Related Research Articles

Amazon Web Services, Inc. (AWS) is a subsidiary of Amazon that provides on-demand cloud computing platforms and APIs to individuals, companies, and governments, on a metered, pay-as-you-go basis. Clients will often use this in combination with autoscaling. These cloud computing web services provide various services related to networking, compute, storage, middleware, IoT and other processing capacity, as well as software tools via AWS server farms. This frees clients from managing, scaling, and patching hardware and operating systems. One of the foundational services is Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), which allows users to have at their disposal a virtual cluster of computers, with extremely high availability, which can be interacted with over the internet via REST APIs, a CLI or the AWS console. AWS's virtual computers emulate most of the attributes of a real computer, including hardware central processing units (CPUs) and graphics processing units (GPUs) for processing; local/RAM memory; hard-disk/SSD storage; a choice of operating systems; networking; and pre-loaded application software such as web servers, databases, and customer relationship management (CRM).
Cascading is a software abstraction layer for Apache Hadoop and Apache Flink. Cascading is used to create and execute complex data processing workflows on a Hadoop cluster using any JVM-based language, hiding the underlying complexity of MapReduce jobs. It is open source and available under the Apache License. Commercial support is available from Driven, Inc.
Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is a part of Amazon.com's cloud-computing platform, Amazon Web Services (AWS), that allows users to rent virtual computers on which to run their own computer applications. EC2 encourages scalable deployment of applications by providing a web service through which a user can boot an Amazon Machine Image (AMI) to configure a virtual machine, which Amazon calls an "instance", containing any software desired. A user can create, launch, and terminate server-instances as needed, paying by the second for active servers – hence the term "elastic". EC2 provides users with control over the geographical location of instances that allows for latency optimization and high levels of redundancy. In November 2010, Amazon switched its own retail website platform to EC2 and AWS.
Truviso is a continuous analytics, venture-backed, startup headquartered in Foster City, California developing and supporting its solution leveraging PostgreSQL, to deliver a proprietary analytics solutions for net-centric customers. Truviso was acquired by Cisco Systems, Inc. on May 4, 2012.

Microsoft Azure, often referred to as Azure, is a cloud computing platform run by Microsoft. It offers access, management, and the development of applications and services through global data centers. It also provides a range of capabilities, including software as a service (SaaS), platform as a service (PaaS), and infrastructure as a service (IaaS). Microsoft Azure supports many programming languages, tools, and frameworks, including Microsoft-specific and third-party software and systems.

Redis is an open-source in-memory storage, used as a distributed, in-memory key–value database, cache and message broker, with optional durability. Because it holds all data in memory and because of its design, Redis offers low-latency reads and writes, making it particularly suitable for use cases that require a cache. Redis is the most popular NoSQL database, and one of the most popular databases overall. Redis is used in companies like Twitter, Airbnb, Tinder, Yahoo, Adobe, Hulu, Amazon and OpenAI.
Amazon Relational Database Service is a distributed relational database service by Amazon Web Services (AWS). It is a web service running "in the cloud" designed to simplify the setup, operation, and scaling of a relational database for use in applications. Administration processes like patching the database software, backing up databases and enabling point-in-time recovery are managed automatically. Scaling storage and compute resources can be performed by a single API call to the AWS control plane on-demand. AWS does not offer an SSH connection to the underlying virtual machine as part of the managed service.
SQLstream is a distributed, SQL standards-compliant plus Java stream processing platform. SQLstream, Inc. is based in San Francisco, California and was launched in 2009 by Damian Black, Edan Kabatchnik and Julian Hyde, author of the open source Mondrian Relational OLAP Server Engine.
A cloud database is a database that typically runs on a cloud computing platform and access to the database is provided as-a-service. There are two common deployment models: users can run databases on the cloud independently, using a virtual machine image, or they can purchase access to a database service, maintained by a cloud database provider. Of the databases available on the cloud, some are SQL-based and some use a NoSQL data model.
Amazon Redshift is a data warehouse product which forms part of the larger cloud-computing platform Amazon Web Services. It is built on top of technology from the massive parallel processing (MPP) data warehouse company ParAccel, to handle large scale data sets and database migrations. Redshift differs from Amazon's other hosted database offering, Amazon RDS, in its ability to handle analytic workloads on big data data sets stored by a column-oriented DBMS principle. Redshift allows up to 16 petabytes of data on a cluster compared to Amazon RDS Aurora's maximum size of 128 terabytes.
Cloud analytics is a marketing term for businesses to carry out analysis using cloud computing. It uses a range of analytical tools and techniques to help companies extract information from massive data and present it in a way that is easily categorised and readily available via a web browser.
Google Cloud Platform (GCP), offered by Google, is a suite of cloud computing services that provides a series of modular cloud services including computing, data storage, data analytics, and machine learning, alongside a set of management tools. It runs on the same infrastructure that Google uses internally for its end-user products, such as Google Search, Gmail, and Google Docs, according to Verma, et.al. Registration requires a credit card or bank account details.
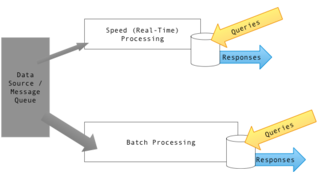
Lambda architecture is a data-processing architecture designed to handle massive quantities of data by taking advantage of both batch and stream-processing methods. This approach to architecture attempts to balance latency, throughput, and fault-tolerance by using batch processing to provide comprehensive and accurate views of batch data, while simultaneously using real-time stream processing to provide views of online data. The two view outputs may be joined before presentation. The rise of lambda architecture is correlated with the growth of big data, real-time analytics, and the drive to mitigate the latencies of map-reduce.

