
Mantis shrimp are carnivorous marine crustaceans of the order Stomatopoda. Stomatopods branched off from other members of the class Malacostraca around 340 million years ago. Mantis shrimp typically grow to around 10 cm (3.9 in) in length, while a few can reach up to 38 cm (15 in). A mantis shrimp's carapace covers only the rear part of the head and the first four segments of the thorax. Varieties range in colour from shades of brown to vivid colours, with more than 520 species of mantis shrimp known. They are among the most important predators in many shallow, tropical and subtropical marine habitats. However, despite being common, they are poorly understood, as many species spend most of their lives sheltering in burrows and holes.

The Carolina mantis is a species of praying mantis of the subfamily Stagmomantinae.

Archimantis latistyla, commonly known as the large brown mantis is a species of mantid native to Australia. The large brown mantis has two subspecies, a widespread subspecies and the stick mantis ghost from Bundabergs Turtle Sands. The stick mantis ghosts are not as aggressive as the widespread species but have a defense display used to make the mantis appear larger by flinging its front legs into the air and putting its head down along with its antennae. Large brown mantids are light brown with short winged female and a long winged male. The subspecies from Bundaberg is a pale cream white with a yellow and black eye in between the arms. The large brown mantis female is short winged - her wings reach only half her abdomen and she is not able to fly— but the long winged male has wings that cover the entire abdomen. They have two pairs of wings - the top pair are the wing covers and the bottom wings enable the mantis to fly.

Archimantis is a genus of praying mantis found in Australia. These species are ranging from 150 mm to 180mm, and can be quite aggressive when full adult.
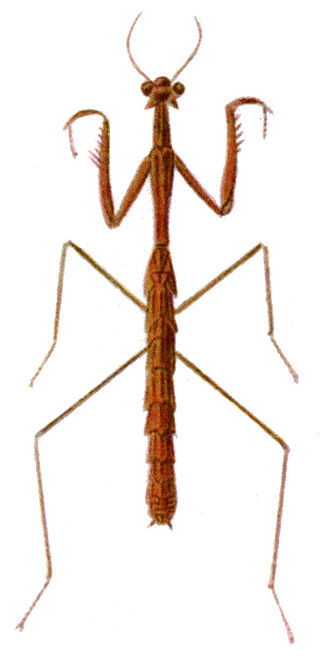
Stick mantis and twig mantis are common names applied to numerous species of mantis that mimic sticks or twigs as camouflage. Often the name serves to identify entire genera such as is the case with:

Chimaera monstrosa, also known as the rabbit fish or rat fish, is a northeast Atlantic and Mediterranean species of cartilaginous fish in the family Chimaeridae. The rabbit fish is known for its characteristically large head and small, tapering body. With large eyes, nostrils, and tooth plates, the head gives them a rabbit-like appearance, hence the nickname “Rabbit fish”. They can grow to 1.5 metres (5 ft) and live for up to 30 years.

Lysiosquillina maculata, the zebra mantis shrimp, striped mantis shrimp or razor mantis, is a species of mantis shrimp found across the Indo-Pacific region from East Africa to the Galápagos and Hawaiian Islands. At a length up to 40 cm, L. maculata is the largest mantis shrimp in the world. L. maculata may be distinguished from its congener L. sulcata by the greater number of teeth on the last segment of its raptorial claw, and by the colouration of the uropodal endopod, the distal half of which is dark in L. maculata but not in L. sulcata. A small artisanal fishery exists for this species.
Archimantis armata is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.
Archimantis brunneriana is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.
Archimantis gracilis is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.
Archimantis quinquelobata is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.

Archimantis sobrina is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.
Archimantis straminea is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae.
Archimantis vittata is a species of praying mantis in the family Mantidae. It is found in Australia.
A. gracilis may refer to:

Mantises are an order (Mantodea) of insects that contains over 2,400 species in about 460 genera in 33 families. The largest family is the Mantidae ("mantids"). Mantises are distributed worldwide in temperate and tropical habitats. They have triangular heads with bulging eyes supported on flexible necks. Their elongated bodies may or may not have wings, but all Mantodea have forelegs that are greatly enlarged and adapted for catching and gripping prey; their upright posture, while remaining stationary with forearms folded, has led to the common name praying mantis.

The Hierodulinae are a subfamily of praying mantids, originally used by Brunner von Wattenwyl. It was restored as part of a major revision of mantid taxonomy, and now contains genera previously placed elsewhere in the family Mantidae.
Podagrion mantis was first described in 1886 by W.H. Ashmead, and was the first species of its genus to have been described from the United States. All species in the genus are parasitoid wasps known only to parasitize mantids. They have been observed most often utilizing the egg case (ootheca) of Stagmomantis carolina, but have also been reported to choose S.limbata or Tenodera angustipennis as hosts, showing a high degree of specialization.










