
Scabiosa is a genus in the honeysuckle family (Caprifoliaceae) of flowering plants. Many of the species in this genus have common names that include the word scabious, but some plants commonly known as scabious are currently classified in related genera such as Knautia and Succisa; at least some of these were formerly placed in Scabiosa. Another common name for members of this genus is pincushion flowers.

Cineraria is a genus of flowering plants in the sunflower family, native primarily to southern Africa with a few species further north. The genus includes herbaceous plants and small subshrubs.

Boswellia is a genus of trees in the order Sapindales, known for its fragrant resin. The biblical incense frankincense is an extract from the resin of the tree Boswellia sacra, and is now produced also from B. frereana. Boswellia species are moderate-sized flowering plants, including both trees and shrubs.

Dovyalis is a genus of shrubs and small trees. Recent genetic evidence has shown the genus to belong to the family Salicaceae; formerly it was classified in the family Flacourtiaceae. The 15 species are native to Africa and southern Asia. Some are cultivated for their fruit.
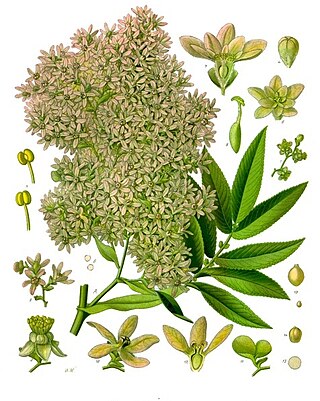
Hagenia is a monotypic genus of flowering plant with the sole species Hagenia abyssinica, native to the high-elevation Afromontane regions of central and eastern Africa. It also has a disjunct distribution in the high mountains of East Africa from Sudan and Ethiopia in the north, through Kenya, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Tanzania, to Malawi and Zambia in the south. A member of the rose family, its closest relative is the Afromontane genus Leucosidea.

Hygrophila, commonly known as swampweeds, is a genus of flowering plants in the acanthus family, Acanthaceae. There are about 80 to 100 species, of which many are aquatic plants. The genus is distributed across the tropical and subtropical world. It is one of only two genera in its family that contains aquatic plants, the other being Justicia. The genus is treated in the tribe Hygrophileae, which is noted as being in need of revision at the genus level, meaning the current taxonomic boundaries of Hygrophila are likely to change in the future.

Taverniera is a genus of legume in the family Fabaceae. It includes 17 species of shrubs or shrublets which range from Egypt eastwards to the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Iran, Pakistan, and India, and southwards to Ethiopia and Somalia. Typical habitats include seasonally-dry tropical and subtropical desert, shrubland, and bushland.

Entada is a genus of flowering plants in the family Fabaceae, in the mimosoid clade of the subfamily Caesalpinioideae. It consists of some 30 species of trees, shrubs and tropical lianas. About 21 species are known from Africa, six from Asia, two from the American tropics and one with a pantropical distribution. They have compound leaves and produce exceptionally large seedpods of up to 1.5 metres (4.9 ft) long. Their seeds are buoyant and survive lengthy journeys via rivers and ocean currents, to eventually wash up on tropical beaches.

Sagina is a genus of 20–30 species of flowering plants in the family Caryophyllaceae. These are flowering herbs native to temperate regions of the Northern Hemisphere extending south to tropical mountain areas at high altitudes, reaching just south of the equator in Africa. They are small annual or perennial herbaceous plants, growing to 5–15 cm. The leaves are opposite, often in tight whorl-like clusters, simple linear, typically 5–20 mm long. The flowers are solitary or in small cymes, with four or five green sepals and an equal number of white petals; the petal size relative to the sepal size is useful in species identification. The fruit is a small capsule containing several seeds.

Smithia is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family, Fabaceae. It includes 20 species of herbs or subshrubs native to sub-Saharan Africa, the Indian subcontinent, Indochina, southern China, Japan, Malesia, and northern Australia. The greatest diversity of species is in the Indian subcontinent, with 11 endemic species. Six more are widespread in southern and eastern Asia, and two of these, S. conferta and S. sensitiva, range further to northern Australia. Two species are endemic to sub-Saharan Africa. S. elliotii is native to Madagascar as well as mainland Africa, and S. conferta is also native to Madagascar. Typical habitats include seasonally-dry tropical grassland, wetlands, and streamsides.

Erythrina abyssinica is a tree species of the genus Erythrina belonging to the plant family of the Fabaceae described by Augustin Pyramus de Candolle in 1825. This leguminous tree species is native to East Africa, Eastern DRC and southern Africa. In Zimbabwe its range overlaps with the similar Erythrina latissima.
Ziziphus abyssinica is a species of shrub in the family Rhamnaceae.

Euphorbia abyssinica, commonly known as the desert candle or candelabra spurge, is a species of plant in the family Euphorbiaceae. E. abyssinica is endemic to Ethiopia, Somalia, Sudan and Eritrea. It was first described in 1791, by the German botanist Johann Friedrich Gmelin. In its native habitat, it can grow up to 10 m (33 ft) tall. The woody stem is used for firewood and as timber in roofing, furniture and other items, and the sap is used in traditional medicine. It is also cultivated as an ornamental house plant.

Dorycnopsis is a genus of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae. It belongs to the subfamily Faboideae. It includes two species of subshrubs, one native to southwestern Europe and Morocco, and the other native to the Horn of Africa and Yemen.
Schlechterella is a genus of plants in the family Apocynaceae. It is native to Africa, found in Ethiopia, Kenya, Mozambique, Somalia, Tanzania and Uganda.

Myosotis abyssinica is a species of herbaceous plant in the family Boraginaceae. It can be found in Ethiopia, Sudan, Bioko Island, Rwanda, the Democratic Republic of Congo (Zaire), Uganda, Kenya, Tanzania, and Cameroon.

Bulbine abyssinica is a species of plant in the genus Bulbine, from eastern and southern Africa.
Astropanax abyssinicus is a flowering plant in the family Araliaceae. It grows in tropical Africa, from southeastern Nigeria to Ethiopia and Zambia.
Lefebvrea is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Apiaceae.














