The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period 358.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, 298.9 Mya. The name Carboniferous means "coal-bearing" and derives from the Latin words carbō ("coal") and ferō, and was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822.
The Mississippian is a subperiod in the geologic timescale or a subsystem of the geologic record. It is the earlier/lower of two subperiods of the Carboniferous period lasting from roughly 358.9 to 323.2 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Mississippian are well identified, but the exact start and end dates are uncertain by a few million years. The Mississippian is so named because rocks with this age are exposed in the Mississippi Valley.
The Pennsylvanian is, in the ICS geologic timescale, the younger of two subperiods of the Carboniferous Period. It lasted from roughly 323.2 million years ago to 298.9 million years ago. As with most other geochronologic units, the rock beds that define the Pennsylvanian are well identified, but the exact date of the start and end are uncertain by a few hundred thousand years. The Pennsylvanian is named after the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, where the coal-productive beds of this age are widespread.
The Permian is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous period 298.9 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic period 251.902 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic era; the following Triassic period belongs to the Mesozoic era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia.
The PaleozoicEra is the earliest of three geologic eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. It is the longest of the Phanerozoic eras, lasting from 541 to 251.902 million years ago, and is subdivided into six geologic periods : the Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous, and Permian. The Paleozoic comes after the Neoproterozoic Era of the Proterozoic Eon and is followed by the Mesozoic Era.

North Cornwall is an area of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is also the name of a former local government district, which was administered from Bodmin and Wadebridge 50.516°N 4.835°W. Other towns in the area are Launceston, Bude, Padstow, and Camelford.

Endopterygota, also known as Holometabola, is a superorder of insects within the infraclass Neoptera that go through distinctive larval, pupal, and adult stages. They undergo a radical metamorphosis, with the larval and adult stages differing considerably in their structure and behaviour. This is called holometabolism, or complete metamorphism.
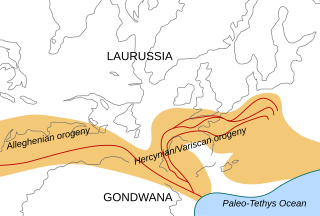
The Variscan or Hercynianorogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
The Tournaisian is in the ICS geologic timescale the lowest stage or oldest age of the Mississippian, the oldest subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Tournaisian age lasted from 358.9 Ma to 346.7 Ma. It is preceded by the Famennian and is followed by the Viséan.
The Serpukhovian is in the ICS geologic timescale the uppermost stage or youngest age of the Mississippian, the lower subsystem of the Carboniferous. The Serpukhovian age lasted from 330.9 Ma to 323.2 Ma. It is preceded by the Visean and is followed by the Bashkirian.

Montceau-les-Mines is a commune in the Saône-et-Loire department in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté in eastern France.

The late Paleozoic icehouse, formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was between 360–260 million years ago (Mya) during which large land-based ice-sheets were present on Earth's surface. It was the second major glacial period of the Phanerozoic. It is named after the tillite found in the Karoo Basin of South Africa, where evidence for this ice age was first clearly identified in the 19th century.

Carboniferous Limestone is a collective term for the succession of limestones occurring widely throughout Great Britain and Ireland that were deposited during the Dinantian Epoch of the Carboniferous Period. These rocks formed between 363 and 325 million years ago. Within England and Wales, the entire limestone succession, which includes subordinate mudstones and some thin sandstones, is known as the Carboniferous Limestone Supergroup.

Dendrerpeton is a genus of an extinct group of temnospondyl amphibians. Its fossils have been found primarily in the Joggins Formation and in Ireland. It lived during the Carboniferous and is said to be around 309–316 million years of age, corresponding to more specifically the Westphalian (stage) age. Of terrestrial temnospondyl amphibians evolution, it represents the first stage. Although multiple species have been proposed, the species unanimously recognized is D. acadianum. This species name comes from “Acadia” which is the name for ancient Indian Nova Scotia. It refers to the location of the coal field at which the fossil was found.

Megarachne is a genus of eurypterid, an extinct group of aquatic arthropods. Fossils of Megarachne have been discovered in deposits of Late Carboniferous age, from the Gzhelian stage, in San Luis, Argentina. The fossils of the single and type species M. servinei have been recovered from deposits that had once been a freshwater environment. The generic name, composed of the Ancient Greek μέγας (megas) meaning "great" and Ancient Greek ἀράχνη (arachne) meaning "spider", translates to "great spider", because the fossil was misidentified as a large prehistoric spider.
Micromelerpetontidae is an extinct family of dissorophoid temnospondyl amphibians that lived from the Late Carboniferous to the Early Permian in what is now Europe, with one Carboniferous species also known from North Africa. They were biologically similar to the related branchiosaurids, but proportionally akin to the unrelated microsaurs.
Limnerpeton is an extinct genus of dissorophoidean euskelian temnospondyl within the family Amphibamidae.

The Aipoceratoidea are a superfamily within the order Nautilida characterized by rapidly expanding, smooth to ribbed, cyrtoconic to coiled shells with rounded or sometimes dorsally flattened or impressed whorls, nearly straight sutures, and a ventral and marginal siphuncle. Septal necks are orthochoanitic ventrally and orthochoanitic or cyrtochoanitic dorsally.

Occidens is an extinct genus of stem tetrapod that lived during the earliest part of the Carboniferous in what is now Northern Ireland. It is known from a single type species, Occidens portlocki, named in 2004 on the basis of a left lower jaw that British geologist Joseph Ellison Portlock described in 1843. Portlock attributed it to the lobe-finned fish Holoptychius and it was housed in the collections of the British Geological Survey for over a century before being reevaluated in 2004 by vertebrate paleontologists Jenny Clack and Per E. Ahlberg, who reclassified it as a new genus and species of early tetrapod. The genus name Occidens refers to its presence west of better-known early tetrapod assemblages in Great Britain, and the species name honors Portlock. The jaw likely comes from the Altagoan Formation and, based on an analysis of fossilized pollen, dates to the late Tournaisian stage of the Early Carboniferous about 350 million years ago. The occurrence of Occidens in the Tournaisian makes it a critically important taxon because it lies within Romer's gap, a time interval spanning most of the Early Carboniferous in which almost no tetrapod fossils are known. Romer's gap separates the first appearance of tetrapods in the Late Devonian from the group's first evolutionary radiation toward the end of the Early Carboniferous. However, the relationship of Occidens to other early tetrapods both before and after the gap remain uncertain, which means that its context in tetrapod evolution remains unknown. Clack and Ahlberg noted several distinctive features of Occidens, including a straight row of teeth along the coronoid bones on the inner surface of the lower jaw, an open groove for a lateral line sense organ on the jaw's outer surface, and a stepped shape to the connection between the dentary and angular bones. The jaw bone is deep, resembling those of Crassigyrinus and whatcheeriids in overall appearance. In most phylogenetic trees produced by Clack and Ahlberg's 2004 analysis, Occidens fell near whatcheeriids and the Devonian taxon Tulerpeton, being more derived than all other Devonian taxa and more basal than Crassigyrinus and the post-Romer's Gap taxa Greererpeton and Megalocephalus. A 2008 phylogenetic analysis by paleontologists Marcello Ruta and John Bolt found Occidens to be the closest relative of Sigournea multidentata, a species from the end of the gap found in Iowa, but could not determine where these two taxa fit relative to other Early Carboniferous tetrapods.
Mattauschia is an extinct genus of trematopid temnospondyls from the Late Carboniferous of the Czech Republic.












