
Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is a parallel expansion card standard, designed for attaching a video card to a computer system to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. It was originally designed as a successor to PCI-type connections for video cards. Since 2004, AGP was progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express (PCIe), which is serial, as opposed to parallel; by mid-2008, PCI Express cards dominated the market and only a few AGP models were available, with GPU manufacturers and add-in board partners eventually dropping support for the interface in favor of PCI Express.

Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles.

The Intel 486, officially named i486 and also known as 80486, is a microprocessor. It is a higher-performance follow-up to the Intel 386. The i486 was introduced in 1989. It represents the fourth generation of binary compatible CPUs following the 8086 of 1978, the Intel 80286 of 1982, and 1985's i386.

A motherboard is the main printed circuit board (PCB) in general-purpose computers and other expandable systems. It holds and allows communication between many of the crucial electronic components of a system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Unlike a backplane, a motherboard usually contains significant sub-systems, such as the central processor, the chipset's input/output and memory controllers, interface connectors, and other components integrated for general use.
Rambus DRAM (RDRAM), and its successors Concurrent Rambus DRAM (CRDRAM) and Direct Rambus DRAM (DRDRAM), are types of synchronous dynamic random-access memory (SDRAM) developed by Rambus from the 1990s through to the early 2000s. The third-generation of Rambus DRAM, DRDRAM was replaced by XDR DRAM. Rambus DRAM was developed for high-bandwidth applications and was positioned by Rambus as replacement for various types of contemporary memories, such as SDRAM. RDRAM is a serial memory bus.
HyperTransport (HT), formerly known as Lightning Data Transport, is a technology for interconnection of computer processors. It is a bidirectional serial/parallel high-bandwidth, low-latency point-to-point link that was introduced on April 2, 2001. The HyperTransport Consortium is in charge of promoting and developing HyperTransport technology.

In a computer system, a chipset is a set of electronic components on one or more integrated circuits that manages the data flow between the processor, memory and peripherals. The chipset is usually found on the motherboard of computers. Chipsets are usually designed to work with a specific family of microprocessors. Because it controls communications between the processor and external devices, the chipset plays a crucial role in determining system performance. Sometimes the term "chipset" is used to describe a system on chip (SoC) used in a mobile phone.

Mini-ITX is a 170 mm × 170 mm motherboard form factor developed by VIA Technologies in 2001. Mini-ITX motherboards have been traditionally used in small-configured computer systems. Originally, Mini-ITX was a niche standard designed for fanless cooling with a low power consumption architecture, which made them useful for home theater PC systems, where fan noise can detract from the cinema experience.

Slot 1 refers to the physical and electrical specification for the connector used by some of Intel's microprocessors, including the Pentium Pro, Celeron, Pentium II and the Pentium III. Both single and dual processor configurations were implemented.

Geode is a series of x86-compatible system-on-a-chip (SoC) microprocessors and I/O companions produced by AMD that was targeted at the embedded computing market.
In the fields of digital electronics and computer hardware, multi-channel memory architecture is a technology that increases the data transfer rate between the DRAM memory and the memory controller by adding more channels of communication between them. Theoretically, this multiplies the data rate by exactly the number of channels present. Dual-channel memory employs two channels. The technique goes back as far as the 1960s having been used in IBM System/360 Model 91 and in CDC 6600.

ALi Corporation is a major designer and manufacturer of embedded systems integrated circuits, and a former manufacturer of personal computer integrated circuits. It is based in Taiwan, and is a subsidiary of the Acer group.
The AMD 700 chipset series is a set of chipsets designed by ATI for AMD Phenom processors to be sold under the AMD brand. Several members were launched in the end of 2007 and the first half of 2008, others launched throughout the rest of 2008.

The Intel 810 chipset was released by Intel in early 1999 with the code-name "Whitney" as a platform for the P6-based Socket 370 CPU series, including the Pentium III and Celeron processors. Some motherboard designs include Slot 1 for older Intel CPUs or a combination of both Socket 370 and Slot 1. It targeted the low-cost segment of the market, offering a robust platform for uniprocessor budget systems with integrated graphics. The 810 was Intel's first chipset design to incorporate a hub architecture which was claimed to have better I/O throughput and an integrated GPU, derived from the Intel740.
Tolapai is the code name of Intel's embedded system on a chip (SoC) which combines a Pentium M (Dothan) processor core, DDR2 memory controllers and input/output (I/O) controllers, and a QuickAssist integrated accelerator unit for security functions.
The Digital Personal Workstation, code named "sports car", is a family of entry-level to mid-range workstation computers developed and manufactured by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC). These workstations are based on the DEC Alpha and Intel Pentium Pro or Pentium II microprocessors. Members of this family can run the Digital UNIX, OpenVMS, and Windows NT operating systems. The i-Series, based on Pentium Pro, was introduced first, on September 23, 1996.
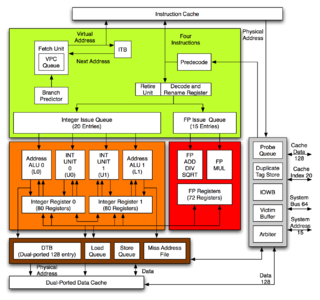
The Alpha 21264 is a RISC microprocessor developed by Digital Equipment Corporation launched on 19 October 1998. The 21264 implemented the Alpha instruction set architecture (ISA).











