
Annona sericea is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname, Trinidad-Tobago and Venezuela. Michel Félix Dunal, the French botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the silky hairs on its branches and leaves. In Brazil its common name is Aratincum do Para.
Annona acutiflora is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to Brazil. Carl Friedrich Philipp von Martius, the German botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the inner petals which come to a sharp point.
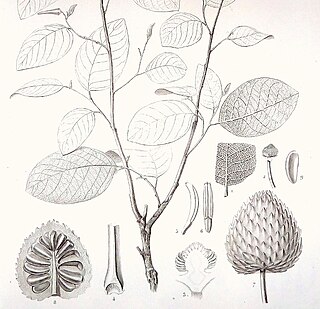
Annona bullata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Cuba. Achille Richard, the French botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the bubbled appearance of the spaces between the fine network of veins in the leaves.

Annona cascarilloides is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is endemic to Cuba. According to William Edwin Safford, the species was named it after the pattern of its leaf veins which resemble species of a different genus, that at the time Safford was writing was called Cascarilla, but is now synonymous with the genera Croton and Ladenbergia. Despite this assertion by Safford, August Grisebach, the German botanist who first formally described the species, makes no mention of Cascarilla in his 1866 entry.

Annona crassivenia is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Cuba. William Edwin Safford, the American botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the thick tertiary veins that interconnect the secondary veins of its leaves.

Annona jahnii is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to the Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela. William Edwin Safford, the American botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the Venezuelan scientist, explorer and mountain climber Alfredo Jahn.

Annona macroprophyllata is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras and Mexico. John Donnell Smith, the American botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its large leaves.
Annona nutans is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil and Paraguay. Robert Elias Fries, the Swedish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its recurved peduncles which give the flowers a nodding appearance.

Annona paludosa is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Brazil, French Guiana, Guyana, Suriname and Venezuela. Jean Baptiste Christophore Fusée Aublet, the French pharmacist and botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its swampy habitat.
Annona stenophylla is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Tanzania and Zambia. Adolf Engler and Ludwig Diels, the German botanists who first formally described the species, named it after its narrow leaves.
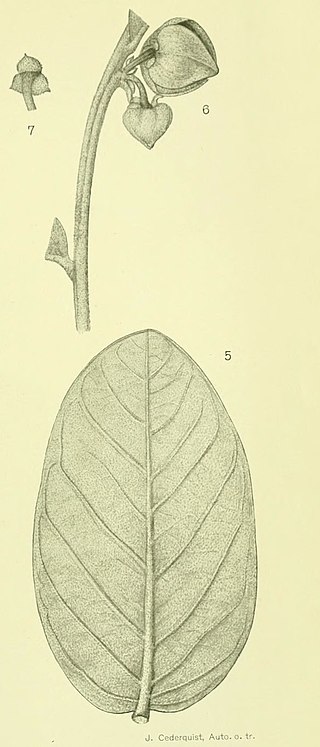
Annona tomentosa is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Bolivia and Brazil. Robert Elias Fries, the Swedish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after the dense woolly hairs covering its branches and leaves.

Asimina pygmaea, the dwarf pawpaw or gopher berry, is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Florida and Georgia in the United States. William Bartram, the American naturalist who first formally described the species using the basionym Annona pygmaea, named it after its dwarfed stature.

Fusaea longifolia is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, Guyana, Peru, Suriname and Venezuela. Jean Baptiste Christophore Fusée Aublet, the French botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Annona longifolia, named it after its long-leaved foliage.

Goniothalamus monospermus is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Fiji. Asa Gray, the American botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Richella monosperma, named it after its fruit's solitary seed which have notable wing-like fringes.
Goniothalamus nitidus is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Borneo. Elmer Drew Merrill, the American botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its shining leaves.
Annona rigida is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Brazil and Colombia. Robert Elias Fries, the Swedish botanist who first formally described the species, named it after its rigid leaves.

Pseuduvaria rugosa is a species of plant in the family Annonaceae. It is native to Java, Laos, the Lesser Sunda Islands, Peninsular Malaysia, Myanmar, the Nicobar Islands, Sumatra and Thailand. Carl Ludwig Blume, the botanist who first formally described the species under the basionym Uvaria rugosa, named it after its wrinkled fruit.
Annona cherimolioides is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to Colombia and Ecuador. José Jerónimo Triana and Jules Émile Planchon, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after its resemblance to another Annona species A. cherimoya.
Annona quinduensis is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to Colombia and Ecuador. Carl Sigismund Kunth, the botanists who first formally described the species, named it after Quindío, a department of Colombia, where the specimen he examined was collected.

Uvariastrum hexaloboides is a species of plant in the Annonaceae family. It is native to Tanzania, Zambia and Zaire. Robert Elias Fries, the botanist who first formally described the species using the basionym Uvaria hexaloboides, named it after a different species Hexalobus monopetalus which he thought its flowers and vegetative parts resembled.














