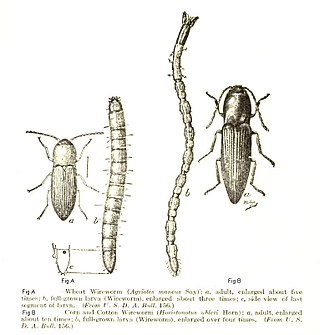
Elateridae or click beetles are a family of beetles. Other names include elaters, snapping beetles, spring beetles or skipjacks. This family was defined by William Elford Leach (1790–1836) in 1815. They are a cosmopolitan beetle family characterized by the unusual click mechanism they possess. There are a few other families of Elateroidea in which a few members have the same mechanism, but most elaterid subfamilies can click. A spine on the prosternum can be snapped into a corresponding notch on the mesosternum, producing a violent "click" that can bounce the beetle into the air. Clicking is mainly used to avoid predation, although it is also useful when the beetle is on its back and needs to right itself. There are about 9300 known species worldwide, and 965 valid species in North America.

The Oriental beetle is a species of shining leaf chafer in the family Scarabaeidae. It is a beetle about 0.7 - 1.1 cm long, with mottled, metallic brown- and black-colored elytra and a similarly colored thorax and head during the adult stage. It is sometimes confused with the larger and more colorful Japanese beetle. During the larval stage, the Oriental beetle can be identified by the parallel line raster pattern.

Anomala is a genus of shining leaf chafers in the family of beetles known as Scarabaeidae. There are at least 1,200 described species in Anomala.

Dynastes is a genus of large beetles belonging to the family Scarabaeidae. They occur in the Nearctic realm and in the Neotropical realm, from the United States to Brazil; four North American species, three with distributions extending from Central America either north or south, and two species endemic to South America.

The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Augustine', originally called 'Augustine Ascending', was cloned by Archie M. Augustine of the Augustine Nursery of Bloomington, Illinois, from a nursery seedling planted in 1927 in Normal, Illinois, and found to be columnar in habit.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Washington', of unknown derivation, was sourced from Princeton Nurseries, Princeton, New Jersey, from 1985, and planted on the National Mall, Washington D.C. It was then selected by H. V. Wester of the U. S. National Park Service and introduced for trials as NPS 3-178. Santamour pointed out that as the historic Washington Elm had been propagated as 'Washington', NPS 3-178, if ever registered as a cultivar, would need a different cultivar name.

The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Lewis & Clark' is a development from the North Dakota State University (NDSU) Research Foundation breeding programme, released in 2004 to commemorate the 200th anniversary of the eponymous expedition. The cultivar was cloned from a tree discovered in 1994 along the Wild Rice River south west of Fargo, North Dakota, where all those around it had succumbed to Dutch elm disease; the tree remains in perfect health (2008). Prairie Expedition proved only moderately successful in the US National Elm Trial, averaging a survival rate of 62.6% overall, potentially due to environmental factors rather than susceptibility to Dutch elm disease.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Lake City' is a semi-fastigiate form cloned in the early 1920s from a ten-year old seedling found growing outside the Lutheran parsonage, Lake City, Minnesota, and released by the Lake City Nurseries there in 1931. The Nurseries published a nine-page booklet on it in 1932, 'The Lake City Elm', with full description, a photograph of the original tree, and commendatory letters. It was later described by Wyman in Trees Magazine 3 (4): 13, 1940.
The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Beebe's Weeping' was propagated from a tree growing in the wild at Galena, Illinois, by Mr. E. Beebe in the mid-19th century. Thomas Meehan, who had received cuttings and called it 'Weeping Slippery Elm' before the flowers revealed that it was not Ulmus fulva, suggested the name 'Beebe's Weeping Elm', as there were already U. americana clones called 'Pendula'. In the early 20th century it was marketed, however, as Ulmus 'American Galena Weeping', "American Weeping Elm", by the Klehm nursery of Arlington Heights, Illinois.
The American elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Ascendens', 'Upright American Elm', was cloned c.1910 by Bernard H. Slavin, Superintendent of Parks, Rochester, New York, from a tree growing in Seneca Park, Rochester, and named in 1927 for its narrow oval form.

The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Columnaris' was propagated by R. E. Horsey of the Rochester N.Y. Parks Department from a tree found by Mr John Dunbar at Conesus Lake, New York, in 1911, and originally described as a forma, Ulmus americana L. f. columnaris, f. nov.Rehder (1922). It was the earliest of a number of compact, columnar American elm cultivars, to be followed by 'Ascendens' and 'Augustine Ascendening'.

Zombia antillarum, commonly known as the zombie palm, is a species of palm tree and the only member of the genus Zombia. It is endemic to the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles. Usually found in dry, hilly areas of northern and southern Haiti and the northwest of the Dominican Republic, Z. antillarum is a relatively short fan palm with clustered stems and a very distinctive appearance caused by its persistent spiny leaf sheaths. Threatened by habitat destruction in Haiti, Z. antillarum is a popular ornamental species due to its distinctive appearance, low maintenance requirements and salt tolerance.
The American Elm cultivar Ulmus americana 'Iowa State' was cloned in the 1980s from a tree discovered by Professor Alexander (Sandy) McNabb of Iowa State University as the sole survivor in 40 acres (16 ha) of diseased elm at Burlington.

Donacia is a large genus of aquatic leaf beetles in the subfamily Donaciinae. Like other members of that subfamily, the beetles have long antennae. They are active and able to fly. Larvae feed on submerged portions of aquatic plants, such as water lilies, and breathe oxygen from plant vessels. Adults live on surface parts of the same plants.

Laemophloeidae, "lined flat bark beetles," is a family in the superfamily Cucujoidea characterized by predominantly dorso-ventrally compressed bodies, head and pronotal discs bordered by ridges or grooves, and inverted male genitalia. Size range of adults is 1–5 mm (0.04–0.2 in) in length. Currently, it contains 40 genera and about 450 species, and is represented on all continents except Antarctica; species richness is greatest in the tropics.

Protaetia is a genus of beetles of the family Scarabaeidae, occurring primarily in Asia, and containing over 300 species.

Monkey beetles are scarab beetles, a group of several genera within the tribe Hopliini. The placement of this tribe within the family Scarabaeidae is uncertain between Melolonthinae and Rutelinae. Many species visit flowers for pollen and nectar, or browse on the petals. The beetles are important pollinators of Aizoaceae and Asteraceae in grazed and ungrazed areas, as well as many others. They tend to favor flowers of white, yellow, pink, orange, and blue pigments. They also tend to favor flowers of symmetrical, abstract patterns Due to their pollination patterns, many plants were able to develop special features that attracted monkey beetles, such as the Iridaceae which now have bright colors and symmetrical, unique patterns.

Ctenicera is a genus of click beetles.

Alocasia cuprea is a species of plant in the genus Alocasia native to Borneo. This species derives its name, cuprea, from the unusual coppery appearance of the leaves, which are up to 24 inches long. This color is especially pronounced on juvenile leaves, and the back of the leaf is a deep purple, but there is also a greener leaf form of the plant. While rare in cultivation, A. cuprea has been known outside its native habitat since it was brought to Europe in the 1850s by Thomas Lobb for Veitch Nurseries.

Anomala albopilosa, known by the common names green chafer, white-haired leaf chafer and sugarcane white grub, is a species of chafer beetle in the family Scarabaeidae. It was originally described in the genus Euchlora by Frederick William Hope in 1839. The beetle is native to the four major islands of Japan, the Ryukyu Islands, Korea, and Taiwan.
















