
Homotherium is an extinct genus of scimitar-toothed cat belonging to the extinct subfamily Machairodontinae that inhabited North America, Eurasia, and Africa during the Pliocene and Pleistocene epochs from around 4 million to 12,000 years ago. It was one of the last surviving members of the subfamily alongside the more famous sabertooth Smilodon, to which it was not particularly closely related. It was a large cat, comparable in size to a lion, functioning as an apex predator in the ecosystems it inhabited. In comparison to Smilodon, the canines of Homotherium were shorter, and it is suggested to have had a different ecology from Smilodon as a pursuit predator adapted to running down large prey in open habitats, with Homotherium also proposed to have likely engaged in cooperative hunting.

Smilodontini is an extinct tribe within the Machairodontinae or "saber-toothed cat" subfamily of the Felidae. The tribe is also known as the "dirk-toothed cats". They were endemic to South America, North America, Europe, Asia, and Africa during the Miocene to Pleistocene, from 10.3 mya—11,000 years ago, existing for approximately 10.3 million years.
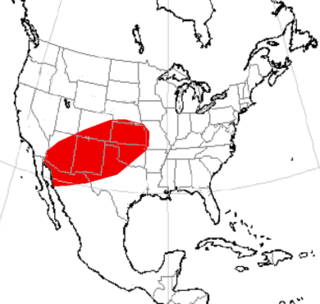
Adelphailurus is an extinct genus of metailurin machairodontine (saber-toothed) cat that inhabited western North America during the middle Pliocene. It is monotypic, containing only the species Adelphailurus kansensis.

The evolution of the horse, a mammal of the family Equidae, occurred over a geologic time scale of 50 million years, transforming the small, dog-sized, forest-dwelling Eohippus into the modern horse. Paleozoologists have been able to piece together a more complete outline of the evolutionary lineage of the modern horse than of any other animal. Much of this evolution took place in North America, where horses originated but became extinct about 10,000 years ago, before being reintroduced in the 15th century.

Buteogallus is a genus of birds of prey in the family Accipitridae. All members of this genus are essentially neotropical, but the distribution of a single species extends slightly into the extreme southwestern United States. Many of the species are fond of large crustaceans and even patrol long stretches of shore or riverbank on foot where such prey abounds, but some have a rather different lifestyle. Unlike many other genera of raptor, some members are referred to as "hawks", and others as "eagles".

Nannippus is an extinct genus of three-toed horse endemic to North America during the Miocene through Pleistocene, about 13.3—1.8 million years ago (Mya), living around 11.5 million years. This ancient species of three-toed horse grew up to 3.5 feet and weighed between 165 pounds to 199 pounds, which was around the same size as a domestic sheep.

Hesperotestudo is an extinct genus of tortoise native to North and Central America from the Early Miocene to the Late Pleistocene. Species of Hesperotestudo varied widely in size, with a large undescribed specimen from the Late Pleistocene of El Salvador reaching 150 cm (4.9 ft) in carapace length, larger than that of extant giant tortoises. Historically considered a subgenus of Geochelone, it is now considered to be distantly related to that genus. Its relationships with other tortoises are uncertain. The exposed areas of the bodies of Hesperotestudo species were extensively covered with large dermal ossicles, which in life were covered in keratin. It has been suggested that species of Hesperotestudo were relatively tolerant of cold weather. Hesperotestudo became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene roughly co-incident with the arrival of the first humans in North America. There is apparently a site in Florida where one individual may have been killed that some suggested were evidence of butchering, although others suggested that the turtle was neither cooked nor does a ledge that was found near it date at the same time as it.

Cynarctus is an extinct genus of the Borophaginae subfamily of canids native to North America. The genus was first founded by W. D. Matthew in 1901, based from a pair of lower jaws, Cynarctus saxitilis, found in the Pawnee Creek Beds of Colorado. It lived during the Middle to Late Miocene 16.0—10.3 mya, existing for approximately 5.7 million years. Fossils have been uncovered in Colorado, California, Maryland, western Nebraska, and Texas. It was likely an omnivore, and lacked the bone-cracking adaptations found in some later borophagines. Newer findings have proved the genus to be described as a large dog-like raccoon, a result from combining characteristics from Canidae with Procyonidae.

