
Ascaris lumbricoides is a large parasitic roundworm of the genus Ascaris. It is the most common parasitic worm in humans. An estimated 807 million–1.2 billion people are infected with A. lumbricoides worldwide. People living in tropical and subtropical countries are at greater risk of infection. Infection by Ascaris lumbricoides is known as ascariasis.

Trichuriasis, also known as whipworm infection, is an infection by the parasitic worm Trichuris trichiura (whipworm). If the infection is only with a few worms, there are often no symptoms. In those who are infected with many worms, there may be abdominal pain, fatigue and diarrhea. The diarrhea sometimes contains blood. Infections in children may cause poor intellectual and physical development. Low red blood cell levels may occur due to loss of blood.

Hymenolepiasis is infestation by one of two species of tapeworm: Hymenolepis nana or H. diminuta. Alternative names are dwarf tapeworm infection and rat tapeworm infection. The disease is a type of helminthiasis which is classified as a neglected tropical disease.

Gnathostomiasis, also known as larva migrans profundus, is the human infection caused by the nematode Gnathostoma spinigerum and/or Gnathostoma hispidum, which infects vertebrates.

Dipylidium caninum, also called the flea tapeworm, double-pored tapeworm, or cucumber tapeworm is a cyclophyllid cestode that infects organisms afflicted with fleas and canine chewing lice, including dogs, cats, and sometimes human pet-owners, especially children.

Hymenolepis diminuta, also known as rat tapeworm, is a species of Hymenolepis tapeworm that causes hymenolepiasis. It has slightly bigger eggs and proglottids than H. nana and infects mammals using insects as intermediate hosts. The adult structure is 20 to 60 cm long and the mature proglottid is similar to that of H. nana, except it is larger.

Paragonimiasis is a food-borne parasitic disease caused by several species of lung flukes belonging to genus Paragonimus. Infection is acquired by eating crustaceans such as crabs and crayfishes which host the infective forms called metacercariae, or by eating raw or undercooked meat of mammals harboring the metacercariae from crustaceans.

Eucestoda, commonly referred to as tapeworms, is the larger of the two subclasses of flatworms in the class Cestoda. Larvae have six posterior hooks on the scolex (head), in contrast to the ten-hooked Cestodaria. All tapeworms are endoparasites of vertebrates, living in the digestive tract or related ducts. Examples are the pork tapeworm with a human definitive host, and pigs as the secondary host, and Moniezia expansa, the definitive hosts of which are ruminants.
Spirometra erinaceieuropaei is a parasitic tapeworm that infects domestic animals and humans. The medical term for this infection in humans and other animals is sparganosis. Morphologically, these worms are similar to other worms in the genus Spirometra. They have a long body consisting of three sections: the scolex, the neck, and the strobilia. They have a complex life cycle that consists of three hosts, and can live in varying environments and bodily tissues. Humans can contract this parasite in three main ways. Historically, humans are considered a paratenic host; however, the first case of an adult S. erinaceieuropaei infection in humans was reported in 2017. Spirometra tapeworms exist worldwide and infection is common in animals, but S. erinaceieuropaei infections are rare in humans. Treatment for infection typically includes surgical removal and anti-worm medication.
Sparganosis is a parasitic infection caused by the plerocercoid larvae of the genus Spirometra including S. mansoni, S. ranarum, S. mansonoides and S. erinacei. It was first described by Patrick Manson in 1882, and the first human case was reported by Charles Wardell Stiles from Florida in 1908. The infection is transmitted by ingestion of contaminated water, ingestion of a second intermediate host such as a frog or snake, or contact between a second intermediate host and an open wound or mucous membrane. Humans are the accidental hosts in the life cycle, while dogs, cats, and other mammals are definitive hosts. Copepods are the first intermediate hosts, and various amphibians and reptiles are second intermediate hosts.
Angiostrongyliasis is an infection by a roundworm of the Angiostrongylus type. Symptoms may vary from none to mild, to meningitis.

Angiostrongylus cantonensis is a nematode (roundworm) parasite that causes angiostrongyliasis, an infection that is the most common cause of eosinophilic meningitis in Southeast Asia and the Pacific Basin. The nematode commonly resides in the pulmonary arteries of rats, giving it the common name rat lungworm. Snails and slugs are the primary intermediate hosts, where larvae develop until they are infectious.

