
Actiniidae is the largest family of sea anemones, to which most common, temperate, shore species belong. Most members of this family do not participate in symbioses with fishes. Three exceptions are the bubble-tip anemone, snakelocks anemone and Urticina piscivora.

Tube-dwelling anemones or ceriantharians look very similar to sea anemones but belong to an entirely different class of anthozoans. They are solitary, living buried in soft sediments. Tube anemones live inside and can withdraw into tubes, which are composed of a fibrous material made from secreted mucus and threads of nematocyst-like organelles known as ptychocysts. Within the tubes of these ceriantharians, more than one polyp is present, which is an exceptional trait because species that create tube systems usually contain only one polyp per tube. Ceriantharians were formerly classified in the taxon Ceriantipatharia along with the black corals but have since been moved to their own class, Ceriantharia.

Actinoscyphia is a genus of sea anemones of the family Actinoscyphiidae.

Batillaria is a genus of small salt marsh or mudflat snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Batillariidae, the horn snails.
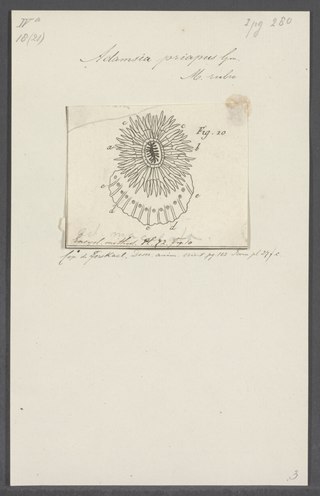
Adamsia is a genus of sea anemones in the family Hormathiidae. Species in this genus are mutually symbiotic with hermit crabs. The anemone gets a place to live and discarded scraps of the crab's food in exchange for its help in the crab's defence. As these anemones grow, they secrete a horny membrane, known as a carcinoecium, which overlies the crab's original snail shell and expands the living space of the crab. This means the anemone does not have to change substrate and the crab does not have to seek a larger shell as they both grow.

Aliciidae is a family of sea anemones, comprising the following genera:

Amphianthus is a genus of sea anemones. It is the only genus in the monotypic family Amphianthidae.

Cereus is a genus of sea anemones in the family Sagartiidae.

Pseudactinia is a genus of sea anemones in the family Actiniidae.

Bunodactis is a genus of sea anemones in the family Actiniidae.

Parazoanthus is a genus of anemone-like anthozoans in the order Zoantharia.

Actinia is a genus of sea anemones in the family Actiniidae. Actinia display a rare form of heteromorphosis in which a cut inflicted on a specimen can develop into a second mouth.

Liponema is a genus of sea anemones, in the family Liponematidae.

Haloclavidae is a family of sea anemones. Members of the family are found worldwide and many live largely buried in soft substrates with only their oral disc and tentacles protruding.

Peachia is a genus of sea anemone in the family Haloclavidae. Members of this genus typically burrow into soft substrates. The only part of the animal that is normally visible is the oral disc and tentacles which lie flat on the sand in a star shape. The type species is Peachia cylindrica.

Actinostolidae is a family of sea anemones in the order Actiniaria. Members of this family are deep sea species, with some occurring at hydrothermal vents.

Actinostola is a genus of sea anemones in the order Actiniaria. All members of this genus are deep-sea species, with some occurring at hydrothermal vents.

Paranthus is a genus of sea anemones in the family Actinostolidae.

Bolocera is a genus of sea anemone in the family Actiniidae.
Oractiidae is a family of sea anemones belonging to the order Actiniaria.















