The University of Tokyo is a public research university in Bunkyō, Tokyo, Japan. Founded in 1877 as the nation's first modern university by the merger of several pre-westernisation era institutions, its direct precursors include the Tenmongata, founded in 1684, and the Shoheizaka Institute.

Ichitaro is a Japanese word processor produced by JustSystems, a Japanese software company. Ichitaro occupies the second share in Japanese word-processing software, behind Microsoft Word. It is one of the main products of the company. Its proprietary file extension is ".JTD". ATOK, an IME developed by JustSystems, is bundled with Ichitaro.

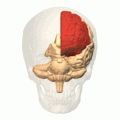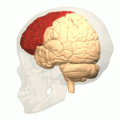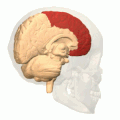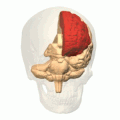
Analysis of Functional NeuroImages (AFNI) is an open-source environment for processing and displaying functional MRI data—a technique for mapping human brain activity.

Princess Tomohito of Mikasa is a member of the Japanese Imperial Family as the widow of Prince Tomohito of Mikasa.

Yukie Nakama is a Japanese actress, singer and former idol.

Ultraman Taro is the sixth show in the Ultra Series. Produced by Tsuburaya Productions, the series aired on Tokyo Broadcasting System from April 6, 1973, to April 5, 1974, with a total of 53 episodes.

GeGeGe no Kitarō (ゲゲゲの鬼太郎), originally known as Hakaba Kitarō, is a Japanese manga series created in 1960 by Shigeru Mizuki. It is best known for its popularization of the folklore creatures known as yōkai, a class of spirit-monster which all of the main characters belong to. This story was an early 20th-century Japanese folk tale performed on kamishibai. It has been adapted for the screen several times, as anime, live action, and video games. The word GeGeGe (ゲゲゲ) in the title is similar to Japanese sound symbolism for a cackling noise but refers to Mizuki's childhood nickname, a mispronounciation of his given name.

Tadashi Takagi, better known by his ring name Sanshiro Takagi, is a Japanese professional wrestler and promoter who works for the Japanese wrestling promotion CyberFight, where he serves as executive vice president. Takagi is the founder of DDT Pro-Wrestling, which is now part of the CyberFight umbrella. As a wrestler, Takagi's gimmick was that of a Stone Cold Steve Austin impersonator.

Tarō Okamoto was a Japanese artist, art theorist, and writer. He is particularly well known for his avant-garde paintings and public sculptures and murals, and for his theorization of traditional Japanese culture and avant-garde artistic practices.

Shippeitaro or Shippei Taro is the name of a helper dog in the Japanese fairy tale by the same name.

MakeHuman is a free and open source 3D computer graphics middleware designed for the prototyping of photorealistic humanoids. It is developed by a community of programmers, artists, and academics interested in 3D character modeling.

Masato Onodera, better known by the ring name Yamato, is a Japanese professional wrestler and former mixed martial artist currently signed to Dragongate, where he is the current and record six-time Open the Dream Gate Champion.

Kyō Kara Ore Wa!! is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Hiroyuki Nishimori. The manga was initially published in Shogakukan's shōnen manga magazine Shōnen Sunday Zōkan, running monthly from September 1988 to August 1990. The series was then transferred to Weekly Shōnen Sunday and serialized from September 1990 to November 1997. Its chapters were collected in 38 tankōbon volumes. A four-chapter manga sequel, titled Kyō Kara Ore wa!!: Yūsha Sagawa to Ano Futari-hen, was serialized in Shōnen Sunday S from November 2018 to February 2019 and collected in a single tankōbon volume.
The KO-DOpenweight Championship is a professional wrestling championship and the highest singles achievement in the DDT Pro-Wrestling (DDT) brand division of the Japanese promotion CyberFight. It is one of CyberFight's major titles, alongside the GHC Heavyweight Championship in Pro Wrestling Noah. The title was established in 2000, and Masao Orihara was the inaugural champion.

Keiichi Aichi was a Japanese physicist. He served as a professor of the physics department at the College of Science, Tohoku Imperial University.
OP Eiga (オーピー映画), also known as Ōkura Eiga (大蔵映画) or Okura Pictures, is the largest and one of the oldest independent Japanese studios which produce and distribute pink films. It was founded in 1961 by Mitsuru Ōkura, former president of film studio Shintōhō. Along with Shintōhō Eiga, Kantō, Million Film, and Kōji Wakamatsu's production studio, Ōkura was one of the most influential studios on the pink film genre. Among the many notable pink films released by the studio are Satoru Kobayashi's Flesh Market (1962), the first film in the pink film genre.
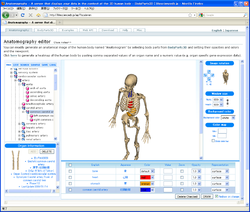
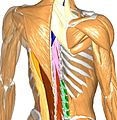
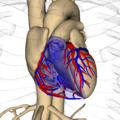
Computational human phantoms are models of the human body used in computerized analysis. Since the 1960s, the radiological science community has developed and applied these models for ionizing radiation dosimetry studies. These models have become increasingly accurate with respect to the internal structure of the human body.

Speed Power Gunbike is an action video game for the PlayStation, released exclusively in Japan on April 23, 1998, from publisher Sony Music Entertainment Japan. It is the first game developed by Inti Creates, a group of designers with similar goals and interests who had recently broken off from Capcom. The game was heavily inspired by science fiction anime of the 1980s.

Yoko Taro is a Japanese video game director and scenario writer. Starting his career at the now defunct game developer Cavia, his best-known work is on the action role-playing video game series Drakengard, and its spin-offs, Nier and Nier: Automata. Yoko was born in Nagoya, Aichi, and studied at the Kobe Design University in the 1990s. While he did not initially intend to pursue a career in video games, after working at Namco and Sony, he joined Cavia and became the director and scenario writer for the first Drakengard game. He has since worked extensively on every game in the series, and on mobile titles after becoming a freelancer following Cavia's absorption into AQ Interactive.

Ultraman Taro is the title character of the 1973 Ultra Series, Ultraman Taro. In the series, Ultraman Taro merged with Kotaro Higashi the latter loses his life during Astromons' rampage. After that, Kotaro joined the battle as a ZAT member and utilized Taro's power to fight against giant monsters while receiving assistance from either his fellow brothers-in-arms or his parents. In the final episode, Kotaro severed his connection to Taro and returned the Ultra Badge, as he wanted to continue living his life as a normal human. He is last seen traveling around the world.