| Alcaligenaceae | |
|---|---|
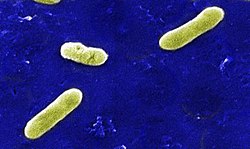 | |
| Bordetella bronchiseptica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Kingdom: | Pseudomonadati |
| Phylum: | Pseudomonadota |
| Class: | Betaproteobacteria |
| Order: | Burkholderiales |
| Family: | Alcaligenaceae De Ley et al., 1986 [1] |
| Genera [2] [3] | |
| |
The Alcaligenaceae are a family of bacteria, included in the order Burkholderiales. Members are found in water, soil, humans, and other animals. [4] Some species, like Bordetella , are pathogenic for humans and for some other animals. [4]