
The genus Cochleanthes is made up of 4 species of orchids native to Mexico, Central America, the West Indies and South America. The name Cochleanthes refers to the shape of the flower.

Adelia is a genus of flowering plants in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, subfamily Acalyphoideae. It is native to Latin America and the Caribbean, with one species extending northward into the southernmost part of Texas.
Acidoton is a genus of plant of the family Euphorbiaceae first described as a genus in 1788. It is native to the Greater Antilles, Central America, and tropical South America.
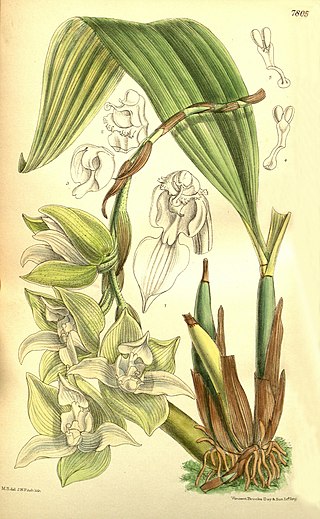
Trevoria is a genus of orchids native to southeastern Central America and northwestern South America. It grows in intermediate temperature and is found from Nicaragua and Costa Rica to Bolivia.

Restrepiella ophiocephala, commonly called the Snake's head restrepiella is an epiphytic orchid native to Mexico, Central America, Colombia, and Florida. The epithet ophiocephala is derived from the Greek words ὄφις, ophis (snake) and κεφαλή, kephalē (head).

Dalechampia dioscoreifolia is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae first described in 1841. It is native to Central America and northern and western South America.

Hypolytrum is a genus of plant in the family Cyperaceae. It contains approximately 60–70 species, native to tropical Africa, Asia, Australia, Latin America and various oceanic islands.

Sievekingia is a genus of orchid, comprising 20 species found in Central and South America, from Nicaragua east to the Guianas and south to Bolivia.

Neonicholsonia is a monotypic genus of flowering plant in the palm family native to Central America. The sole species is Neonicholsonia watsonii. The genus and species names honor George Nicholson, a former curator of the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and his successor William Watson.

Psilochilus is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to South America, Central America, Mexico and the West Indies.
- Psilochilus carinatusGaray - Colombia
- Psilochilus dusenianusKraenzl. ex Garay & Dunst. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus macrophyllus(Lindl.) Ames - widespread from central Mexico and the West indies south to Peru
- Psilochilus maderoi(Schltr.) Schltr. - Colombia
- Psilochilus modestusBarb.Rodr. - Venezuela, Brazil
- Psilochilus mollisGaray - Ecuador
- Psilochilus physurifolius(Rchb.f.) Løjtnant - Venezuela, Guyana
- Psilochilus vallecaucanusKolan. & Szlach. - Colombia

Schiedeella is a genus of flowering plants from the orchid family, Orchidaceae. It is native to the Western Hemisphere: Mexico, the West Indies and Central America, with one species (S. arizonica) in the southwestern United States.

Aristolochia maxima is a plant species native to Central and South America, naturalized in southern Florida. Common names include Florida Dutchman's-pipe (US), canastilla (Guatemala), guaco, and tecolotillo (Mexico). In Florida, it grows in hammocks in the Everglades at elevations below 50 m.

Celtis ehrenbergiana, called the desert hackberry or spiny hackberry, is a plant species that has long been called C. pallida by many authors, including in the "Flora of North America" database. It is native to Arizona, Florida, New Mexico and Texas, and to Latin America as far south as central Argentina. It grows in dry locations such as deserts, brushlands, canyons, mesas and grasslands.
Calycolpus warscewiczianus is a plant species native to Nicaragua, Costa Rica, Panamá and Venezuela.
Randia nicaraguensis is a plant species endemic to Nicaragua. It occurs in tropical drought-deciduous forests at elevations below 850 m.

Ludovia is a genus of plants first described as a genus in 1861. All the known species are native to Central and South America.

Bidens bipinnata is a common and widespread species of flowering plant in the family Asteraceae.
Xyris ambigua, the coastal plain yelloweyed grass, is a North American species of flowering plant in the yellow-eyed-grass family. It is native to southern and eastern Mexico, Central America, Cuba, and the southeastern and south-central United States.
Xyris baldwiniana, common name Baldwin's yelloweyed grass, is a North American species of flowering plant in the yellow-eyed-grass family. It is native to southern Mexico (Chiapas), Central America, and the southeastern and south-central United States.
Xyris elliottii, common name Elliott's yelloweyed grass, is a North American species of flowering plant in the yellow-eyed-grass family. It is native to the coastal plain of the United States from Mississippi to South Carolina plus southern Mexico (Tabasco), Central America and the West Indies.