Apache Flink is an open-source, unified stream-processing and batch-processing framework developed by the Apache Software Foundation. The core of Apache Flink is a distributed streaming data-flow engine written in Java and Scala. Flink executes arbitrary dataflow programs in a data-parallel and pipelined manner. Flink's pipelined runtime system enables the execution of bulk/batch and stream processing programs. Furthermore, Flink's runtime supports the execution of iterative algorithms natively.
Presto is a distributed query engine for big data using the SQL query language. Its architecture allows users to query data sources such as Hadoop, Cassandra, Kafka, AWS S3, Alluxio, MySQL, MongoDB and Teradata, and allows use of multiple data sources within a query. Presto is community-driven open-source software released under the Apache License.
This is a timeline of Amazon Web Services, which offers a suite of cloud computing services that make up an on-demand computing platform.
Function as a service (FaaS) is a category of cloud computing services that provides a platform allowing customers to develop, run, and manage application functionalities without the complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. Building an application following this model is one way of achieving a "serverless" architecture, and is typically used when building microservices applications.
Microsoft Azure Stream Analytics is a serverless scalable complex event processing engine by Microsoft that enables users to develop and run real-time analytics on multiple streams of data from sources such as devices, sensors, web sites, social media, and other applications. Users can set up alerts to detect anomalies, predict trends, trigger necessary workflows when certain conditions are observed, and make data available to other downstream applications and services for presentation, archiving, or further analysis.
Kyvos is a business intelligence acceleration platform for cloud and big data platforms developed by an American privately held company named Kyvos Insights. The company, headquartered in Los Gatos, California, was founded by Praveen Kankariya, CEO of Impetus Technologies. The software provides OLAP-based multidimensional analysis on big data and cloud platforms and was launched officially in June 2015. In December the same year, the company was listed among the 10 Coolest Big Data Startups of 2015 by CRN Magazine.
Amazon SageMaker is a cloud based machine-learning platform that allows the creation, training, and deployment by developers of machine-learning (ML) models on the cloud. It can be used to deploy ML models on embedded systems and edge-devices. SageMaker was launched in November 2017.
References
- ↑ Jeff Barr (2013-11-14). "Amazon Kinesis - Real-Time Stream Processing" . Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- 1 2 Makota, Tarik; Maguire, Brian; Gagne, Danny; Chakrabarti, Rajeev (2021-03-31). Scalable Data Streaming with Amazon Kinesis: Design and secure highly available, cost-effective data streaming applications with Amazon Kinesis. Packt Publishing Ltd. ISBN 978-1-80056-433-6.
- 1 2 "Amazon Kinesis". Amazon Web Services. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ "AWS Launches Amazon Kinesis Data Streams On-Demand". InfoQ. Retrieved 2023-03-25.
- ↑ "Amazon Releases Kinesis Firehose". InfoQ. Retrieved 2023-03-25.
- ↑ "Amazon Kinesis Video Streams". Amazon Web Services. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ "Amazon Kinesis Integrations". Amazon Web Services. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ Srivastava, Mayank; Yadav, Pradduman (2021-10-22). "Build a Log Analytic Solution on AWS". 2021 5th International Conference on Information Systems and Computer Networks (ISCON). pp. 1–5. doi:10.1109/ISCON52037.2021.9702374. ISBN 978-1-6654-0341-2. S2CID 246870198.
- ↑ Quadri, Nasreen Sultana; Yadav, Kusum (2018-04-25). "Efficient Data Classification for IoT Devices using AWS Kinesis Platform". 2018 21st Saudi Computer Society National Computer Conference (NCC). pp. 1–5. doi:10.1109/NCG.2018.8593105. ISBN 978-1-5386-4110-1. S2CID 57364493.
- ↑ "Amazon Kinesis Pricing". Amazon Web Services. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ "AWS Free Tier". Amazon Web Services. Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ Jeff Barr (2013-11-14). "Amazon Kinesis - Real-Time Stream Processing" . Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ Jeff Barr (2015-08-05). "Amazon Kinesis Firehose – Simple & Highly Scalable Data Ingestion" . Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ Jeff Barr (2016-08-11). "Amazon Kinesis Analytics – Process Streaming Data in Real Time with SQL" . Retrieved 2023-03-24.
- ↑ Jeff Barr (2017-11-27). "Amazon Kinesis Video Streams – Serverless Video Ingestion and Storage for Vision-Enabled Apps" . Retrieved 2023-03-24.