
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin, an essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of glucose and amino acids.

Thiaminase is an enzyme that metabolizes or breaks down thiamine into two molecular parts. It is an antinutrient when consumed.
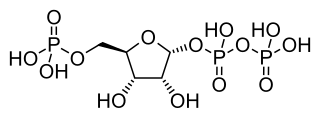
Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) is a pentose phosphate. It is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, as well as in pyrimidine nucleotide formation. Hence it is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin, and the amino acid tryptophan also contain fragments derived from PRPP. It is formed from ribose 5-phosphate (R5P) by the enzyme ribose-phosphate diphosphokinase:

Phosphoribosylamine (PRA) is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from PRA.
In enzymology, a thiamine oxidase (EC 1.1.3.23) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dCTP deaminase (EC 3.5.4.13) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a thiamine-phosphate diphosphorylase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydroxymethylpyrimidine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

5′-Phosphoribosyl-5-aminoimidazole is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from AIR. It is an intermediate in the adenine pathway and is synthesized from 5′-phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine by AIR synthetase.
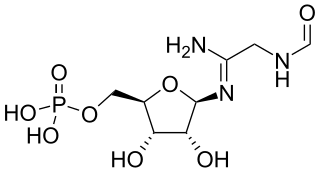
5′-Phosphoribosylformylglycinamidine is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from FGAM.

Glycineamide ribonucleotide is a biochemical intermediate in the formation of purine nucleotides via inosine-5-monophosphate, and hence is a building block for DNA and RNA. The vitamins thiamine and cobalamin also contain fragments derived from GAR.
FAD-dependent urate hydroxylase is an enzyme with systematic name urate,NADH:oxygen oxidoreductase . A non-homologous isofunctional enzyme (NISE) to HpxO was found, and named HpyO. HpyO was determined to be a typical Michaelian enzyme. These FAD-dependent urate hydroxylases are flavoproteins.
Sulfur carrier protein ThiS adenylyltransferase is an enzyme with systematic name ATP:(ThiS) adenylyltransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Thiazole synthase (EC 2.8.1.10, thiG (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 1-deoxy-D-xylulose 5-phosphate:thiol sulfurtransferase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Methylenediurea deaminase (EC 3.5.3.21, methylenediurease) is an enzyme with systematic name methylenediurea aminohydrolase found in Brucella anthropi, a bacterium. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:

6-carboxytetrahydropterin synthase (EC 4.1.2.50, CPH4 synthase, queD (gene), ToyB, ykvK (gene)) is an enzyme with systematic name 7,8-dihydroneopterin 3'-triphosphate acetaldehyde-lyase (6-carboxy-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropterin and triphosphate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following reversible chemical reaction.
Phosphomethylpyrimidine synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 5-amino-1-(5-phospho-D-ribosyl)imidazole formate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate synthase (glutamine hydrolysing) (EC 4.3.3.6, PdxST) is an enzyme with systematic name D-ribose 5-phosphate,D-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate pyridoxal 5′-phosphate-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Thiazole tautomerase is an enzyme with systematic name 2-(2-carboxy-4-methylthiazol-5-yl)ethyl phosphate isomerase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Within the field of biochemistry, 4-amino-5-hydroxymethyl-2-methylpyrimidine (HMP) also known as toxopyrimidine together with its mono phosphate (HMP-P) and pyrophosphate (HMP-PP) esters are biogenetic precursors to the important biochemical cofactor thiamine pyrophosphate (TPP), a derivative of thiamine (vitamin B1).











