
Bancroft is a small, bowl-shaped impact crater located to the southwest of Archimedes on the Mare Imbrium. A wide, shallow depression runs from the rim of Bancroft southeast to the Montes Archimedes. There are some clefts at the edge of the mare to the west and southwest of the crater. Other prominent craters are two small craters nearly to the west named Feuillée and Beer.

Aryabhata, named after Indian astronomer Aryabhata, is the remnant of a lunar impact crater located in the eastern Mare Tranquillitatis. The crater has been almost submerged by lava-flow, and now only an arc-shaped ridge formed from the eastern half of the rim remains above the lunar mare. This crater was previously identified as Maskelyne E before being named by the IAU in 1979. Maskelyne itself is to the southwest.

Bessarion is a lunar impact crater located near the southwest edge of Mare Imbrium. It is named after Greek scholar Bessarion. Some distance to the east is the crater T. Mayer. Bessarion is a bowl-shaped crater with a low central rise and a higher albedo than the maria, making it a brighter feature when the sun is overhead.

Ameghino is a lunar impact crater located to the north of the Sinus Successus, a bay in the northeast part of Mare Fecunditatis. Less than 15 kilometers to the northwest of Ameghino were the landing sites of the Soviet Luna 18 and Luna 20 probes.

Censorinus is a tiny lunar impact crater located on a rise to the southeast of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after the ancient Roman writer Censorinus. To the northeast is the crater Maskelyne.

Al-Marrakushi is a small, relatively isolated lunar impact crater in the eastern Mare Fecunditatis. It is a circular, symmetrical formation, with inner walls that slope down to the midpoint. To the northeast is the prominent crater Langrenus. The mare near Al-Marrakushi is marked by ray material from its larger neighbor.

Abbot is a small lunar impact crater that lies on the rugged ground between the Mare Fecunditatis in the south and west, and the Mare Crisium to the north. It is a circular crater with a cup-shaped interior. The inner walls slope downward to the midpoint, and no impacts of significant mark the interior or the rim.

Beketov is a small lunar impact crater that lies in the northern reaches of the Mare Tranquillitatis. It is named after Russian chemist Nikolay Beketov. To the south is the ghost crater Jansen R. Northeast of Beketov, along the edge of the mare, is the crater Vitruvius. Beketov was previously designated Jansen C before being named by the IAU. The flooded crater Jansen itself lies to the south.

Bombelli is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the highlands to the north of the Sinus Successus. It was named after Italian mathematician Raphael Bombelli. It was previously designated Apollonius T. The crater Apollonius is located to the east-southeast.

Cartan is a small lunar impact crater near the eastern edge of the Moon. It lies just to the west of the larger Apollonius. The rim is circular with a tiny crater along the eastern side. The interior floor is about half the diameter of the crater. A smaller crater attached to the southern rim is also attached to the north rim of Apollonius H, forming a short crater chain.

Diophantus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southwestern part of the Mare Imbrium. It was named after ancient Greek mathematician Diophantus. It forms a pair with the larger crater Delisle to the north. Diophantus has a wide inner wall and a low central rise. To the north of Diophantus is the sinuous rille designated Rima Diophantus, named after the crater. Diophantus C lies near the exterior of the southwest wall.
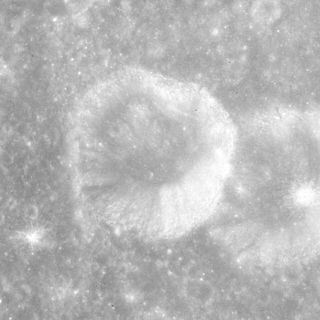
Daly is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon, to the northwest of the crater Apollonius. This formation is relatively circular, with a slight inward bulge along the northern rim. The inner wall is wider in the southern half than in the north. The crater intrudes into the comparably sized crater Apollonius F to the east-southeast.

Petit is a small, bowl-shaped lunar impact crater that is located on the northwestern edge of the Mare Spumans. The crater has a prominent ray system. The name is appropriate, since Petit means small in French. But it was actually named in honor of Alexis Thérèse Petit, a French physicist.
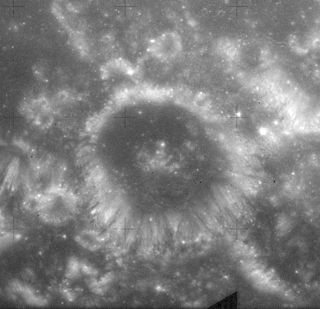
Shapley is a lunar impact crater that lies along the southern edge of Mare Crisium. It was named after American astronomer Harlow Shapley. It was previously designated Picard H. However the crater Picard lies about 150 kilometers to the north-northwest across the Mare Crisium. Somewhat closer to this crater are Tebbutt to the west, and Firmicus to the east-southeast.

C. Mayer is a lunar impact crater that is located at the northern edge of the Mare Frigoris, due north of the prominent crater Aristoteles. Also to the south, but only a third as distant, is the smaller crater Sheepshanks. Due east of C. Mayer is the flooded crater Kane.

Condon is a lunar impact crater that lies on the eastern shore of the Sinus Successus, a bay along the northeast edge of Mare Fecunditatis. It was named after American physicist Edward U. Condon. It lies midway between the larger crater Apollonius to the north and the smaller Webb to the south on the Mare Fecunditatis. Condon was previously designated Webb R.

Townley is a small lunar impact crater that is located in the eastern part of the Moon. It was named after American astronomer Sidney Dean Townley. It lies to the northwest of Mare Spumans and southeast of the crater Apollonius. This crater was previously designated Apollonius G.

van Albada is a lunar impact crater that is attached to the south-southeastern rim of Auzout. It lies southeast of Mare Crisium, and north-northeast of the larger crater Firmicus. Directly to the east is Krogh.
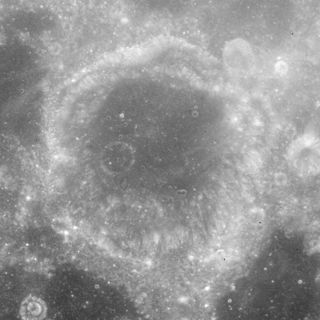
Dubyago is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern limb of the Moon. It was named after Russian astronomers Dmitry Dubyago and Alexander Dubyago. It appears significantly foreshortened when viewed from the Earth. It lies along the southern shore of the Mare Undarum, to the southeast of the crater Firmicus.

Firmicus is a lunar impact crater that lies in the eastern part of the Moon's near side, so that from Earth it appears oval in shape due to foreshortening. It is, however, very nearly circular. The crater is located to the west of the Mare Undarum, and northeast of the similar-sized crater Apollonius. To the north of Firmicus are the craters van Albada and Auzout. Attached to its northwest rim is the Lacus Perseverantiae, a miniature lunar mare.



























