In chemistry, amines are compounds and functional groups that contain a basic nitrogen atom with a lone pair. Amines are formally derivatives of ammonia, wherein one or more hydrogen atoms have been replaced by a substituent such as an alkyl or aryl group. Important amines include amino acids, biogenic amines, trimethylamine, and aniline. Inorganic derivatives of ammonia are also called amines, such as monochloramine.

In organic chemistry, a carboxylic acid is an organic acid that contains a carboxyl group attached to an R-group. The general formula of a carboxylic acid is R−COOH or R−CO2H, with R referring to the alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, or other group. Carboxylic acids occur widely. Important examples include the amino acids and fatty acids. Deprotonation of a carboxylic acid gives a carboxylate anion.

Aniline is an organic compound with the formula C6H5NH2. Consisting of a phenyl group attached to an amino group, aniline is the simplest aromatic amine. It is an industrially significant commodity chemical, as well as a versatile starting material for fine chemical synthesis. Its main use is in the manufacture of precursors to polyurethane, dyes, and other industrial chemicals. Like most volatile amines, it has the odor of rotten fish. It ignites readily, burning with a smoky flame characteristic of aromatic compounds. It is toxic to humans.
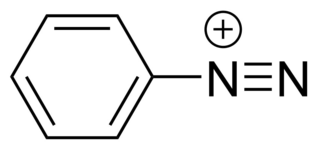
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group [R−N+≡N]X− where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
In enzymology, a 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate dehydrogenase (EC 1.2.1.88) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acylpyruvate hydrolase (EC 3.7.1.5) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme acyl-CoA hydrolase (EC 3.1.2.20) catalyzes the reaction
The enzyme wax-ester hydrolase (EC 3.1.1.50) catalyzes the reaction
In enzymology, a 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase (EC 3.5.99.7) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 1-pyrroline-4-hydroxy-2-carboxylate deaminase (EC 3.5.4.22) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an acyl-lysine deacylase (EC 3.5.1.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an allophanate hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.54) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an arylformamidase (EC 3.5.1.9) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a hydroxyisourate hydrolase (EC 3.5.2.17) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a long-chain-fatty-acyl-glutamate deacylase (EC 3.5.1.55) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acyl-D-aspartate deacylase (EC 3.5.1.83) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-acyl-D-glutamate deacylase (EC 3.5.1.82) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-carbamoyl-L-amino-acid hydrolase (EC 3.5.1.87) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a N-(long-chain-acyl)ethanolamine deacylase (EC 3.5.1.60) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a penicillin amidase (EC 3.5.1.11) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction



