
Molybdopterins are a class of cofactors found in most molybdenum-containing and all tungsten-containing enzymes. Synonyms for molybdopterin are: MPT and pyranopterin-dithiolate. The nomenclature for this biomolecule can be confusing: Molybdopterin itself contains no molybdenum; rather, this is the name of the ligand that will bind the active metal. After molybdopterin is eventually complexed with molybdenum, the complete ligand is usually called molybdenum cofactor.
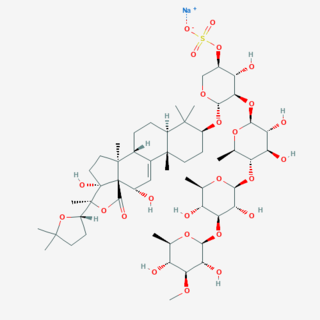
The holothurins are a group of toxins originally isolated from the sea cucumber Actinopyga agassizii. They are contained within clusters of sticky threads called Cuvierian tubules which are expelled from the sea cucumber as a mode of self-defence. The holothurins belong to the class of compounds known as saponins and are anionic surfactants which can cause red blood cells to rupture. The holothurins can be toxic to humans if ingested in high amounts.
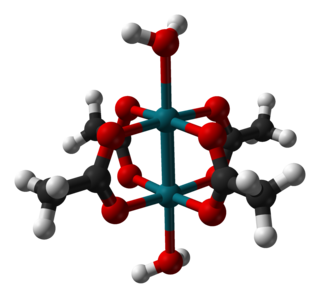
Rhodium(II) acetate is the coordination compound with the formula Rh2(AcO)4, where AcO− is the acetate ion (CH
3CO−
2). This dark green powder is slightly soluble in polar solvents, including water. It is used as a catalyst for cyclopropanation of alkenes. It is a widely studied example of a transition metal carboxylate complex.
In chemistry, methanetetracarboxylate is a tetravalent anion with formula C
5O4−
8 or C(COO−)4. It has four carboxylate groups attached to a central carbon atom; so it has the same carbon backbone as neopentane. It is an oxocarbon anion, that is, consists only of carbon and oxygen.

Lithium cyanide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula LiCN. It is a toxic, white colored, hygroscopic, water-soluble salt that finds only niche uses.
Sodium bromite is a sodium salt of bromous acid. Its trihydrous form has been isolated in crystal form. It is used by the textile refining industry as a desizing agent for oxidative starch removal.
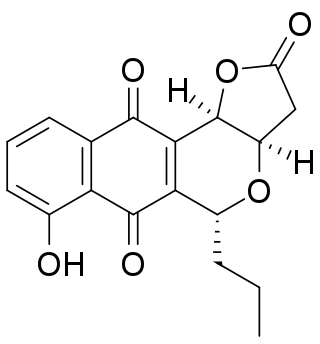
Frenolicin B is an antibiotic and antitumor agent with the molecular formula C18H16O6 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces roseofulvus. Frenolicin B is a selective inhibitor of glutaredoxin 3 and peroxiredoxin 1.
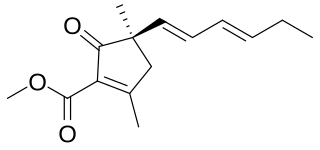
Gregatin B is a metabolite of the fungi Cephalosporium gregatum and Aspergillus panamensis with the molecular formula C14H18O4 Gregatin B is a weak antibiotic. Gregatin B was discovered on 1982.
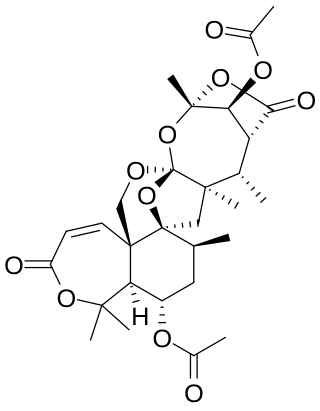
Fumigatonin is a meroterpenoid of the fungi Aspergillus fumigatus with the molecular formula C28H38O11.

Phlebiarubrone is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C19H12O4 which is produced by the fungi Punctularia strigosozonata.

Folipastatin is a depsidone phospholipase A2 inhibitor which is produced by the fungi Aspergillus unguis and Wicklowia aquatica. Folipastatin has the molecular formula C23H24O5.

Geodin is an antibiotic against Gram-positive bacteria with the molecular formula C17H8CL2O7. Geodin is produced by the fungus Aspergillus terreus.

Abikoviromycin is an antiviral antibiotic piperidine alkaloid with the molecular formula C10H11ON which is produced by the bacteria Streptomyces abikoensis and Streptomyces rubescens.

Aurantimycin A is an depsipeptide antibiotic with the molecular formula C38H64N8O14. Aurantimycin A is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces aurantiacus. Aurantimycin A also show cytotoxic properties.
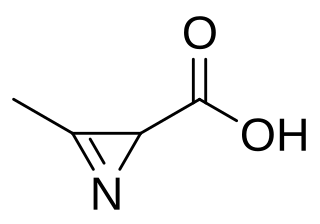
Azirinomycin is an antibiotic azirine derivative with the molecular formula C4H5NO2 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces aureus. Azirinomycin was first isolated in 1971. Azirinomycin is toxic and therefore it cannot not be used in human medicine.
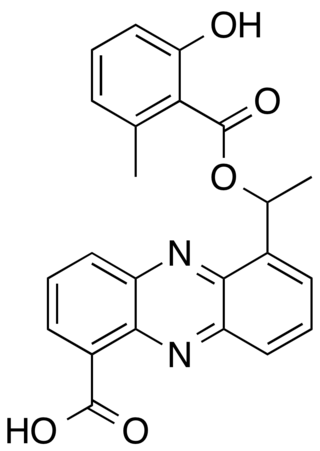
Saphenamycin is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C23H18N2O5 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces canarius and other Streptomyces species.

Amphomycin is an antibiotic with the molecular formula C58H91N13O20 which is produced by the bacterium Streptomyces canus.

Pyrrolostatin is a lipid peroxidation inhibitor with the molecular formula C15H21NO2 which has been isolated from the bacterium Streptomyces chrestomyceticus.
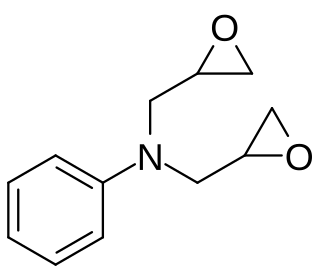
Diglycidyl aniline is an aromatic organic chemical in the glycidyl compound family. It is used to reduce the viscosity of epoxy resin systems. It has the empirical formula C12H15NO2 and the IUPAC name is N,N-bis(oxiran-2-ylmethyl)aniline. The CAS number is 2095-06-9. It is REACH registered in Europe with the EC number 218-259-5. A key use is in the viscosity reduction of epoxy resin systems functioning as a reactive diluent.


















