
Apogon is a large genus of fish in the family Apogonidae, the cardinalfishes. They are among the most common fish on coral reefs. Over 200 species have been classified in genus Apogon as members of several subgenera. Some of these subgenera, such as Ostorhinchus, have been elevated to genus status, leaving just over 50 species in the genus.

Anahoplites is a genus of rather involute, compressed hoplitid ammonites with flat sides, narrow flat or grooved venters, and flexious ribs or striae arising from weak umbilicle tubercles that end in fine dense ventrolateral nodes. The elements of their sutures are short, wide and jaggedy. Specimens of Annahoplites have diameters typically in the range of 4–6 centimetres (1.6–2.4 in) although some with diameters of as much as 19 centimetres (7.5 in) have been reported. The genus lived during the Cretaceous, from the Middle to the late Albian.
Austrotrachyceras is a genus of ammonite cephalopod, belonging to the order Ceratitida.
Okribites is a perisphinctoidean ammonite from the middle Jurassic of the Republic of Georgia. It is assigned to the family Parkinsoniidae, a group of strongly but evenly ribbed evolute, commonly discoidal ammonites. Parkinsonia is a related genus.

Hyperlioceras is an extinct genus of cephalopod included in the ammonitid family Graphoceratidae that lived during the Bajocian stage of the Middle Jurassic. The type species is Hyperlioceras discites

Hildoceras is a genus of ammonite from the Jurassic period in the family Hildoceratidae. The shells are characterized by a narrow discoidal evolute shape, keeled venter, concave ribs along the outer flanks, and a shallow spiral groove running along smooth inner flanks. Whorls slightly overlap, cross sections are compressed. The ventral keel is bordered on either side by a shallow groove. The genus was named by Alpheus Hyatt after Saint Hilda in 1876.

Bostrychoceras is a genus of heteromorph ammonite from the family Nostoceratidae. Fossils have been found in Late Cretaceous sediments in Europe and North America.
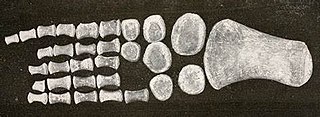
Ogmodirus is an extinct genus of plesiosaur found in the Cenomanian-Turonian Greenhorn Limestone of Kansas. The type species, O. martini, was named by Samuel Wendell Williston and Roy Lee Moodie in 1913.
Crenilepis is an extinct genus of prehistoric bony fish that lived in the seas of present-day Europe during the Anisian stage of the Middle Triassic epoch.

Clymeniida is an order of ammonoid cephalopods from the Upper Devonian characterized by having an unusual dorsal siphuncle. They measured about 4 cm (1.6 in) in diameter and are restricted to Europe, North Africa, and possibly Australia.

Odontochile is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Dalmanitidae.

Lytoceras is an ammonite genus that was extant during most of the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods, and is the type genus for the family Lytoceratidae. These cephalopods were fast-moving nektonic carnivores.
Pleuroacanthites is one of two genera included in the Early Jurassic Pleuroacanthitidae and sole representative of the subfamily Pleuroacanthitinae. The shell of Pleuroacanthites is very evolute, with numerous whorls subcircular in section becoming incipiently keeled in the adult. Early whorls have parabolic nodes, later whorls are covered with oblique line which form a long ventral sinus. Sutures have lytoceratid (moss-like) lobes but more or less phylloid saddle endings.

Neocomites is a genus of ammonite from the Lower Cretaceous, Berriasian to Hauterivian, and type genus for the Neocomitidae.

Puzosia is a genus of desmoceratid ammonites, and the type genus for the Puzosiinae, which lived during the middle part of the Cretaceous, from early Aptian to Maastrichtian. Sepkoski defines the range from Albian to Santonian. The generic name comes from the Serbian words "Puž" (snail) and "oce/ose" (axis), gaining its name from the shell's snail-like appearance.
Melchiorites is a desmoceratid ammonite genus included in the subfamily Puzosiinae. Member species are characterized by an essentially evolute shell in which the early whorls are smooth, with sinuous radial or oblique constrictions but in which later whorls have feeble intermediate ribs on the outer part of the sides and venter.

Hemihoplites is an extinct genus of ammonoid cephalopods belonging to the family Hemihoplitidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived in the Cretaceous period, from Hauterivian age to Barremian age.

Olcostephanus is an extinct ammonoid cephalopod genus belonging to the family Olcostephanidae. These fast-moving nektonic carnivores lived during the Cretaceous, from the upper Valanginian to the lower Hauterivian age.

Parkinsoniidae is a family of ammonites belonging to the order Ammonitida. The cephalopod family lived from the Bajocian stage to the Bathonian age of the Middle Jurassic.

Trachyceras is a genus belonging to the extinct subclass of cephalopods known as ammonites. Specifically it belongs in the order Ceratitida. They are distributed in Afghanistan, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Canada, China, Germany, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Italy, the Russian Federation, Slovenia, United States.














