Related Research Articles

Mosquitoes are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae. The word "mosquito" is Spanish and Portuguese for "little fly". Mosquitoes have a slender segmented body, one pair of wings, one pair of halteres, three pairs of long hair-like legs, and elongated mouthparts.

Aedes is a genus of mosquitoes originally found in tropical and subtropical zones, but now found on all continents except Antarctica. Some species have been spread by human activity: Aedes albopictus, a particularly invasive species, was spread to the New World, including the United States, in the 1980s, by the used-tire trade.

Anopheles is a genus of mosquito first described and named by J. W. Meigen in 1818. About 460 species are recognised; while over 100 can transmit human malaria, only 30–40 commonly transmit parasites of the genus Plasmodium, which cause malaria in humans in endemic areas. Anopheles gambiae is one of the best known, because of its predominant role in the transmission of the most dangerous malaria parasite species – Plasmodium falciparum.

Wolbachia is a genus of intracellular bacteria that infects mainly arthropod species, including a high proportion of insects, and also some nematodes. It is one of the most common parasitic microbes and is possibly the most common reproductive parasite in the biosphere. Its interactions with its hosts are often complex, and in some cases have evolved to be mutualistic rather than parasitic. Some host species cannot reproduce, or even survive, without Wolbachia colonisation. One study concluded that more than 16% of neotropical insect species carry bacteria of this genus, and as many as 25 to 70% of all insect species are estimated to be potential hosts.

Ensembl genome database project is a scientific project at the European Bioinformatics Institute, which was launched in 1999 in response to the imminent completion of the Human Genome Project. Ensembl aims to provide a centralized resource for geneticists, molecular biologists and other researchers studying the genomes of our own species and other vertebrates and model organisms. Ensembl is one of several well known genome browsers for the retrieval of genomic information.

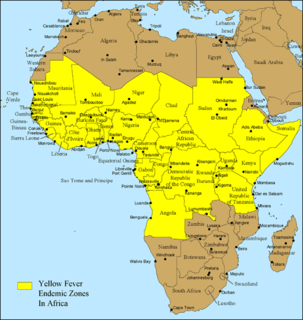
Aedes aegypti, the yellow fever mosquito, is a mosquito that can spread dengue fever, chikungunya, Zika fever, Mayaro and yellow fever viruses, and other disease agents. The mosquito can be recognized by black and white markings on its legs and a marking in the form of a lyre on the upper surface of its thorax. This mosquito originated in Africa, but is now found in tropical, subtropical and temperate regions throughout the world.

The Anopheles gambiae complex consists of at least seven morphologically indistinguishable species of mosquitoes in the genus Anopheles. The complex was recognised in the 1960s and includes the most important vectors of malaria in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly of the most dangerous malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum. It is one of the most efficient malaria vectors known. The An. gambiae mosquito additionally transmits Wuchereria bancrofti which causes lymphatic filariasis, a symptom of which is elephantiasis.
Paratransgenesis is a technique that attempts to eliminate a pathogen from vector populations through transgenesis of a symbiont of the vector. The goal of this technique is to control vector-borne diseases. The first step is to identify proteins that prevent the vector species from transmitting the pathogen. The genes coding for these proteins are then introduced into the symbiont, so that they can be expressed in the vector. The final step in the strategy is to introduce these transgenic symbionts into vector populations in the wild. One use of this technique is to prevent mortality for humans from insect-borne diseases. Preventive methods and current controls against vector-borne diseases depend on insecticides, even though some mosquito breeds may be resistant to them. There are other ways to fully eliminate them. “Paratransgenesis focuses on utilizing genetically modified insect symbionts to express molecules within the vector that are deleterious to pathogens they transmit.” The acidic bacteria Asaia symbionts are beneficial in the normal development of mosquito larvae; however, it is unknown what Asais symbionts do to adult mosquitoes.

The discipline of medical entomology, or public health entomology, and also veterinary entomology is focused upon insects and arthropods that impact human health. Veterinary entomology is included in this category, because many animal diseases can "jump species" and become a human health threat, for example, bovine encephalitis. Medical entomology also includes scientific research on the behavior, ecology, and epidemiology of arthropod disease vectors, and involves a tremendous outreach to the public, including local and state officials and other stake holders in the interest of public safety.

Ixodes scapularis is commonly known as the deer tick or black-legged tick, and in some parts of the US as the bear tick. It is a hard-bodied tick found in the eastern and northern Midwest of the United States as well as in southeastern Canada. It is a vector for several diseases of animals, including humans and is known as the deer tick owing to its habit of parasitizing the white-tailed deer. It is also known to parasitize mice, lizards, migratory birds, etc. especially while the tick is in the larval or nymphal stage.
Lysinibacillus sphaericus is a Gram-positive, mesophilic, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found on soil. It can form resistant endospores that are tolerant to high temperatures, chemicals and ultraviolet light and can remain viable for long periods of time. It is of particular interest to the World Health Organization due to the larvicide effect of some strains against two mosquito genera, more effective than Bacillus thuringiensis, frequently used as a biological pest control. L. sphaericus cells in a vegetative state are also effective against Aedes aegypti larvae, an important vector of yellow fever and dengue viruses.
Mosquito-borne diseases or mosquito-borne illnesses are diseases caused by bacteria, viruses or parasites transmitted by mosquitoes. Nearly 700 million people get a mosquito-borne illness each year resulting in over one million deaths.
Rickettsia felis is a species of bacterium, the pathogen that causes cat-flea typhus in humans. In cats the disease is known as flea-borne spotted fever. Rickettsia felis also is regarded as the causative organism of many cases of illnesses generally classed as fevers of unknown origin in humans in Africa.

