
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about 50 miles (80 km) east-southeast of Portland, on the border between Clackamas and Hood River counties. In addition to being Oregon's highest mountain, it is one of the loftiest mountains in the nation based on its prominence, and it offers the only year-round lift-served skiing in North America.

The Greenwell Glacier is a major tributary glacier, 45 nautical miles long, draining northwest between the Mirabito Range and the Everett Range to enter Lillie Glacier below Mount Works, in northwest Victoria Land, Antarctica. This geographical feature was first mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and from U.S. Navy aerial photography, 1960–63, and was so named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Commander Martin D. Greenwell, U.S. Navy, Commander of Antarctic Squadron Six (VX-6), 1961–62. The glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare.

Hispar Glacier is a 49 km (30 mi) long glacier in the Karakoram Mountains of Gilgit–Baltistan, Pakistan which meets the 67
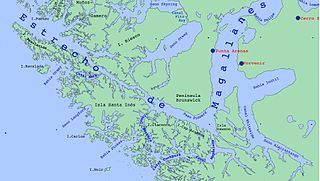
Almirantazgo Fjord, also known as Almirantazgo Sound or Admiralty Sound, is a Chilean fjord located in the far south of the country at 54°19′S69°30′W. The fjord cuts deeply into the west coast of the Isla Grande de Tierra del Fuego, extending southeastwards from the Whiteside Channel, which separates Isla Grande from Dawson Island. On its south side several smaller fjords and bays make significant indentations into the north coastline of the Cordillera Darwin. One of these, Ainsworth Bay, is home to a colony of elephant seals. Azopardo River empties into the head of the fjord.
Grey Lake is a glacially fed lake in Torres del Paine National Park, southern Chile.

The Arctic Yellow River Station was established by the Polar Research Institute of China in Ny-Ålesund, on Svalbard, in 2003.

Haas Glacier is a steep tributary glacier draining northward from Rawson Plateau to enter the south side of Bowman Glacier, in the Queen Maud Mountains of Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1960–64, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Charles G. Haas, a meteorologist in the South Pole Station winter party, 1960.

Haffner Glacier is a small glacier discharging into Berg Bay along the north coast of Victoria Land, Antarctica. It was first charted by the British Antarctic Expedition, 1898–1900, under Carsten. E. Borchgrevink, who named it for Colonel Haffner, Director of the Government Survey of Norway. This glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare.
Daspit Glacier is a glacier 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, flowing east-northeast along the south side of Mount Shelby to the head of Trail Inlet, on the east coast of Graham Land, Antarctica. It was discovered by members of the East Base of the United States Antarctic Service, 1939–41, and was originally named Fleming Glacier after Rev. W.L.S. Fleming. It was photographed from the air in 1947 by the Ronne Antarctic Research Expedition under Finn Ronne, and charted in 1948 by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey. It was renamed by Ronne for Captain Lawrence R. Daspit, U.S. Navy, who assisted in obtaining Navy support for the Ronne expedition, the original name being transferred to Fleming Glacier on the Rymill Coast.

The Carter Glaciers are in Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. The glaciers are situated along a ridge immediately to the east of the Continental Divide, mainly below an unnamed peak which rises to 9,164 feet (2,793 m). The glaciers cover an area of approximately 50 acres (0.20 km2) at an elevation between 8,500 feet (2,600 m) and 7,200 feet (2,200 m) above sea level. The Carter Glaciers consist of between three and four separate small glacial remnants (glacierets), none of which meet the threshold of 25 acres (0.10 km2) often cited as being the minimum size to qualify as an active glacier.

Kintla Glacier is in Glacier National Park in the U.S. state of Montana. The glacier is situated on a plateau 2 miles (3.2 km) southwest of Kintla Peak at an elevation between 8,700 feet (2,700 m) and 7,700 feet (2,300 m) above sea level. The glacier has numerous crevasses and is actually two glaciers with a combined area of 280 acres (110 ha) as of 2005. This is a 34 percent decrease in area from 1966.

Français Glacier is a glacier 4 nautical miles (7 km) wide and 12 nautical miles (22 km) long, flowing north-northeast from the continental ice to the Antarctic coast close west of Ravin Bay. Though no glaciers were noted on Captain Jules Dumont d'Urville's chart of this coast, the close correlation of his "Baie des Ravins" feature and narrative description with the indentation of the coast near the mouth of this glacier suggests first sighting of this feature by the French Antarctic Expedition, 1837–40. During December 1912 members of the Main Base Party of the Australasian Antarctic Expedition (AAE) camped on the upland slopes close east of the glacier, but no reference was made to the glacier in the AAE reports, though a clear view and unpublished sketch were obtained of the distant coast to the northwest.
Gourdon Glacier is a glacier 4 nautical miles (7 km) long on the east side of James Ross Island, flowing southeast into Markham Bay between Saint Rita Point and Rabot Point. It has a conspicuous rock wall at its head. The glacier was first surveyed by the Swedish Antarctic Expedition under Otto Nordenskiöld, 1901–04, who named it for Ernest Gourdon, geologist and glaciologist of the French Antarctic Expedition, 1903–05.

Graveson Glacier is a broad north-flowing tributary to the Lillie Glacier, draining that portion of the Bowers Mountains between the Posey Range and the southern part of Explorers Range, Victoria Land, Antarctica. The geographical feature is fed by several lesser tributaries and enters Lillie Glacier via Flensing Icefall. The glacier was so named by the northern party of the New Zealand Geological Survey Antarctic Expedition, 1963–64, for F. Graveson, a mining engineer who wintered at Scott Base in 1963 and was field assistant on this expedition. The glacier lies situated on the Pennell Coast, a portion of Antarctica lying between Cape Williams and Cape Adare.

Hale Glacier is a glacier about 6 nautical miles (11 km) long, located just east of Mount Simpson on Thurston Island, Antarctica, and flowing southwest to the Abbot Ice Shelf in Peacock Sound. It was delineated from air photos taken by U.S. Navy Squadron VX-6 in January 1960, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) for Lieutenant Bill J. Hale, U.S. Navy, a helicopter pilot aboard USS Burton Island who made exploratory flights to Thurston Island in February 1960.

Hyde Glacier is a short glacier flowing east through the Edson Hills to join Union Glacier, in the Heritage Range, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–66, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for William H. Hyde, an ionospheric scientist at Little America V Station in 1958.

Thordarhyrna is one of seven subglacial volcanoes beneath the Vatnajokull glacier Iceland.

Holanda Glacier is a glacier located in Alberto de Agostini National Park, Chile. It is located at the east end of a group of glaciers line up on the north shore of the northwest arm of the Beagle Channel. The glacier terminus ends in a small proglacial lake.

Romanche Glacier is a glacier located in Alberto de Agostini National Park, Chile. A cascade from the glacier tumbles into the Beagle Channel.

Italia Glacier is a tidewater glacier located in Alberto de Agostini National Park, Chile. It flows down in a southwest direction to its terminus in the Beagle Channel.














