
The peanut, also known as the groundnut, goober (US), pindar (US) or monkey nut (UK), is a legume crop grown mainly for its edible seeds. It is widely grown in the tropics and subtropics, important to both small and large commercial producers. It is classified as both a grain legume and, due to its high oil content, an oil crop. World annual production of shelled peanuts was 44 million tonnes in 2016, led by China with 38% of the world total. Atypically among legume crop plants, peanut pods develop underground (geocarpy) rather than above ground. With this characteristic in mind, the botanist Carl Linnaeus gave peanuts the specific epithet hypogaea, which means "under the earth".

Arachis is a genus of about 70 species of annual and perennial flowering plants in the family (Fabaceae), native to South America, and was recently assigned to the informal monophyletic Pterocarpus clade of the Dalbergieae. At least one species, the peanut, is a major food crop species of global importance; some of the other species are cultivated for food to a small extent in South America. Other species such as A. pintoi are cultivated worldwide as forage and soil conditioner plants, with the leaves providing high-protein feed for grazing livestock and a nitrogen source in agroforestry and permaculture systems.

The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) Red List of Threatened Species, also known as the IUCN Red List or Red Data Book, founded in 1964, is the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of precise criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red Lists are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

Arachidyl alcohol, also 1-icosanol, is a waxy substance used as an emollient in cosmetics. It is a straight-chain fatty alcohol with 20 carbon atoms, typically obtained via the hydrogenation of arachidic acid or arachidonic acid, both of which are present in peanut oil. Its name is derived from that of the peanut plant.
Arachis ipaensis is a herb in the Faboideae subfamily. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut. Its genome has been sequenced.
Arachis archeri is a herb native to Mato Grosso vegetation in Brazil. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut.
Arachis batizocoi is a herb native to Bolivia and Paraguay. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut.
Arachis correntina is a herb native to Argentina and Paraguay. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut.
Arachis diogoi is a perennial herb found in Africa, Indian Ocean and South America. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut.

Arachis duranensis is a herb found in South America, specially in North Argentina, Bolivia, and Paraguay. This plant is cited as gene sources for research in plant biology of peanut.
Arachis villosulicarpa is a perennial peanut species, which is cultivated by indigenous people in Mato Grosso, a state of Brazil. Its wild progenitor is thought to be Arachis pietrarellii. Although it is related to the common peanut, Arachis hypogaea, it was separately domesticated: A. villosulicarpa is diploid, whereas A. hypogaea is tetraploid.

Arachis glabrata is a high-quality forage plant native to Argentina, Brazil, and Paraguay vegetation. This plant is also used for soil conservation and as an ornamental plant.
Bean yellow mosaic virus is a plant pathogenic virus in the genus Potyvirus and the virus family Potyviridae. Like other members of the Potyvirus genus, it is a monopartite strand of positive-sense, single-stranded RNA surrounded by a capsid made for a single viral encoded protein. The virus is a filamentous particle that measures about 750 nm in length. This virus is transmitted by species of aphids and by mechanical inoculation.
The Ghana mole-rat or Togo mole-rat is a species of rodent in the family Bathyergidae. It is endemic to Ghana.

Arachis pintoi, the Pinto peanut, is a forage plant native to Cerrado vegetation in Brazil. It is native to the valleys of the upper São Francisco and the Jequitinhonha rivers of Minas Gerais. It has been named after the Brazilian botanist Geraldo Pinto, who first collected the plant at the locality of Boca do Córrego, município de Belmonte in 1954 and suggested its potential as a forage. The species has been first described by A. Krapovickas and W. Gregory in 1994.
Billbergia cardenasii is a species of flowering plant in the genus Billbergia. This species is endemic to Bolivia. It has clear yellow petals and equal sepals.
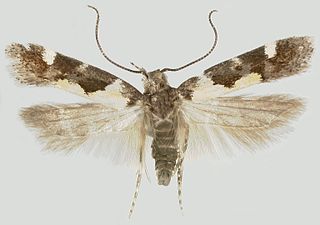
Stegasta bosqueella is a species of moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in North America, including Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Illinois, Iowa, North Carolina, Oklahoma, South Carolina, Texas and Virginia.

Capsicum cardenasii is a plant species in the genus Capsicum and the family Solanaceae. It is a diploid with 2n=2x=24. It is a member within the C. pubescens complex, a group of closely related Capsicum species. It is closely related to C. eximium. It is native to the Andes, and it can be found in Bolivia and Peru. The native name is ulupica.









