The flatworms, flat worms, Platyhelminthes, or platyhelminths are a phylum of relatively simple bilaterian, unsegmented, soft-bodied invertebrates. Unlike other bilaterians, they are acoelomates, and have no specialized circulatory and respiratory organs, which restricts them to having flattened shapes that allow oxygen and nutrients to pass through their bodies by diffusion. The digestive cavity has only one opening for both ingestion and egestion ; as a result, the food cannot be processed continuously.
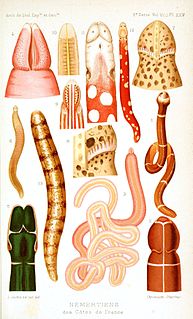
Nemertea is a phylum of invertebrate animals also known as ribbon worms or proboscis worms. Alternative names for the phylum have included Nemertini, Nemertinea and Rhynchocoela. Most are very slim, usually only a few millimeters wide, although a few have relatively short but wide bodies. Many have patterns of yellow, orange, red and green coloration. The foregut, stomach and intestine run a little below the midline of the body, the anus is at the tip of the tail, and the mouth is under the front. A little above the gut is the rhynchocoel, a cavity which mostly runs above the midline and ends a little short of the rear of the body. All species have a proboscis which lies in the rhynchocoel when inactive but everts to emerge just above the mouth and capture the animal's prey with venom. A highly extensible muscle in the back of the rhynchocoel pulls the proboscis in when an attack ends. A few species with stubby bodies filter feed and have suckers at the front and back ends, with which they attach to a host.
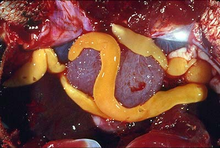
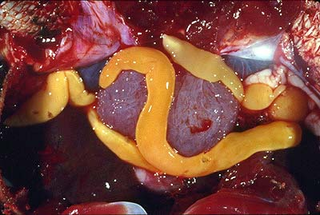
Schistosoma is a genus of trematodes, commonly known as blood flukes. They are parasitic flatworms responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed schistosomiasis, which is considered by the World Health Organization as the second-most socioeconomically devastating parasitic disease, with hundreds of millions infected worldwide.

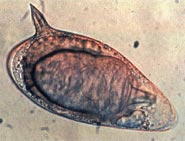
A planarian is one of many flatworms of the traditional class Turbellaria. It usually describes free-living flatworms of the order Tricladida (triclads), although this common name is also used for a wide number of free-living platyhelminthes. Planaria are common to many parts of the world, living in both saltwater and freshwater ponds and rivers. Some species are terrestrial and are found under logs, in or on the soil, and on plants in humid areas.

Digenea is a class of trematodes in the Platyhelminthes phylum, consisting of parasitic flatworms with a syncytial tegument and, usually, two suckers, one ventral and one oral. Adults commonly live within the digestive tract, but occur throughout the organ systems of all classes of vertebrates. Once thought to be related to the Monogenea, it is now recognised that they are closest to the Aspidogastrea and that the Monogenea are more closely allied with the Cestoda. Around 6,000 species have been described to date.
Spirometra is a genus of pseudophyllid cestodes that reproduce in canines and felines, but can also cause pathology in humans if infected. As an adult, this tapeworm lives in the small intestine of its definitive host and produces eggs that pass with the animal's feces. When the eggs reach water, the eggs hatch into coracidia which are eaten by copepods. The copepods are eaten by a second intermediate host to continue the life cycle. Humans can become infected if they accidentally eat frog legs or fish with the plerocercoid stage encysted in the muscle. In humans, an infection of Spirometra is termed sparganosis.

Echinococcus is a genus within cestoda, a parasitic class of the platyhelminthes phylum. Human echinococcosis is an infectious disease caused by the following species: E. granulosus, E. multilocularis, or E. vogeli.

A leafhopper is the common name for any species from the family Cicadellidae. These minute insects, colloquially known as hoppers, are plant feeders that suck plant sap from grass, shrubs, or trees. Their hind legs are modified for jumping, and are covered with hairs that facilitate the spreading of a secretion over their bodies that acts as a water repellent and carrier of pheromones. They undergo a partial metamorphosis, and have various host associations, varying from very generalized to very specific. Some species have a cosmopolitan distribution, or occur throughout the temperate and tropical regions. Some are pests or vectors of plant viruses and phytoplasmas. The family is distributed all over the world, and constitutes the second-largest hemipteran family, with at least 20,000 described species.