Culex quinquefasciatus, commonly known as the southern house mosquito, is a medium-sized mosquito found in tropical and subtropical regions of the world. It is a vector of Wuchereria bancrofti, avian malaria, and arboviruses including St. Louis encephalitis virus, Western equine encephalitis virus, Zika virus and West Nile virus. It is taxonomically regarded as a member of the Culex pipiens species complex. Its genome was sequenced in 2010, and was shown to have 18,883 protein-coding genes.

OrthoDB presents a catalog of orthologous protein-coding genes across vertebrates, arthropods, fungi, plants, and bacteria. Orthology refers to the last common ancestor of the species under consideration, and thus OrthoDB explicitly delineates orthologs at each major radiation along the species phylogeny. The database of orthologs presents available protein descriptors, together with Gene Ontology and InterPro attributes, which serve to provide general descriptive annotations of the orthologous groups, and facilitate comprehensive orthology database querying. OrthoDB also provides computed evolutionary traits of orthologs, such as gene duplicability and loss profiles, divergence rates, sibling groups, and gene intron-exon architectures.
Anopheles sinensis is a species of mosquito that transmits malaria as well as lymphatic filariasis. It is regarded as the most important vector of these human parasitic diseases in Southeast Asia. It is the primary vector of vivax malaria in many regions. In China it also transmits the filalarial parasite, and arthropod roundworm. In Japan it is also a vector of a roundworm Setaria digitata in sheep and goats.

Christos Louis, nicknamed Kitsos, is a Greek Molecular Geneticist. He graduated from the Medical School of the University of Marburg in 1974 and joined the team of Prof. C.E. Sekeris, first at Marburg and then at the German Cancer Research Center Heidelberg, obtaining his doctoral degree in Cell biology from Heidelberg University in 1977. His work focuses on Genomics and Bioinformatics of insects and vector-borne/tropical diseases.
Spondweni virus is an arbovirus, or arthropod-borne virus, which is a member of the family Flaviviridae and the genus Flavivirus. It is part of the Spondweni serogroup which consists of the Sponweni virus and the Zika virus (ZIKV). The Spondweni virus was first isolated in Nigeria in 1952, and ever since, SPONV transmission and activity have been reported throughout Africa. Its primary vector of transmission is the sylvatic mosquito Aedes circumluteolus, though it has been isolated from several different types of mosquito. Transmission of the virus into humans can lead to a viral infection known as Spondweni fever, with symptoms ranging from headache and nausea to myalgia and arthralgia. However, SPONV is phylogenetically close to the ZIKV, it is commonly misdiagnosed as ZIKV along with other viral illnesses.
Eilat virus (EILV) is a unique Alphavirus which is known mainly for its host range restriction generally to insects by means of RNA replication. The virus is found in the Negev desert. It is incapable of infecting vertebrate cells, differentiating it from other alphaviruses.
References
- ↑ Lawson, D; Arensburger, P; Atkinson, P; Besansky, NJ; Bruggner, RV; Butler, R; Campbell, KS; Christophides, GK; et al. (2007). "VectorBase: a home for invertebrate vectors of human pathogens". Nucleic Acids Research. 35 (Database issue): D503–5. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl960. PMC 1751530 . PMID 17145709.
- ↑ Lawson, D; Arensburger, P; Atkinson, P; Besansky, NJ; Bruggner, RV; Butler, R; Campbell, KS; Christophides, GK; et al. (2009). "VectorBase: a data resource for invertebrate vector genomics". Nucleic Acids Research. 37 (Database issue): D583–7. doi:10.1093/nar/gkn857. PMC 2686483 . PMID 19028744.
- ↑ Nene, V; Wortman, JR; Lawson, D; Haas, B; Kodira, C; Tu, ZJ; Loftus, B; Xi, Z; et al. (2007). "Genome sequence of Aedes aegypti, a major arbovirus vector". Science. 316 (5832): 1718–23. Bibcode:2007Sci...316.1718N. doi:10.1126/science.1138878. PMC 2868357 . PMID 17510324.
- ↑ Holt, RA; Subramanian, GM; Halpern, A; Sutton, GG; Charlab, R; Nusskern, DR; Wincker, P; Clark, AG; et al. (2002). "The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae". Science. 298 (5591): 129–49. Bibcode:2002Sci...298..129H. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.149.9058 . doi:10.1126/science.1076181. PMID 12364791. S2CID 4512225.
- ↑ Topalis, P; Tzavlaki, C; Vestaki, K; Dialynas, E; Sonenshine, DE; Butler, R; Bruggner, RV; Stinson, EO; et al. (2008). "Anatomical ontologies of mosquitoes and ticks, and their web browsers in VectorBase". Insect Molecular Biology. 17 (1): 87–9. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2583.2008.00781.x. PMID 18237287. S2CID 8618269.