Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Unlike most antibiotics, antiviral drugs do not destroy their target pathogen; instead they inhibit its development.

Nucleoside analogues are nucleosides which contain a nucleic acid analogue and a sugar. Nucleotide analogs are nucleotides which contain a nucleic acid analogue, a sugar, and a phosphate groups with one to three phosphates.

Aglaia silvestris is a species of plant in the family Meliaceae. It is found in Cambodia, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Solomon Islands, Thailand, and Vietnam. This plant initiated the naming of the Rocaglamide derivatives silvestrol and episilvestrol. In fact they were derived from the fruits and twigs of Aglaia foveolata.

Sorivudine (INN), is a nucleoside analogue antiviral drug, marketed under trade names such as Usevir and Brovavir (BMS). It is used for the treatment of varicella zoster virus infections.

FGI-104 is the name of an experimental broad-spectrum antiviral drug, with activity against a range of viruses including hepatitis B, hepatitis C, HIV, Ebola virus, and Venezuelan equine encephalitis virus.

Antiviral proteins are proteins that are induced by human or animal cells to interfere with viral replication. These proteins are isolated to inhibit the virus from replicating in a host's cells and stop it from spreading to other cells. The Pokeweed antiviral protein and the Zinc-Finger antiviral protein are two major antiviral proteins that have undergone several tests for viruses, including HIV and influenza.
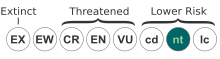
Favipiravir, sold under the brand name Avigan among others, is an antiviral medication used to treat influenza in Japan. It is also being studied to treat a number of other viral infections, including SARS-CoV-2. Like the experimental antiviral drugs T-1105 and T-1106, it is a pyrazinecarboxamide derivative.

Galidesivir is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog. It is developed by BioCryst Pharmaceuticals with funding from NIAID, originally intended as a treatment for hepatitis C, but subsequently developed as a potential treatment for deadly filovirus infections such as Ebola virus disease, Marburg virus disease, and Zika virus. Currently, galidesivir is under phase 1 human trial in Brazil for coronavirus.
Scytovirin is a 95-amino acid antiviral protein isolated from the cyanobacteria Scytonema varium. It has been cultured in E. coli and its structure investigated in detail. Scytovirin is thought to be produced by the bacteria to protect itself from viruses that might otherwise attack it, but as it has broad-spectrum antiviral activity against a range of enveloped viruses, scytovirin has also been found to be useful against a range of major human pathogens, most notably HIV / AIDS but also including SARS coronavirus and filoviruses such as Ebola virus and Marburg virus. While some lectins such as cyanovirin and Urtica dioica agglutinin are thought likely to be too allergenic to be used internally in humans, studies so far on scytovirin and griffithsin have not shown a similar level of immunogenicity. Scytovirin and griffithsin are currently being investigated as potential microbicides for topical use.
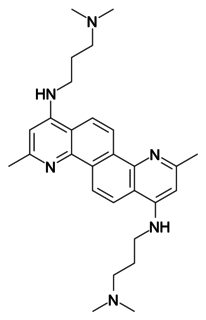
FGI-106 is a broad-spectrum antiviral drug developed as a potential treatment for enveloped RNA viruses, in particular viral hemorrhagic fevers from the bunyavirus, flavivirus and filovirus families. It acts as an inhibitor which blocks viral entry into host cells. In animal tests FGI-106 shows both prophylactic and curative action against a range of deadly viruses for which few existing treatments are available, including the bunyaviruses hantavirus, Rift Valley fever virus and Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus, the flavivirus dengue virus, and the filoviruses Ebola virus and Marburg virus.

MK-608 is an antiviral drug, an adenosine analog. It was originally developed by Merck & Co. as a treatment for hepatitis C, but despite promising results in animal studies, it was ultimately unsuccessful in clinical trials. Subsequently it has been widely used in antiviral research and has shown activity against a range of viruses, including Dengue fever, tick-borne encephalitis virus, poliovirus, and most recently Zika virus, in both in vitro and animal models. Since it has already failed in human clinical trials previously, it is unlikely MK-608 itself will be developed as an antiviral medication, but the continuing lack of treatment options for these emerging viral diseases means that much research continues using MK-608 and related antiviral drugs.
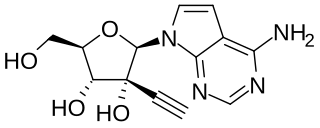
NITD008 is an antiviral drug classified as an adenosine analog. It was developed as a potential treatment for flavivirus infections and shows broad spectrum antiviral activity against many related viruses such as dengue virus, West Nile virus, yellow fever virus, Powassan virus, hepatitis C virus, Kyasanur Forest disease virus, Omsk hemorrhagic fever virus, and Zika virus. However, NITD008 proved too toxic in pre-clinical animal testing to be suitable for human trials, but it continues to be used in research to find improved treatments for emerging viral diseases.

