
Zollernia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes 10 species native to South America, ranging from Venezuela and the Guianas to southern Brazil. Zollernia are trees or shrubs that flower annually. Species are most commonly found in dense moist forests, but also grow in seasonally-dry cerrado and caatinga.

Hevea is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, with about ten members. It is also one of many names used commercially for the wood of the most economically important rubber tree, H. brasiliensis. The genus is native to tropical South America but is widely cultivated in other tropical countries and naturalized in several of them. It was first described in 1775.

Pouteria is a genus of flowering trees in the gutta-percha family, Sapotaceae. The genus is widespread throughout the tropical Americas, with outlier species in Cameroon and Malesia. It includes the canistel, the mamey sapote, and the lucuma. Commonly, this genus is known as pouteria trees, or in some cases, eggfruits.

Dipteryx is a genus containing a number of species of large trees and possibly shrubs. It belongs to the "papilionoid" subfamily – Faboideae – of the family Fabaceae. This genus is native to South and Central America and the Caribbean. Formerly, the related genus Taralea was included in Dipteryx.
Lecointea is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It contains seven species native to the tropical Americas.

Myrocarpus is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It includes five species of trees native to tropical South America, ranging from Venezuela to northern Argentina. Typical habitats include wet to seasonally-dry tropical lowland forest and woodland.

Ormosia is a genus of legumes. 131 living species, mostly trees or large shrubs, are native to the tropical Americas, from southwestern Mexico to Bolivia and southern Brazil, to southern, southeastern, and eastern Asia, and to New Guinea and Queensland. Most are tropical, while some extend into temperate regions of China. A few species are threatened by habitat destruction, while the Hainan ormosia is probably extinct already.

Hirtella is a genus of 110 species of woody trees in family Chrysobalanaceae. It was first described as a genus by Linnaeus in 1753. Hirtella naturally occurs in tropical forests throughout Latin America, the West Indies, southeast Africa, and Madagascar. The flowers are mainly pollinated by butterflies.

Pradosia is a genus of plants in the family Sapotaceae described as a genus in 1872.
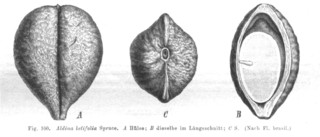
Aldina is a genus of trees in the Fabaceae native to the Guiana Shield and northern Amazonia. It is found in lowland humid forests. It is included in the Andira clade.

Eperua is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to subfamily Detarioideae. It includes 16 species native to northern South America, in Colombia, Venezuela, the Guianas, and northern Brazil. They live in the jungles, often along rivers or streams. The leaves are compound pinnate, with smooth margins, and the fruits are long pods. The wood of E. falcata is called wallaba and is often used in construction.

Bocoa is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae (Leguminosae). It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae (Papilionoideae). Several species in the genus were recently reclassified as Trischidium.
Candolleodendron brachystachyum is a species of flowering plant in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It is the only member of the genus Candolleodendron. It is a tree native to the Amazon rain forest of northern Brazil (Pará), Suriname, and French Guiana.
Clathrotropis is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It includes 7 species native to northern South America, ranging from Peru to Colombia, Venezuela, the Guianas, and northern Brazil. The genus belongs to subfamily Faboideae.

Hymenolobium is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It includes 14 species of trees native to Central America and northern South America, ranging from Honduras to Bolivia and southeastern Brazil. Most species are native to Brazil, the Guianas, and Venezuela, with one extending into Peru, another into Ecuador, and one native to Central America. Trees are typically very tall and emergent in tropical humid lowland rain forest.
Monopteryx is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae. It includes three species of trees native to the Amazon rainforest of northern South America, ranging through parts of Colombia, Venezuela, northern Brazil, and French Guiana. They grow in non-inundated lowland tropical rain forest on sandy soil. The genus belongs to subfamily Faboideae. Members of this genus produce hydroxypipecolic acids in their leaves.
Petaladenium urceoliferum is a species of flowering plant in the family Fabaceae. It is a tree native to northern Brazil. It grows in tropical lowland Amazon rainforest in the basin of the Rio Negro, a northern tributary of the Amazon. It is the only member of the genus Petaladenium. The genus belongs to tribe Amburaneae in subfamily Faboideae.
Vataireopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes four species of small to emergent trees, native to northern South America, ranging from Colombia, Venezuela, and the Guianas to Bolivia and southern Brazil. They grow in tropical lowland rain forest, in both the Amazon and Atlantic Forest.

Schnella is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Cercidoideae. All of its species are neotropical lianas.
Saxo-fridericia is a group of plants in the family Rapateaceae described as a genus in 1845.












