the Mediterranean Sea, and the Black Sea. It was originally thought to be a subspecies of the chub mackerel Scomber japonicus colias.

South Korea is a major center of aquaculture production, and the world's third largest producer of farmed algae as of 2020.

Marsupenaeus is a monotypic genus of prawn. It contains a single species, Marsupenaeus japonicus, known as the kuruma shrimp, kuruma prawn, or Japanese tiger prawn. It occurs naturally in bays and seas of the Indo-West Pacific, but has also reached the Mediterranean Sea as a Lessepsian migrant. It is one of the largest species of prawns, and is accordingly one of the most economically important species in the family.

The Japanese jack mackerel, also known as the Japanese horse mackerel or Japanese scad, is a species named after its resemblance to mackerel but which is in the family Carangidae, the jacks, pompanos, trevallies and scads. Their maximum reported length is 50 cm (20 in) with a common length of 35 cm (14 in). They have a maximum reported weight of 0.66 kg (1.5 lb) and a maximum reported age of 12 years. They are found around the coast of Japan, except Okinawa Island, usually on sandy bottoms of 50–275 m (164–902 ft) deep. They feed mainly on small crustaceans such as copepods, as well as shrimp and small fish. They are similar to the yellowtail horse mackerel around New Zealand and Australia, apart from having more gill rakers and larger eyes.

A shrimp is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily swimming mode of locomotion – typically belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata of the order Decapoda, although some crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp".
Aquaculture in Madagascar started to take off in the 1980s. The industry includes the cultivation of sea cucumbers, seaweed, fish and shrimp and is being used to stimulate the country's economy, increase the wages of fishermen and women, and improve the regions ocean water quality. Coastal regions of Madagascar are reliant on the Indian Ocean's marine resources as a source of food, income, and cultural identity.
The fishing industry in Thailand, in accordance with usage by The World Bank, the UN's Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and other multinational bodies, refers to and encompasses recreational fishing, aquaculture, and wild fisheries both onshore and offshore.


