Silvestrol is a natural product from the flavagline family, with a cyclopenta[b]benzofuran core structure and an unusual dioxane ether side chain, which is found in the bark of trees from the genus Aglaia, especially Aglaia silvestris and Aglaia foveolata.
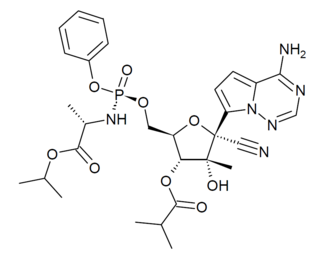
GS-6620 is an antiviral drug which is a nucleotide analogue. It was developed for the treatment of Hepatitis C but while it showed potent antiviral effects in early testing, it could not be successfully formulated into an oral dosage form due to low and variable absorption in the intestines which made blood levels unpredictable. It has however continued to be researched as a potential treatment for other viral diseases such as Ebola virus disease.
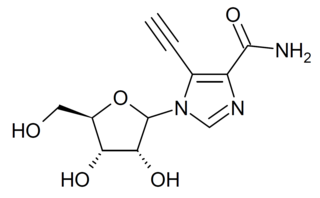
EICAR is a drug which acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme IMP dehydrogenase. It is a nucleoside derivative which has both anti-cancer and antiviral effects, and was originally developed for the treatment of leukemia, but was unsuccessful in human clinical trials. It has broad spectrum antiviral effects with activity against pox viruses, Semliki forest virus, Junin virus, reovirus, influenza, measles virus and respiratory syncytial virus among others, although it is not active against coronaviridae such as SARS-CoV-1. This useful spectrum of activity means that EICAR and related derivatives continue to be investigated for the treatment of viral diseases.
Broad-spectrum antivirals (BSAs) are a class of compounds, which inhibit replication of a broad range of viruses. BSAs could be divided into experimental and investigational agents, and approved drugs. BSAs work by inhibiting viral proteins or by targeting host cell factors and processes exploited by different viruses during infection. As of 2021, there are 150 known BSAs in varying stages of development, effective against 78 human viruses. BSAs are potential candidates for treatment of emerging and re-emerging viruses, such as ebola, marburg, and SARS-CoV-2. Many BSAs show antiviral activity against other viruses than originally investigated. Efforts in drug repurposing for SARS-CoV-2 is currently underway. A database of BSAs and viruses they inhibit could be found here.
Sara R. Cherry is an American microbiologist who is a Professor of Microbiology at the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Her research involves genetic and mechanistic studies of virus–host interactions. During the COVID-19 pandemic, Cherry looked to identify novel therapeutic strategies.

Merimepodib (VX-497) is a drug which acts as an inhibitor of the enzyme inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase, which is required for the synthesis of nucleotide bases containing guanine. This consequently inhibits synthesis of DNA and RNA, and results in antiviral and immunosuppressive effects. It progressed as far as Phase 2b human clinical trials against Hepatitis C but showed only modest benefits in comparison to existing treatments, however it continues to be researched, and also shows activity against other viral diseases such as Zika virus and foot and mouth disease virus.
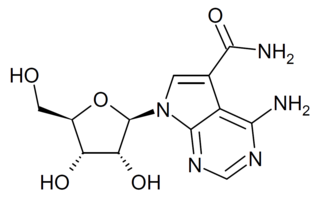
Sangivamycin is a natural product originally isolated from Streptomyces rimosus, which is a nucleoside analogue. It acts as an inhibitor of protein kinase C. It has antibiotic, antiviral and anti-cancer properties and has been investigated for various medical applications, though never approved for clinical use itself. However, a number of related derivatives continue to be researched.

S416 (GTPL-11164) is a drug which acts as a selective inhibitor of the enzyme dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH). This enzyme is involved in the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleosides in the body, which are required for the synthesis of DNA and RNA. This is an important rate-limiting step in the replication of viruses, and so DHODH inhibitors may have applications as broad-spectrum antiviral drugs. In tests in vitro, S416 was found to have antiviral activity against a range of pathogenic RNA viruses including influenza, Zika virus, Ebola virus and SARS-CoV-2.