Toxascaris leonina is a common parasitic roundworm found in dogs, cats, foxes, and related host species. T. leonina is an ascarid nematode, a worldwide distributed helminth parasite which is in a division of eukaryotic parasites that, unlike external parasites such as lice and fleas, live inside their host. The definitive hosts of T. leonina include canids and felines (cats), while the intermediate hosts are usually rodents, such as mice or rats. Infection occurs in the definitive host when the animal eats an infected rodent. While T. leonina can occur in either dogs or cats, it is far more frequent in cats.
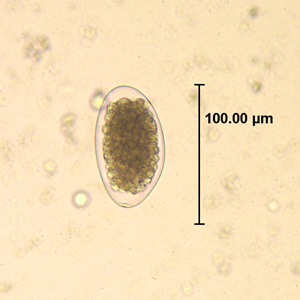
Trichostrongylus species are nematodes, which are ubiquitous among herbivores worldwide, including cattle, sheep, donkeys, goats, deer, and rabbits. At least 10 Trichostrongylus species have been associated with human infections. Infections occur via ingestion of infective larvae from contaminated vegetables or water. Epidemiological studies indicate a worldwide distribution of Trichostrongylus infections in humans, with the highest prevalence rates observed in individuals from regions with poor sanitary conditions, in rural areas, or who are farmers / herders. Human infections are most prevalent in the Middle East and Asia, with a worldwide estimated prevalence of 5.5 million people.

Angiostrongylus vasorum, also known as French heartworm, is a species of parasitic nematode in the family Metastrongylidae. It causes the disease canine angiostrongylosis in dogs. It is not zoonotic, that is, it cannot be transmitted to humans.

Baylisascaris procyonis, also known by the common name raccoon roundworm, is a roundworm nematode, found ubiquitously in raccoons, the definitive hosts. It is named after H. A. Baylis, who studied them in the 1920s–30s, and Greek askaris. Baylisascaris larvae in paratenic hosts can migrate, causing larva migrans. Baylisascariasis as the zoonotic infection of humans is rare, though extremely dangerous due to the ability of the parasite's larvae to migrate into brain tissue and cause damage. Concern for human infection has been increasing over the years due to the urbanization of rural areas, resulting in the increase in proximity and potential human interaction with raccoons.
Taenia serialis, also known as a canid tapeworm, is found within canines such as foxes and dogs. Adult T. serialis are parasites of carnivores, particularly dogs, with herbivorous lagomorph mammals such as rabbits and hares, serving as intermediate hosts. In definitive hosts, T. serialis is acquired by eating tissues from a variety of intermediate hosts. Accidental infection of humans though, can occur when eggs are ingested from food or water contaminated with dog feces and the human then becomes the T. serialis intermediate host.

Gastropod-borne parasitic diseases (GPDs) are a group of infectious diseases that require a gastropod species to serve as an intermediate host for a parasitic organism that can infect humans upon ingesting the parasite or coming into contact with contaminated water sources. These diseases can cause a range of symptoms, from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening conditions, with them being prevalent in many parts of the world, particularly in developing regions. Preventive measures such as proper sanitation and hygiene practices, avoiding contact with infected gastropods and cooking or boiling food properly can help to reduce the risk of these diseases.

Cat worm infections, the infection of cats (Felidae) with parasitic worms, occur frequently. Most worm species occur worldwide in both domestic and other cats, but there are regional, species and lifestyle differences in the frequency of infestation. According to the classification of the corresponding parasites in the zoological system, infections can be divided into those caused by nematode and flatworms - in the case of the latter, mainly cestoda and trematoda - while other strains are of no veterinary significance. While threadworms usually do not require an intermediate host for their reproduction, the development cycle of flatworms always proceeds via alternate hosts.
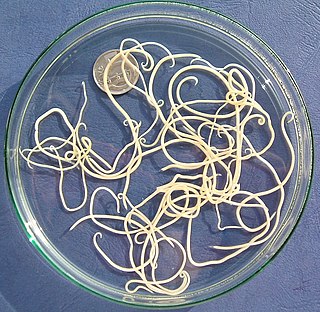
Nematode infection in dogs - the infection of dogs with parasitic nemamotodes - are, along with tapeworm infections and infections with protozoa, frequent parasitoses in veterinary practice. Nematodes, as so-called endoparasites, colonize various internal organs - most of them the digestive tract - and the skin. To date, about 30 different species of nematode have been identified in domestic dogs; they are essentially also found in wild dog species. However, the majority of them often cause no or only minor symptoms of disease in adult animals. The infection therefore does not necessarily have to manifest itself in a worm disease (helminthosis). For most nematodes, an infection can be detected by examining the feces for eggs or larvae. Roundworm infection in dogs and the hookworm in dogs is of particular health significance in Central Europe, as they can also be transmitted to humans (zoonosis). Regular deworming can significantly reduce the frequency of infection and thus the risk of infection for humans and dogs.














