
Botrytis cinerea is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or "gray mold".

A leaf spot is a limited, discoloured, diseased area of a leaf that is caused by fungal, bacterial or viral plant diseases, or by injuries from nematodes, insects, environmental factors, toxicity or herbicides. These discoloured spots or lesions often have a centre of necrosis. Symptoms can overlap across causal agents, however differing signs and symptoms of certain pathogens can lead to the diagnosis of the type of leaf spot disease. Prolonged wet and humid conditions promote leaf spot disease and most pathogens are spread by wind, splashing rain or irrigation that carry the disease to other leaves.
A biopesticide is a biological substance or organism that damages, kills, or repels organisms seen as pests. Biological pest management intervention involves predatory, parasitic, or chemical relationships.

In trees, heart rot is a fungal disease that causes the decay of wood at the center of the trunk and branches. Fungi enter the tree through wounds in the bark and decay the heartwood. The diseased heartwood softens, making trees structurally weaker and prone to breakage. Heart rot is a major factor in the economics of logging and the natural growth dynamic of many older forests. Heart rot is prevalent throughout the world affecting all hardwood trees and can be very difficult to prevent. A good indication of heart rot is the presence of mushrooms or fungus conks on the tree.

Trichoderma viride is a fungus and a biofungicide.

Cochliobolus miyabeanus is a fungus that causes brown spot disease in rice.

Rhizoctonia solani is a species of fungus in the order Cantharellales. Basidiocarps are thin, effused, and web-like, but the fungus is more typically encountered in its anamorphic state, as hyphae and sclerotia. The name Rhizoctonia solani is currently applied to a complex of related species that await further research. In its wide sense, Rhizoctonia solani is a facultative plant pathogen with a wide host range and worldwide distribution. It causes various plant diseases such as root rot, damping off, and wire stem. It can also form mycorrhizal associations with orchids.

Damping off is a horticultural disease or condition, caused by several different pathogens that kill or weaken seeds or seedlings before or after they germinate. It is most prevalent in wet and cool conditions.
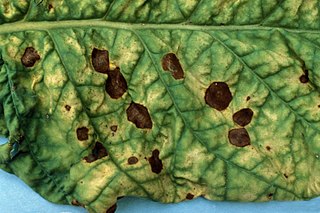
Alternaria alternata is a fungus causing leaf spots, rots, and blights on many plant parts, and other diseases. It is an opportunistic pathogen on over 380 host species of plant.

Colletotrichum acutatum is a plant pathogen and endophyte. It is the organism that causes the most destructive fungal disease, anthracnose, of lupin species worldwide. It also causes the disease postbloom fruit drop on many varieties of citrus, especially Valencia and navel oranges in Florida.

Macrophomina phaseolina is a Botryosphaeriaceae plant pathogen fungus that causes damping off, seedling blight, collar rot, stem rot, charcoal rot, basal stem rot, and root rot on many plant species.
Pythium aphanidermatum is a soil borne plant pathogen. Pythium is a genus in the class Oomycetes, which are also known as water molds. Oomycetes are not true fungi, as their cell walls are made of cellulose instead of chitin, they are diploid in their vegetative state, and they form coenocytic hyphae. Also, they reproduce asexually with motile biflagelette zoospores that require water to move towards and infect a host. Sexually, they reproduce with structures called antheridia, oogonia, and oospores.
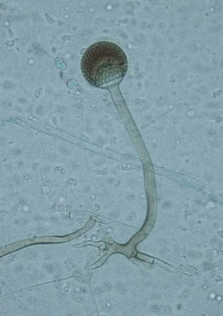
Rhizopus microsporus is a fungal plant pathogen infecting maize, sunflower, and rice.

Didymella rabiei, commonly called chickpea ascochyta blight fungus, is a fungal plant pathogen of chickpea. Didymella rabiei is the teleomorph of Ascochyta rabiei, which is the anamorph, but both names are the same species.
Fusarium redolens is a species of fungus in the genus Fusarium and family Nectriaceae. This species is a soil-borne plant pathogen in temperate prairies. It causes diseases such as root, crown, and spear rot, seedling damping-off, and wilting disease. It is a known producer of the alkaloids peimisine and imperialine-3β-d-glucoside, which has implications for traditional Chinese medicine.
Pythium dissotocum is a plant pathogen infecting strawberry and rice.

Sarocladium oryzae (Sawada) is a plant pathogen causing the Sheath rot disease of rice and Bamboo blight of Bambusoideae spp. in Asia.
Sporisorium reilianum Langdon & Full., (1978), previously known as Sphacelotheca reiliana, and Sporisorium reilianum, is a species of biotrophic fungus in the family Ustilaginaceae. It is a plant pathogen that infects maize and sorghum.

Colletotrichum coccodes is a plant pathogen, which causes anthracnose on tomato and black dot disease of potato. Fungi survive on crop debris and disease emergence is favored by warm temperatures and wet weather.

Gibberella fujikuroi is a fungal plant pathogen. It causes bakanae disease in rice seedlings.














