
The Ichneumonidae, also known as ichneumon wasps, ichneumonid wasps, ichneumonids, or Darwin wasps, are a family of parasitoid wasps of the insect order Hymenoptera. They are one of the most diverse groups within the Hymenoptera with roughly 25,000 species described as of 2016. However, this likely represents less than a quarter of their true richness as reliable estimates are lacking, along with much of the most basic knowledge about their ecology, distribution, and evolution. It is estimated that there are more species in this family than there are species of birds and mammals combined. Ichneumonid wasps, with very few exceptions, attack the immature stages of holometabolous insects and spiders, eventually killing their hosts. They play an important role as regulators of insect populations, both in natural and semi-natural systems, making them promising agents for biological control.

The Braconidae are a family of parasitoid wasps. After the closely related Ichneumonidae, braconids make up the second-largest family in the order Hymenoptera, with about 17,000 recognized species and many thousands more undescribed. One analysis estimated a total between 30,000 and 50,000, and another provided a narrower estimate between 42,000 and 43,000 species.

Microgastrinae is a subfamily of braconid wasps, encompassing almost 3,000 described species, with an estimated 30,000–50,000 total species. This makes it one of the richest subfamilies with the most species of parasitoid wasps.

The Doryctinae or doryctine wasps are a large subfamily of parasitoid wasps within the family Braconidae.
Pauesia is a genus of parasitoid wasps in the subfamily Aphidiinae. The species in the genus use the conifer aphids as their host.

Bracon is a genus of wasps in the Braconidae, a family of parasitoid wasps. There are several hundred described species but there are thousands still undescribed. The genus is cosmopolitan, distributed throughout the world, with most of the described species occurring in the Palearctic realm.

The Rogadinae are a large subfamily of braconid parasitoid wasps. Several Rogadinae species parasitize pest caterpillars and are important for naturally occurring biological control.

The Cardiochilinae are a subfamily of braconid parasitoid wasps. This subfamily has been treated as a tribe of Microgastrinae in the past. Some species including Toxoneuron nigriceps have been used in biocontrol programs.
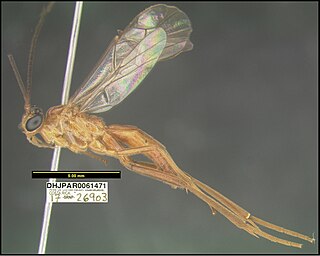
The Homolobinae are a subfamily of braconid parasitoid wasps.
Dirrhope is the only extant genus in the subfamily Dirrhopinae of braconid parasitoid wasps. Dirrope was included in the Microgastrinae until 1984. Specimens of this genus have been found fossilsed in amber dating from the Cretaceous period.

Meteorinae is a subfamily of braconid parasitoid wasps; however, since 2015, most scientists have treated this clade as the Tribe Meteorini in Euphorinae. Several species have been used in biological control programs. The name for this group comes from the pupal stage, which, in species attacking Lepidopteran hosts, hangs suspended from a long thread of silk.

Brachistinae is a subfamily of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae.

Helconinae is a subfamily of braconid wasps in the family Braconidae.

Lysiphlebus testaceipes is a species of small braconid parasitoid wasp in the subfamily Aphidiinae. L. testaceipes can utilize numerous species of aphids as hosts and has often been used as a biological control agent against aphid pests. It is considered an invasive species in several European countries.
Binodoxys is a genus of parasitoid wasp of the subfamily Aphidiinae which are noted parasitoids of aphids. Its species generally prey on aphids which live on herbaceous plants.

Aphidius is a genus of insects of the family Braconidae.

Lysiphlebus is a genus of parasitoid wasps belonging to the family Braconidae.
Rogadini is a tribe of parasitoid wasp in the family Braconidae. It is represented in the entire world. It is the largest tribe within the subfamily Rogadinae with 40 extant genera. It is also considered to be the most basal tribe in the subfamily.
Stiropiini is a tribe of parasitoid wasp in the family Braconidae. It is represented across the New World. It is the second tribe to diverge within the subfamily Rogadinae. Rogadini was the first to diverge.
Yeliconini is a tribe of parasitoid wasp in the family Braconidae. It is represented across the world. Aleiodini is the sister tribe to Yeliconini Butcher, B. A., Quicke, D. L., Shreevihar, S., & Ranjith, A. P. (2016). Major range extensions for two genera of the parasitoid subtribe Facitorina, with a new generic synonymy. ZooKeys, (584), 109.</ref>


















