Iqaluit, meaning "place of fish", is the capital of the Canadian territory of Nunavut, its largest community, and its only city. It was known as Frobisher Bay from 1942 to 1987, after the large bay on the coast of which the city is situated, when the traditional Inuktitut name was restored.

The Inuit languages are a closely related group of indigenous American languages traditionally spoken across the North American Arctic and to some extent in the subarctic in Labrador. The related Yupik languages are spoken in western and southern Alaska and in the far east of Russia, but are severely endangered in Russia today and spoken only in a few villages on the Chukchi Peninsula. The Inuit live primarily in three countries: Greenland, Canada, and the United States.

Inuktitut syllabics is an abugida-type writing system used in Canada by the Inuktitut-speaking Inuit of the territory of Nunavut and the Nunavik region in Quebec. In 1976, the Language Commission of the Inuit Cultural Institute made it the co-official script for the Inuit languages, along with the Latin script.
Inuvialuktun, also known as Western Canadian Inuit, Western Canadian Inuktitut, and Western Canadian Inuktun, comprises several Inuit language varieties spoken in the northern Northwest Territories and Nunavut by those Canadian Inuit who call themselves Inuvialuit.

Inuinnaqtun, is an indigenous Inuit language of Canada and a dialect of Inuvialuktun. It is related very closely to Inuktitut, and some scholars, such as Richard Condon, believe that Inuinnaqtun is more appropriately classified as a dialect of Inuktitut. The governments of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut recognise Inuinnaqtun as an official language in addition to Inuktitut. The Official Languages Act of Nunavut, passed by the Senate of Canada on June 11, 2009, recognized Inuinnaqtun as one of the official languages of Nunavut.

Nunavut is a federal electoral district in Nunavut, Canada, that has been represented in the House of Commons of Canada since 1979. Before 1997, it was known as Nunatsiaq, and was one of two electoral districts in Northwest Territories.

Inuktitut, also Eastern Canadian Inuktitut, is one of the principal Inuit languages of Canada. It is spoken in all areas north of the tree line, including parts of the provinces of Newfoundland and Labrador, Quebec, to some extent in northeastern Manitoba as well as the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is one of the aboriginal languages written with Canadian Aboriginal syllabics.

Canadian Aboriginal syllabic writing, or simply syllabics, is a family of abugidas used to write a number of indigenous Canadian languages of the Algonquian, Inuit, and (formerly) Athabaskan language families. They are valued for their distinctiveness from the Latin script of the dominant languages and for the ease with which literacy can be achieved; indeed, by the late 19th century the Cree had achieved what may have been one of the highest rates of literacy in the world.
The Inuit language, like other Eskimo–Aleut languages, exhibits a regular agglutinative and heavily suffixing morphology. The language is rich in suffixes, up to 700 per dialect, making words very long and potentially unique. For example, in Nunavut Inuktitut:

CBC North is the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation's radio and television service in Northern Canada. It began operations in 1958 as the CBC Northern Service with radio broadcasts. It took over CFYK, a community-run station in Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, which began broadcasting in 1948. CFYK had been opened by the Royal Canadian Signal Corps.

Taloyoak or Talurjuaq, formerly known as Spence Bay until 1 July 1992; is located on the Boothia Peninsula, Kitikmeot, in Canada's Nunavut Territory. The community is served only by air and by annual supply sealift. Taloyoak may mean "large blind", referring to a stone caribou blind or a screen used for caribou hunting. The community is situated 460 km (290 mi) east of the regional centre of Cambridge Bay, 1,224 km (761 mi) northeast of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. Taloyoak is the northernmost community in mainland Canada.

Kugaaruk, formerly known as Pelly Bay until 3 December 1999, is located on the shore of Pelly Bay, just off the Gulf of Boothia, Simpson Peninsula, Kitikmeot, in Canada's Nunavut territory. Access is by air by the Kugaaruk Airport and by annual supply sealift. Kugaaruk means "little stream", the traditional name of the brook that flows through the hamlet.

Umingmaktok is a now abandoned settlement located in Bathurst Inlet in the Kitikmeot Region of the Canadian territory of Nunavut. The community was previously known as Bay Chimo and the Inuit refer to the community as Umingmaktuuq.
Nunavut is one of Canada's territories, and has established several territorial symbols.
Deer Island is one of the uninhabited Canadian Arctic islands in the Qikiqtaaluk Region, Nunavut, Canada. The island is located in Foxe Basin just north of Jens Munk Island.
This article discusses the phonology of the Inuit languages. Unless otherwise noted, statements refer to Inuktitut dialects of Canada.

Netsilik, Natsilik,Nattilik, Netsilingmiut, Natsilingmiutut, Nattilingmiutut, Nattiliŋmiutut is a dialect of Inuvialuktun language once spoken in the Nattilik area of Nunavut, Canada by Netsilik Inuit.

The North Baffin dialect of Inuktitut is spoken on the northern part of Baffin Island, at Igloolik and the adjacent part of the Melville Peninsula, and in other Inuit communities in the far north of Nunavut, like Resolute, Grise Fiord, Pond Inlet, Clyde River, and Arctic Bay.

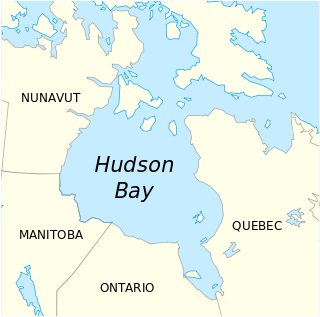
Kivalliq, also known as Kivallirmiutut, Caribou Eskimo, or formerly as Keewatin, is a Canadian dialect of Inuvialuktun spoken along the northwestern shores of Hudson Bay in Nunavut. The governments of Nunavut and the Northwest Territories generally consider it to be a dialect of Inuktitut due to its location, but linguists generally classify it as a dialect of Inuvialuktun. However, Inuktitut and Inuvialuk form a dialect continuum with few sharp boundaries.