
| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2020) |
The National Institute of Genetics ("Japanese Institute of Genetics") is a Japanese institution founded in 1949. [1]
It hosts the DNA Data Bank of Japan.

| | This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (February 2020) |
The National Institute of Genetics ("Japanese Institute of Genetics") is a Japanese institution founded in 1949. [1]
It hosts the DNA Data Bank of Japan.

Theodosius Grigorievich Dobzhansky was an American geneticist and evolutionary biologist. He was a central figure in the field of evolutionary biology for his work in shaping the modern synthesis. Born in the Russian Empire, Dobzhansky emigrated to the United States in 1927, aged 27.

Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) is a private, non-profit institution with research programs focusing on cancer, neuroscience, plant biology, genomics, and quantitative biology. It is located in Laurel Hollow on Long Island, New York.

Motoo Kimura was a Japanese biologist best known for introducing the neutral theory of molecular evolution in 1968. He became one of the most influential theoretical population geneticists. He is remembered in genetics for his innovative use of diffusion equations to calculate the probability of fixation of beneficial, deleterious, or neutral alleles. Combining theoretical population genetics with molecular evolution data, he also developed the neutral theory of molecular evolution in which genetic drift is the main force changing allele frequencies. James F. Crow, himself a renowned population geneticist, considered Kimura to be one of the two greatest evolutionary geneticists, along with Gustave Malécot, after the great trio of the modern synthesis, Ronald Fisher, J. B. S. Haldane, and Sewall Wright.

Victor Almon McKusick was an American internist and medical geneticist, and Professor of Medicine at the Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore. He was a proponent of the mapping of the human genome due to its use for studying congenital diseases. He is well known for his studies of the Amish. He was the original author and, until his death, remained chief editor of Mendelian Inheritance in Man (MIM) and its online counterpart Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM). He is widely known as the "father of medical genetics".

Bruce Nathan Ames is a prominent American biochemist. He is a professor of biochemistry and Molecular Biology Emeritus at the University of California, Berkeley, and was a senior scientist at Children's Hospital Oakland Research Institute (CHORI). Throughout his career, Dr. Ames has made significant contributions to understanding the mechanisms of mutagenesis and DNA repair. One of his most notable achievements is the invention of the Ames test, a widely used assay for easily and cheaply evaluating the mutagenicity of compounds. The test revolutionized the field of toxicology and has played a crucial role in identifying numerous environmental and industrial carcinogens.

The Bulgarian Academy of Sciences is the National Academy of Bulgaria, established in 1869.

Tomoko Ohta is a Japanese scientist and Professor Emeritus of the National Institute of Genetics. Ohta works on population genetics/molecular evolution and is known for developing the nearly neutral theory of evolution.

The Jackson Laboratory is an independent, non-profit biomedical research institution which was founded by Clarence Cook Little in 1929. It employs over 3,000 employees in Bar Harbor, Maine; Sacramento, California; Farmington, Connecticut; Shanghai, China; and Yokohama, Japan. The institution is a National Cancer Institute-designated Cancer Center and has NIH Centers of Excellence in aging and systems genetics. The stated mission of The Jackson Laboratory is "to discover the genetic basis for preventing, treating and curing human diseases, and to enable research and education for the global biomedical community."
The DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) is a biological database that collects DNA sequences. It is located at the National Institute of Genetics (NIG) in the Shizuoka prefecture of Japan. It is also a member of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration or INSDC. It exchanges its data with European Molecular Biology Laboratory at the European Bioinformatics Institute and with GenBank at the National Center for Biotechnology Information on a daily basis. Thus these three databanks contain the same data at any given time.

Takashi Gojobori is a Japanese molecular biologist, Vice-Director of the National Institute of Genetics (NIG) and the DNA Data Bank of Japan (DDBJ) at NIG, in Mishima, Japan. Gojobori is a Distinguished Professor at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Thuwal, Saudi Arabia. He is a Professor of Bioscience and Acting Director at the Computational Bioscience Research Center at KAUST.

The Graduate University for Advanced Studies, SOKENDAI is one of the national universities of Japan, headquartered in Shonan Village (湘南国際村) in the town of Hayama in Kanagawa Prefecture. Sōkendai (総研大), as it is generally called in its abbreviated form, was established in 1988, with Dr. Saburo Nagakura as its president. SOKENDAI is the first national university in Japan having offered exclusively graduate programs. Graduate students are trained at affiliated research institutes distributed around Japan and the world. It has both five-year doctoral programs for students with a bachelor's degree and three-year programs for those with a master's degree.

Japonica rice, sometimes called sinica rice, is one of the two major domestic types of Asian rice varieties. Japonica rice is extensively cultivated and consumed in East Asia, whereas in most other regions indica rice is the dominant type of rice. Japonica rice originated from Central China, where it was first domesticated along the Yangtze River basin approximately 9,500 to 6,000 years ago.
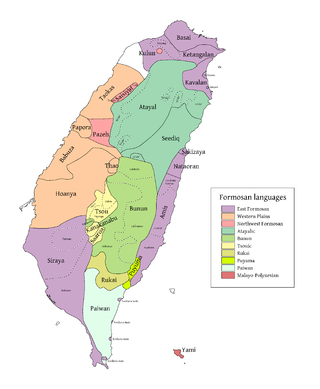
The Tsouic languages are three Formosan languages, Tsou proper and the Southern languages Kanakanavu and Saaroa. The Southern Tsouic languages of Kanakanavu and Saaroa have the smallest phonemic inventories out of all the Formosan languages, with each language having only 13 consonants and 4 vowels. These two languages are highly endangered, as many Southern Tsouic speakers are shifting to Bunun and Mandarin Chinese.

Mitsuhiro Yanagida ForMemRS is a Japanese molecular biologist known for research on cell cycle and chromosome structure using the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. He was elected as a foreign member of the Royal Society on 11 May 2000.

Hitoshi Kihara was a Japanese geneticist known for his work on the genetics of wheat.

Tasuku Honjo is a Japanese physician-scientist and immunologist. He won the 2018 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine and is best known for his identification of programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1). He is also known for his molecular identification of cytokines: IL-4 and IL-5, as well as the discovery of activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) that is essential for class switch recombination and somatic hypermutation.
Krishnaswamy Ramiah was an Indian agricultural scientist, geneticist, parliamentarian and the founder director of Central Rice Research Institute, Cuttack, credited with introducing systematic hybridisation programmes in rice breeding in India. The Government of India honoured him in 1957, with the award of Padma Shri, the fourth-highest Indian civilian award for his services to the nation and followed it up with the third-highest civilian honour of the Padma Bhushan in 1970.
Yo Takenaka was a Japanese plant geneticist and a Professor of Department of Cell Genetics, National Institute of Genetics. He is notable for researching the phylogenetic classification of cherry blossom. He discovered that Prunus × yedoensis is a crossbreed of two wild species of Japanese cherry; Prunus spachiana forma ascendens and Prunus speciosa by crossing experiments. He was also known as a researcher on Japanese morning glory and Nicotiana.

Dipankar Chatterji is an Indian molecular biologist and the Honorary Professor at Molecular Biophysics Unit, Indian Institute of Science, a multidisciplinary research institute under the Department of Science and Technology of the Government of India. He is known for his pioneering research on bacterial transcription. He is a recipient of Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize and is an elected fellow of all the major Indian science academies. The Government of India awarded him the fourth highest civilian honour of the Padma Shri, in 2016, for his contributions to science and engineering.