Parasitic worms, also known as helminths, are large macroparasites; adults can generally be seen with the naked eye. Many are intestinal worms that are soil-transmitted and infect the gastrointestinal tract. Other parasitic worms such as schistosomes reside in blood vessels.
Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, are the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda. Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodaria. All tapeworms are endoparasites of vertebrates, living in the digestive tract or related ducts. Examples are the pork tapeworm with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, and Moniezia expansa, the definitive hosts of which are ruminants.

Leucochloridium paradoxum, the green-banded broodsac, is a parasitic flatworm that uses gastropods as an intermediate host. It is typically found in land snails of the genus Succinea.

The red-cheeked parrot is a species of parrot in the family Psittaculidae found in Indonesia, Papua New Guinea and the tip of northern Australia. There are 17 subspecies currently recognized. It is a stocky short-tailed parrot with predominantly green plumage. It exhibits sexual dimorphism; the adult male has red cheeks and a mauve nape and top of head, while the female is duller with a brown head.

Worms are many different distantly related animals that typically have a long cylindrical tube-like body, no limbs, and no eyes. Worms vary in size from microscopic to over 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length for marine polychaete worms, 6.7 metres (22 ft) for the African giant earthworm, Microchaetus rappi, and 58 metres (190 ft) for the marine nemertean worm, Lineus longissimus. Various types of worm occupy a small variety of parasitic niches, living inside the bodies of other animals. Free-living worm species do not live on land, but instead, live in marine or freshwater environments, or underground by burrowing. In biology, "worm" refers to an obsolete taxon, vermes, used by Carolus Linnaeus and Jean-Baptiste Lamarck for all non-arthropod invertebrate animals, now seen to be paraphyletic. The name stems from the Old English word wyrm. Most animals called "worms" are invertebrates, but the term is also used for the amphibian caecilians and the slowworm Anguis, a legless burrowing lizard. Invertebrate animals commonly called "worms" include annelids, nematodes (roundworms), platyhelminthes (flatworms), marine nemertean worms, marine Chaetognatha, priapulid worms, and insect larvae such as grubs and maggots.

Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids - essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish parasites.

Klaus Rohde is a German biologist at the University of New England (UNE), Australia, known particularly for his work on marine parasitology, evolutionary ecology/zoogeography, and phylogeny/ultrastructure of lower invertebrates.

Hymenolepis microstoma, also known as the rodent tapeworm, is an intestinal dwelling parasite. Adult worms live in the bile duct and small intestines of mice and rats, and larvae metamorphose in the haemocoel of beetles. It belongs to the genus Hymenolepis; tapeworms that cause hymenolepiasis. H. microstoma is prevalent in rodents worldwide, but rarely infects humans.

The Bucephaloidea are a superfamily of trematode flatworms, belonging to the large group Digenea. Many species are endoparasites of mollusks and fish. The name Bucephalus meaning "ox head" was originally applied to the genus Bucephalus because of the horn-like appearance of the forked tail (furcae) of its cercaria larva. By what Manter calls a "curious circumstance", horns are also suggested by the long tentacles of adult worms.

A sucker in zoology refers to specialised attachment organ of an animal. It acts as an adhesion device in parasitic worms, several flatworms, cephalopods, certain fishes, amphibians, and bats. It is a muscular structure for suction on a host or substrate. In parasitic annelids, flatworms and roundworms, suckers are the organs of attachment to the host tissues. In tapeworms and flukes, they are a parasitic adaptation for attachment on the internal tissues of the host, such as intestines and blood vessels. In roundworms and flatworms they serve as attachment between individuals particularly during mating. In annelids, a sucker can be both a functional mouth and a locomotory organ. The structure and number of suckers are often used as basic taxonomic diagnosis between different species, since they are unique in each species. In tapeworms there are two distinct classes of suckers, namely "bothridia" for true suckers, and "bothria" for false suckers. In digeneal flukes there are usually an oral sucker at the mouth and a ventral sucker posterior to the mouth. Roundworms have their sucker just in front of the anus; hence it is often called a pre-anal sucker.
Raillietina cesticillus is a parasitic tapeworm of the family Davaineidae. Sometimes called 'broad-headed tapeworm', it infects the small intestine of chicken and occasionally other birds, such as guinea fowl and turkey, which are generally in close proximity to backyard poultry. It is a relatively harmless species among intestinal cestodes in spite of a high prevalence. In fact it probably is the most common parasitic platyhelminth in modern poultry facilities throughout the world.
Australamphilina elongata is a species of parasitic worm in the order Amphilinidea. Amphilinids are commonly considered to be tapeworms, yet differ from true tapeworms, subclass Eucestoda, because their bodies are unsegmented and are not divided into proglottids. It is an internal parasite of freshwater turtles including the eastern long-necked turtle. It is found in eastern Australia.