Eremotherium is an extinct genus of giant ground sloth in the family Megatheriidae. Eremotherium lived in southern North America, Central America, and northern South America from the Pliocene, around 5.3 million years ago, to the end of the Late Pleistocene, around 10,000 years ago. Eremotherium was one of the largest ground sloths, with a body size comparable to elephants, weighing around 4.5 tonnes and measuring about 6 metres (20 ft) long, slightly larger than its close relative Megatherium.

Paramylodon is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Mylodontidae endemic to North America during the Pliocene through Pleistocene epochs, living from around ~4.9 Mya–12,000 years ago.

Hemiauchenia is a genus of laminoid camelids that evolved in North America in the Miocene period about 10 million years ago. This genus diversified and entered South America in the Late Pliocene about three to two million years ago, as part of the Great American Biotic Interchange. The genus became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene. The monophyly of the genus has been considered questionable, with phylogenetic analyses finding the genus to paraphyletic or polyphyletic, with some species suggested to be more closely related to living lamines than to other Hemiauchenia species.

Woodward's eagle is an extinct species of black hawk that lived in North America and the Caribbean during the Late Pleistocene. Remains have been found in the La Brea Tar Pits in the United States and in Cuba. Despite the common name, the species is technically a gigantic variety of hawk as it is a member of the still extant black hawk genus, Buteogallus, within the Buteoninae subfamily that are chiefly referred to as hawks, and not the Aquilinae subfamily most eagles belong to.
Titanohierax gloveralleni, also known as the Bahama eagle, is a large species of extinct hawk from the Late Quaternary of the Caribbean. Remains of the animal have been found on multiple islands in The Bahamas. The animal is known from a handful of bones found across multiple islands, including a tarsometatarsus, partial metacarpal, and nearly complete right ulna. The animal was described based on the former two by Alexander Wetmore in 1937, with all other currently referred material being assigned by Storrs Olson and colleagues in 1982.
Hexing is an extinct genus of basal ornithomimosaur dinosaur known from the Early Cretaceous of northeastern China. It contains a single species, Hexing qingyi.

Diabolotherium is an extinct genus of megatheriine ground sloth, known from the Late Pleistocene of Peru. Unlike most other extinct mainland sloths, it seems to have been a climber, similar to extinct sloths from the Caribbean. Fossils of the genus were found at the coastal Piedra Escrita site and the Andean Casa del Diablo cave.

Capromeryx is an extinct genus of dwarf pronghorns (Antilocapridae) that originated in North America during the Pliocene about 5 million years ago. Antilocaprines began to decline in diversity during the Late Miocene, and the closest living relative and only surviving antilocaprine is the North American pronghorn.
Alligator hailensis, or Haile alligator, is a large, extinct species of Alligator known from the early Pleistocene of Florida. It is named after the town of Haile, Florida, where it was found. Its age and skeletal morphology is intermediate between the geologically older Alligator mefferdi and the modern American alligator, making it a transitional fossil.
Grabauornis is an extinct genus of enantiornitheans from the Early Cretaceous of China.
Asmodeus is an extinct genus of mammal, belonging to the order Notoungulata. It lived during the Late Oligocene, in what is today South America.
Simomylodon is an extinct genus of ground sloths from the family Mylodontidae. It lived from the Late Miocene to the Middle Pliocene of what is now Bolivia and Argentina, 5.3 to 2.8 million years ago. The most important find material comes from the central Altiplano in Bolivia and includes several skulls and dentition remains. Thus, the so far documented body skeleton is the best known and most significant of a Miocene representative of the Mylodontidae. On the basis of the remains, it can be concluded that it is a rather small member of the Mylodontidae. The construction of the limbs supports ground-dwelling locomotion, but this does not exclude occasional digging or climbing. The type and only known species is Simomylodon uccasamamensis.













